
Water at 20°C is siphoned from a reservoir as shown in Fig. P5-53. For d = 8 cm and D = 16 cm, determine (a) the minimum flow rate that can be achieved without cavitation occurring in the piping system and (b) the maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system to avoid cavitation. (c) Also, discuss the ways of increasing the maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system to avoid cavitation.
(a)
The minimum flow rate in the piping system.
Answer to Problem 53P
The minimum flow rate in the piping system is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diameter of smaller the pipe is
The figure below shows the different sections in the piping system.
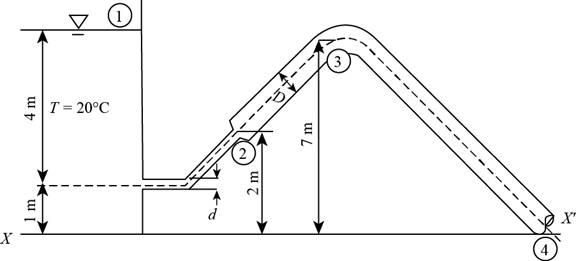
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for Bernoulli's equation between section
Here, the atmospheric pressure is
Write the expression for discharge of fluid from the pipe.
Here, the area of the section
Write the expression for the area of the section
Here, the diameter of the larger pipe is
Write the expression for velocity of the fluid at section
Here, the diameter of smaller the pipe is
Write the expression for Bernoulli's equation between section
Here, the datum head at section
Write the expression for minimum flow rate in the pipe.
Here, the area of the section
Write the expression for area of the section
Calculation:
The velocity at section
The line
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer to the Table A-3 "Properties of saturated water" to obtain the value of absolute pressure as
The density of the water is
Substitute
The value of pressure at section
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The minimum flow rate in the piping system is
(b)
The maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system.
Answer to Problem 53P
The maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the velocity at section
Here, the diameter of the larger pipe is
Write the expression for Bernoulli's equation between section
Here, the datum head at section
Calculation Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system is
(c)
The way of increasing the maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system to avoid cavitation.
Explanation of Solution
By increasing the diameter of the siphoned pipe, the elevation of the highest point of the piping system can be increased because the value of pressure at section is greater than absolute pressure, hence cavitation can be avoided in the pipe.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- As5arrow_forwardcould you please help me calculate theheigth in metres of the fluid at time t= 100sarrow_forwardA large, open tank contains oil and is connected to a 0.3 cm diameter conduit as shown in Figure. A circular seal is used to seal the conduit. Determine (1) the magnitude of the friction force between the pipe wall and the seal. (2) the volume of oil flows across the pipe in 111 s after removal seal. (Patm-100 kpa & Pou = 10° g/m) 125 cm 30 om Water sealarrow_forward
- Solve this pleasearrow_forwardWater is flowing in AF pipe (Figure 1) at a velocity of 2 m/s and a pressure of 102400 Pa, the pipe lengthis 100 m. If the water pressure needs to be at a pressure of 1.6 atm on a lower level. What should bethe different in elevation between the upper and lower levels in order to achieve this pressure? Takethe density of water 1000 kg/m3 and gravity is 9.81 m/s2, consider the energy loss.arrow_forwardWater flows in a 15-cm-diameter pipe at a velocity of 1.8 m/s. If the head loss along the pipe is estimated to be 19 m, the required pumping power (in kW) to overcome this head loss is ?"arrow_forward
- Water at 20°C is to be pumped from a reservoir (Z₁ = 5 m) to another reservoir at a higher elevation (zB = 13 m) through two 36-m-long pipes connected in parallel, as shown in Fig. 1. The pipes are made of commercial steel, and the diameters of the two pipes are 4 and 8 cm. Water is to be pumped by a 70 percent efficient motor-pump combination that draws 8 kW of electric power during operation. The minor losses and the head loss in pipes that connect the parallel pipes to the two reservoirs are considered to be negligible. Write a Matlab code to determine the 13 unknown quantities, namely i. ii. iii. iv. V. vi. vii. viii. the total flow rate (ỷ) between the reservoirs the volume flow rate (V₁ and V₂) through each of the parallel pipes. the velocities (V₁ and V2) through each of the parallel pipes. The total head loss, h₁ the head loss (hL,1 and h₁2) through each of the parallel pipes. Useful Pump head, hpump,u the Reynolds number (Re₁ and Rе2) through each of the parallel pipes. the…arrow_forwardThe pump is used to transfer fluid from one location to another of different height. At inlet and outlet atmospheric conditions are present. The pipe diameter increases after the pump outlet. Determine all the surviving terms of energy equation after simplification. FUM kinetic energy, potential energy, pipe losses none pipe losses, potential energy, pressure increase pressure increase, pipe losses, potential energy kinetic energy, pressure increase, pipe losses OOOarrow_forwardthe maximum value of h ?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





