
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in
Concept Introduction:
Mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
For an element
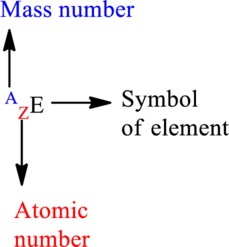
The letter A represents mass number.
The letter Z represents atomic number.
(a)
Answer to Problem 21PE
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number of
The mass number of
Atomic number of an element tells about the number of protons present.
The number of protons present will be equal to the number of electrons.
Atomic number of
The number of neutrons is the difference between the mass number and the atomic number.
The number of neutrons is calculated as,
Number of neutrons=
Number of neutrons=
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 21PE
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number of
The mass number of
Atomic number of an element tells about the number of protons present.
The number of protons present will be equal to the number of electrons.
Atomic number of
The number of neutrons is the difference between the mass number and the atomic number.
The number of neutrons is calculated as,
Number of neutrons=
Number of neutrons=
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 21PE
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number of
The mass number of
Atomic number of an element tells about the number of protons present.
The number of protons present will be equal to the number of electrons.
Atomic number of
The number of neutrons is the difference between the mass number and the atomic number.
The number of neutrons is calculated as,
Number of neutrons=
Number of neutrons=
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 21PE
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number of
The mass number of
Atomic number of an element tells about the number of protons present.
The number of protons present will be equal to the number of electrons.
Atomic number of
The number of neutrons is the difference between the mass number and the atomic number.
The number of neutrons is calculated as,
Number of neutrons=
Number of neutrons=
The number of protons in
The number of electrons in
The number of neutrons in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEMISTRY
- 2.11 Define the term isotope.arrow_forwardDuring nuclear decay a 238U atom can break apart into a helium-4 atom and one other atom. Assuming that no subatomic particles are destroyed during this decay process, what is the other element produced?arrow_forwardTwo elements, R and Q, combine to form two binary compounds. In the first compound, 14.0 g of R combines with 3.00 g of Q. In the second compound, 7.00 g of R combines with 4.50 g of Q. Show that these data are in accord with the law of multiple proportions. If the formula of the second compound is RQ, what is the formula of the first compound?arrow_forward
- Oxygen consists of three different _____, each having eight protons but different numbers of neutrons.arrow_forwardGive the complete symbol (XZA), including atomic number and mass number, of (a) a nickel atom with 31 neutrons, and (b) a tungsten atom with 110 neutrons.arrow_forwardIf the volume of a proton is similar to the volume of an electron, how will the densities of these two particles compare to each other?arrow_forward
- Which of the following are isotopes of element X, the atomic number for which is 9: 919X, 920X, 189X, and 921X?arrow_forwardDefine the term atomic weight. Why might the values of atomic weights on a planet elsewhere in the universe be different from those on earth?arrow_forwardTwo compounds of iron and chlorine, A and B, contain 1.270 g and 1.904 g of chlorine, respectively, for each gram of iron. Show that these amounts are in the ratio 2 : 3. Is this consistent with the law of multiple proportions? Explain.arrow_forward
- 2.75 Chlorine has only two isotopes, one with mass 35 and the other with mass 37. One is present at roughly 75% abundance, and the atomic weight of chlorine on a periodic table is 35.45. Which must be the correct mass spectrum for chlorine?arrow_forward2.90 Naturally occurring europium has an average atomic weight of 151.964 amu. If the only isotopes of europium present are 151Eu and 153Eu, describe how you would determine the relative abundance of the two isotopes. Include in your description any information that would need to be looked up.arrow_forwardThere are 2.619 1022 atoms in 1.000 g of sodium. Assume that sodium atoms are spheres of radius 1.86 and that they are lined up side by side. How many miles in length is the line of sodium atoms?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





