
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 4, Problem 21CTQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: Sentence that describes each curved arrow in reaction 2 should be determined.
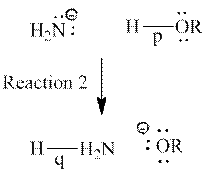
Concept introduction: Curved arrows are used to represent breakage and formation of bonds. Curved arrow is shown as follows:

The tail of curved arrow indicates the point that gives electrons and its head represents point where electrons are moved. Curved arrows can be single-barbed or double-barbed. Double-barbed arrow indicates transference of two electrons and is shown as follows:

Single-barbed arrow indicates transference of only one electron and is shown as follows:
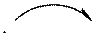
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Give detailed mechanism Solution with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solution
Show work with explanation needed....don't give Ai generated solution
1.
6. Draw the products for the following reaction:
2.
Diels-Aider
reaction
NOH O
OH
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Ch. 4 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 4 - Figure 4.1 is a cartoon depiction of liquid water...Ch. 4 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 4CTQCh. 4 - In HF , neither H nor F holds a full formal charge...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 7CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 4 - Within any one section of Table 4.2, boiling...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 4 - Prob. 11CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 13CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 15CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 16CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 17CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 18CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 19CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 20CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 21CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 22CTQCh. 4 - (E) Label each of the following as strong acid,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 24CTQCh. 4 - Draw the structure of the conjugate base of water....Ch. 4 - Does Cl have a conjugate acid? If so, what is it?...Ch. 4 - Draw the conjugate base of CH4 (methane).Ch. 4 - For the previous four questions, label each...Ch. 4 - Prob. 29CTQCh. 4 - According to the conventions above, what is the...Ch. 4 - Draw an arrow on Figure 4.13 representing Hrxn4 ....Ch. 4 - Prob. 32CTQCh. 4 - Add a + or above each curved arrow in Figure 4.11...Ch. 4 - Prob. 34CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 35CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 36CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 37CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 38CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 39CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 40CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 41CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 42CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 43CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 44CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 45CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 46CTQCh. 4 - For NH3 (ammonia) and H2O (water)... a. Use curved...Ch. 4 - Prob. 48CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 49CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 50CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 51CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 52CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 53CTQCh. 4 - Prob. 1ECh. 4 - Prob. 2ECh. 4 - Prob. 3ECh. 4 - Prob. 4ECh. 4 - Prob. 5ECh. 4 - Prob. 6ECh. 4 - Prob. 7ECh. 4 - Prob. 8ECh. 4 - Propanal (bp 48°C) and propanol (bp 97°C), both...Ch. 4 - Rank the following molecules from lowest to...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12ECh. 4 - For each molecule below, draw the conjugate acid...Ch. 4 - For each structure you drew in the answer to the...Ch. 4 - Mark each of the following statements True or...Ch. 4 - Organic chemistry is a bit like cooking. Later in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 17ECh. 4 - Prob. 18ECh. 4 - Are endothermic reactions favorable or...Ch. 4 - Prob. 20ECh. 4 - Is bond formation endothermic or exothermic? Write...Ch. 4 - Summarize the relationship between pKa and acid...Ch. 4 - Summarize the relationship between pKa and base...Ch. 4 - Prob. 25ECh. 4 - Consider the following bases: a. For each base...Ch. 4 - Prob. 27ECh. 4 - The following are equivalent ways of asking about...Ch. 4 - Prob. 29E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning