
An electronic chess game has a useful life that is exponential with a mean of 30 month. Determine each of the following:
a. The probability that any given unit will operate for at least (1) 39 months. (2) 48 men the (3) 60 months.
b. The probability that any given unit will fail sooner than (1) 33 months. (2) 15 months. (3) 6 months.
c. The length of service tune after which the percentage of tilled units will approximately equal (1) 50 percent, (2) 85 percent, (3) 95 percent, (4) 99 percent.
a)
To determine: The probability the unit will operate at least for the following times.
Introduction:
Mean time between failures (MTBF):
The mean time between failures is a term which denotes the time that is elapsed between the first failure of a product and the second failure of a product. It is calculated during the normal system operation.
Answer to Problem 12P
1) 39 months = 0.2725
2) 48 months = 0.2019
3) 60 months = 0.1353
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
MTBF = 30 months
Formula to calculate the probability of no failure before a time period:
Calculation of probability:
1) 39 months:
Hence, the probability the unit will operate at least for the 39 months is 0.2725.
2) 48 months:
Hence, the probability the unit will operate at least for the 48 months is 0.2019.
3) 60 months:
Hence, the probability the unit will operate at least for the 60 months is 0.1353.
b)
To determine: The probability the unit will fail before the following times.
Introduction:
Mean time between failures (MTBF):
The mean time between failures is a term which denotes the time that is elapsed between the first failure of a product and the second failure of a product. It is calculated during the normal system operation.
Answer to Problem 12P
1) 33 months = 0.6671
2) 15 months = 0.3935
3) 6 months = 0.1813
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
MTBF = 30 months
Formula to calculate the probability of failure before a time period:
Calculation of probability:
1) 33 months:
Hence, the probability the unit will fail before 33 months is 0.6671.
2) 15 months:
Hence, the probability the unit will fail before 15 months is 0.3935.
3) 6 months:
Hence, the probability the unit will fail before 6 months is 0.1813.
c)
To determine: The length of service time for the percentage of failed units.
Introduction:
Mean time between failures (MTBF):
The mean time between failures is a term which denotes the time that is elapsed between the first failure of a product and the second failure of a product. It is calculated during the normal system operation.
Answer to Problem 12P
1) 50 percent = 21 months.
2) 85 percent = 57 months.
3) 95 percent = 90 months.
4) 99 percent = 138 months.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
MTBF = 30 months
Formula to calculate the probability of no failure before a time period:
Calculation of probability:
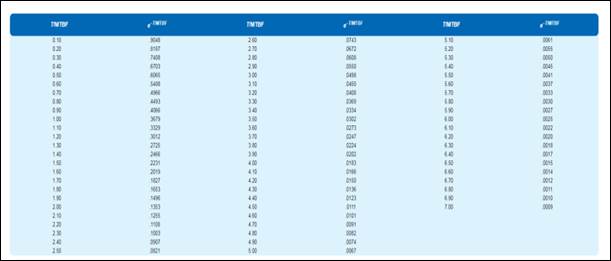
The different probabilities are obtained from the above table.
1) 50 percent:
From the table for the value of 0.50 is equivalent to:
Therefore,
Hence, the length of service time for the percentage of failed units is 21 months.
2) 85 percent:
From the table for the value of 0.15 is equivalent to:
Therefore,
Hence, the length of service time for the percentage of failed units is 57 months.
3) 95 percent:
From the table for the value of 0.05 is equivalent to:
Therefore,
Hence, the length of service time for the percentage of failed units is 90 months.
4) 99 percent:
From the table for the value of 0.01 is equivalent to:
Therefore,
Hence, the length of service time for the percentage of failed units is 138 months.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Operations Management
- In the context of the material in Chapter 9, provide a critical analysis of the decisions that Henry has made in assigning Martin to this role.arrow_forwardpanies (pp. 80-118). New York, NY: Times Books, specifically Chap. 4, "Robert Eaton and Robert Lutz; The Copilots." CASE STUDY 9-2 Performance Management Leadership at Henry's Commercial Sales and Leasing H enry is the owner of a small real estate agency that handles the sale and leasing of commercial property. He has two real estate agents working in the office, along with himself. He also has two customer service representatives (CSRs), each of whom has a real estate license, and one receptionist who has worked for the company for about three months. Henry has recently decided that he needs another customer service representative. He hasarrow_forwardDiscuss possible solutions to help Tara become an effective CSR. What should martin be doing to help her?arrow_forward
- What are the ethical challenges regarding employees (i.e., diversity, discrimination, sexual harassment, privacy, employee theft, bad leadership, etc.) that Apple Inc. has faced over the past five to ten years and that they should prepare to face in the next five to ten years. Once a developed list of challenges is created, consider how having faced those challenges will impact and be impacted by the social cause you've selected. Propose the findings on the ethical challenges faced by Apple Inc. in recent history and the near future. Analyze ways in which each challenge was (and/or could be) appropriately handled and areas for improvement. Evaluate the ethical/moral aspects of Apple Inc. that protected it from ethical challenges in the past and could protect it in the future. Assess how ethical challenges and handling of ethical challenges could positively or negatively impact the charitable cause are selected and how the selection of your social cause could positively or negatively…arrow_forwardBy selecting Cigna Accredo pharmacy that i identify in my resand compare the current feedback system against the “Characteristics of a Good Multiple Source Feedback Systems” described in section 8-3-3. What can be improved? As a consultant, what recommendations would you make?arrow_forwardScenario You have been given a task to create a demand forecast for the second year of sales of a premium outdoor grill. Accurate forecasts are important for many reasons, including for the company to ensure they have the materials they need to create the products required in a certain period of time. Your objective is to minimize the forecast error, which will be measured using the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) with a goal of being below 25%. You have historical monthly sales data for the past year and access to software that provides forecasts based on five different forecasting techniques (Naïve, 3-Month Moving Average, Exponential Smoothing for .2, Exponential Smooth for .5, and Seasonal) to help determine the best forecast for that particular month. Based on the given data, you will identify trends and patterns to create a more accurate forecast. Approach Consider the previous month's forecast to identify which technique is most effective. Use that to forecast the next…arrow_forward
- Approach Consider the previous month's forecast to identify which technique is most effective. Use that to forecast the next month. Remember to select the forecasting technique that produces the forecast error nearest to zero. For example: a. Naïve Forecast is 230 and the Forecast Error is -15. b. 3-Month Moving Forecast is 290 and the Forecast Error is -75. c. Exponential Smoothing Forecast for .2 is 308 and the Forecast Error is -93. d. Exponential Smoothing Forecast for .5 is 279 and the Forecast Error is -64. e. Seasonal Forecast is 297 and the Forecast Error is -82. The forecast for the next month would be 230 as the Naïve Forecast had the Forecast Error closest to zero with a -15. This forecasting technique was the best performing technique for that month. You do not need to do any external analysis-the forecast error for each strategy is already calculated for you in the tables below. Naïve Month Period Actual Demand Naïve Forecast Error 3- Month Moving Forecast 3- Month Moving…arrow_forwardScenario You have been given a task to create a demand forecast for the second year of sales of a premium outdoor grill. Accurate forecasts are important for many reasons, including for the company to ensure they have the materials they need to create the products required in a certain period of time. Your objective is to minimize the forecast error, which will be measured using the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) with a goal of being below 25%. You have historical monthly sales data for the past year and access to software that provides forecasts based on five different forecasting techniques (Naïve, 3-Month Moving Average, Exponential Smoothing for .2, Exponential Smooth for .5, and Seasonal) to help determine the best forecast for that particular month. Based on the given data, you will identify trends and patterns to create a more accurate forecast. Approach Consider the previous month's forecast to identify which technique is most effective. Use that to forecast the next…arrow_forwardUse the internet to obtain crash safety ratings for passenger vehicles. Then, answer thesequestions:a. Which vehicles received the highest ratings? The lowest ratings?b. How important are crash-safety ratings to new car buyers? Does the degree of importancedepend on the circumstances of the buyer?c. Which types of buyers would you expect to be the most concerned with crash-safety ratings?d. Are there other features of a new car that might sway a buyer from focusing solely on crashsafety? If so, what might they be?arrow_forward
- “Implementing a Performance Management Communication Plan at Accounting, Inc.” Evaluate Accounting Inc.’s communication plan. Specifically, does it answer all of the questions that a good communication plan should answer? Which questions are left unanswered? How would you provide answers to the unanswered questions? “Implementing an Appeals Process at Accounting, Inc.” If you were to design an appeals process to handle these complaints well, what would be the appeal process? Describe the recommended process and why.arrow_forwardThe annual demand for water bottles at Mega Stores is 500 units, with an ordering cost of Rs. 200 per order. If the annual inventory holding cost is estimated to be 20%. of unit cost, how frequently should he replenish his stocks? Further, suppose the supplier offers him a discount on bulk ordering as given below. Can the manager reduce his costs by taking advantage of either of these discounts? Recommend the best ordering policy for the store. Order size Unit cost (Rs.) 1 – 49 pcs. 20.00 50 – 149 pcs. 19.50 150 – 299 pcs. 19.00 300 pcs. or more 18.00arrow_forwardHelp answer showing level work and formulasarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
