
a)
The mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
a)
Answer to Problem 5.6P
In the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium, Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 1/3 and (boxing) 2/3.
Explanation of Solution
In the study of
If all the playoffs are doubles, the table of battle of sexes will be,
| Husband | |||
| Wife | Ballet | Boxing | |
| Ballet | 4, 2 | 0, 0 | |
| Boxing | 0, 0 | 2, 4 |
Wife prefers the Ballet having the probability of w
Wife prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-w)
Equating both the equation, we get,
Husband prefers the Ballet having the probability of h
Husband prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-h)
Equating both the equation, we get,
From the above calculation, doubling of payoff never changes the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium. Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 1/3 and (boxing) 2/3.
Introduction: The game theory is preferable to oligopoly for better understanding. It is the detailed study of interactions between the players, business firms. The aim of this strategic decision is to deduce the responses to actions.
b)
The mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
b)
Answer to Problem 5.6P
In the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium, Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/5 and (boxing) 4/5. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3.
The new diagram is shown.
Explanation of Solution
In the study of game theory, the payoff is the numeric value that is involved with a possible outcome of a game. It represents the motivation of the players. A Strategy is the plan of action that provides the best payoff in a game.Nash equilibrium is one of the strategies and solutions for games.
If all the playoffs are doubles, the new playoff table will be,
| Husband | |||
| Wife | Ballet | Boxing | |
| Ballet | 4, 1 | 0, 0 | |
| Boxing | 0, 0 | 1, 2 |
Wife prefers the Ballet having the probability of w
Wife prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-w)
Equating both the equation, we get,
Husband prefers the Ballet having the probability of h
Husband prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-h)
Equating both the equation, we get,
From the above calculation, doubling of payoff never changes the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium. Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/5 and (boxing) 4/5. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3.
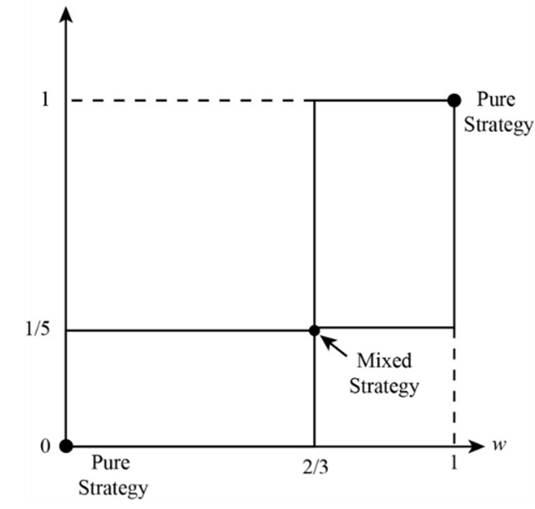
Introduction: The game theory is preferable to oligopoly for better understanding. It is the detailed study of interactions between the players, business firms. The aim of this strategic decision is to deduce the responses to actions.
c)
The mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
c)
Answer to Problem 5.6P
In the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium, Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/4 and (boxing) 3/4. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/4.
The new diagram is shown.
Explanation of Solution
In the study of game theory, the payoff is the numeric value that is involved with a possible outcome of a game. It represents the motivation of the players. A Strategy is the plan of action that provides the best payoff in a game.Nash equilibrium is one of the strategies and solutions for games.
If changes in the preferred activity from 0 to 1/2, the new playoff table will be,
| Husband | |||
| Wife | Ballet | Boxing | |
| Ballet | 2, 1 | 1/2, 0 | |
| Boxing | 1/2, 0 | 1, 2 |
Wife prefers the Ballet having the probability of w
Wife prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-w)
Equating both the equation, we get,
Husband prefers the Ballet having the probability of h
Husband prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-h)
Equating both the equation, we get,
From the above calculation, doubling of payoff never changes the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium. Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/4 and (boxing) 3/4. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/4.
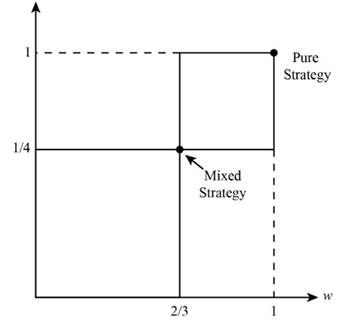
The above diagram is the new diagram
Introduction: The game theory is preferable to oligopoly for better understanding. It is the detailed study of interactions between the players, business firms. The aim of this strategic decision is to deduce the responses to actions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS AND ITS
- A payoff matrix is shown below. With the payoffs in each field indicated in the form (Player 1’s payoff, Player 2’s payoff). Player 2 Left Right Player 1 Up ($1, $1) ($2, $4) Down ($7, $8) ($3, $3) Which of the following is true? The only Nash Equilibrium is Player 1 playing ‘Up’ and Player 2 playing ‘Right’. The only Nash Equilibrium is Player 1 playing ‘Down’ and Player 2 playing ‘Left’. The only Nash Equilibrium is Player 1 playing ‘Down’ and Player 2 playing ‘Right’. None of the other answers provided are true.arrow_forwardSuppose two players play a two-period repeated game, where the stage game is the normal-form game shown below. Is there a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium in which the players select (A, X) in the first period? If so, fully describe such equilibrium. If not, explain why not. Player 1 has choice A, B; Player 2 has choice X, Y, Z. Payoff: (A,X)-(5,7), (A,Y)-(2,4), (A,Z)-(3,8), (B,X)-(1,4), (B,Y)-(3,5), (B,Z)-(1,4)arrow_forwardConsider a simultaneous move game with two players. Player 1 has three possible actions (A, B, or C) and Player 2 has two possible actions (D or E.) In the payoff matrix below, each cell contains the payoff for Player 1 followed by the payoff for Player 2. Identify any pure strategy Nash Equilibria in this game. If there are none, state this clearly.arrow_forward
- Economics Represent the following games in a normal form and find their Nash equilibria. b) Firm A decides whether to enter the market in which firm B already operates. Firm B knows about firm A’s considerations. If firm A enters the market, both firms decide at the same time whether to run an advertising campaign. In the opposite case, only firm B decides about running an advertising campaign. When both firms are in the market, each obtains profit of $3 mln if both pursue a campaign, or of $5 mln if both decide not to run a campaign. If only one firm runs a campaign, it obtains $6 mln, whereas the other firm gets $1 mln. If only firm B operates in the market, it obtains $4 mln when it advertises its product, or $3.5 mln if it does not. Firm A receives $0 if it does not enter the market.arrow_forwardConsider the game shown below. In this game, players 1 and 2 must move at the same time without knowledge of the other player’s move. Player 1’s choices are shown in the row headings (A, B, C, D), Player 2’s choices are shown in the column headings (E, F, G). The first payoff is for the row player (Player1) and the second payoff is for the column player (Player 2). Player 2 Player 1 E F G A 2, 7 7, 2 2, 6 B 5, 5 5, 4 8, 4 C 4, 6 8, 4 7, 5 D 1, 6 3, 5 6, 4 Highlight the correct answer: Player 1: Has a dominant strategy to choose A Has a dominant strategy to choose B Has a dominant strategy to choose C Has a dominant strategy to choose D Does not have a dominant strategy Player 2: Has a dominant strategy to choose E Has a dominant strategy to choose F Has a dominant strategy to choose G Does not have a dominant strategy The Nash equilibrium outcome to this game is: A/F B/E B/G C/F C/G There is no pure strategy Nash…arrow_forwardConsider the following representation of a hockey shootout. The shooter can shoot on their forehand, or deke to their backhand, and the goalie can anticipate either move. The number in each cell in the table below represents the percentage chance that the shooter scores for each pair of pure strategies. Anticipate Forehand Anticipate Backhand Shoot Forehand 20 40 Deke Backhand 40 10 In the mixed strategy Nash equilibrium of this game, what is the percentage chance that the player scores? (ie. An 80% chance should be recorded as 80)arrow_forward
- Find all of the Nash equilibrium of the following three player game. Player 1 chooses rows (a,b). Player 2 chooses columns (c,d). Player 3 chooses matrices (x.y). Player 3 receives the third listed payoff for cach outcome. 5,5,5 4,4,0 8,8,3 7,7,3 1,3,1 4,2,0 3,2,4 3,1,0 a by A) (b,d.x) and (a,d.y) B) (b.cy) OC) (b,d,x) D) (a,d,x) and (b,c.y) E) (b,c,x) OF) (a,d.x)arrow_forwardThe centipede game, first introduced by Robert Rosenthal in 1981, is an extensive form game in which two players take turns choosing either to take a slightly larger share of an increasing pot, or to pass the pot to the other player. In other words, player 1 chooses between D (Down) and A (Across), where D is pocketing the pot and A is passing the pot to the player 2. Similarly, player 2 chooses between A and D. The payoffs are arranged so that if one passes the pot to one's opponent and the opponent takes the pot on the next round, one receives slightly less than if one had taken the pot on this round. A 2 A A 2 A 1 A (3,5) Ꭰ D D D D (1,0) (0,2) (3,1) (2,4) (4,3) 1. Find the subgame perfect Nash Equilibrium using backward induction.arrow_forwardConsider the game shown below. In this game, players 1 and 2 must move at the same time without knowledge of the other player’s move. Player 1’s choices are shown in the row headings (A/B), Player 2’s choices are shown in the column headings (C/D). The first payoff is for the row player (Player1) and the second payoff is for the column player (Player 2). Player 2 Player 1 C D A 8, 3 2, 4 B 7, 4 3, 5 Pick the correct answer: Player 1: Has a dominant strategy to choose A Has a dominant strategy to choose B Has a dominant strategy to choose C Has a dominant strategy to choose D Does not have a dominant strategy Player 2: Has a dominant strategy to choose A Has a dominant strategy to choose B Has a dominant strategy to choose C Has a dominant strategy to choose D Does not have a dominant strategy The Nash equilibrium outcome to this game is: A/C A/D B/C B/D There is no pure strategy Nash equilibrium for this gamearrow_forward
- Two individuals are bargaining over the distribution of $100 in which payoffs must be in increments of $5. Each player must submit a one-time bid. If the sum of the bids is less than or equal to $100, each player gets the amount of the bid and the game ends. If the sum of the bids is greater than $100, the game ends and the players get nothing. Does this game have a Nash equilibrium? What is the most likely equilibrium strategy profile for this game?arrow_forwardConsider a two-player game in which the players take turns, with player 1 moving first. When it is a player's turn, she must announce a number between 1 and 3. The announced number is added to the previously announced numbers. The player who announces the number such that the sum of all announced numbers is 6 wins (receives 1) and the other loses (receives 0). Please indicate whether or not each of the following sequences of announcements is a Nash equilibrium of the game. Hint: Think about how one verifies whether or not a pair of strategies is a Nash equilibrium. P1 says 3, then P2 says 2, then P1 says 1 P1 says 1, then P2 says 3, then P1 says 2 P1 says 2, then P2 says 3, then P1 says 1 P1 says 3, then P2 says 1, then P1 says 2arrow_forwardA and B are competitors in the mobile phone industry. Both A and B have to decide whether to participate or not to participate in a Phone for the Future Trade Fair next month. The matrix payoff below shows the profits (USD million) corresponding to their actions. a) What is the Nash equilibrium of the above game? b) Is the Nash equilibrium Pareto Optima? Explain. c) Suppose B is pessimistic of A's rationality, what is B's strategy? Compare and comment on B's strategy in (a) and (c). A Participate Do not participate B Participate Do not participate 400,1000 200,200 500,500 1000,400arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc




