
Concept explainers
The lens and mirror in Figure P36.77 are separated by d = 1.00 m and have focal lengths of +80.0 cm and
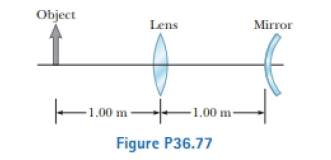
-50.0 cm, respectively. An object is placed p = 1.00 m to the left of the lens as shown, (a) Locate the final image, formed by light that has gone through the lens twice. (b) Determine the overall magnification of the image and (c) state whether the image is upright or inverted.
(a)
The exact position of the final image formed by light.
Answer to Problem 36.77AP
The exact position of the final image formed by light is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The object distance from the lens is
Write the expression for the image distance from the lens,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the image distance from the lens is
This image distance act as an object for the mirror with an object distance of,
Substitute
Write the expression for the image distance from the mirror,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the image distance from the mirror is
This image distance act as an object for the lens when the light passes through right to left,
The object distance for the lens is,
Substitute
Write the expression for the image distance from the thin lens,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the exact position of the final image formed by light is
(b)
The overall magnification of the image.
Answer to Problem 36.77AP
The overall magnification of the image is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: : The object distance from the lens is
From the part (a) the image distance from the lens is
Formula to calculate the overall magnification is,
Formula to calculate the magnification of lens is,
Formula to calculate the magnification of mirror is,
Formula to calculation the magnification of lens when the light passes through right to left is,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the overall magnification of the image is
(c)
Whether the image is upright or inverted.
Answer to Problem 36.77AP
The image is inverted.
Explanation of Solution
From part (b) the overall magnification of the image is
Since, the overall magnification of the image is less than zero
Conclusion:
Therefore, the image is inverted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- Figure P38.43 shows a concave meniscus lens. If |r1| = 8.50 cm and |r2| = 6.50 cm, find the focal length and determine whether the lens is converging or diverging. The lens is made of glass with index of refraction n = 1.55. CHECK and THINK: How do your answers change if the object is placed on the right side of the lens? FIGURE P38.43arrow_forwardTwo converging lenses having focal lengths of f1 = 10.0 cm and f2 = 20.0 cm are placed a distance d = 50.0 cm apart as shown in Figure P35.48. The image due to light passing through both lenses is to be located between the lenses at the position x = 31.0 cm indicated. (a) At what value of p should the object be positioned to the left of the first lens? (b) What is the magnification of the final image? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted? (d) Is the final image real or virtual?arrow_forwardA converging lens made of crown glass has a focal length of 15.0 cm when used in air. If the lens is immersed in water, what is its focal length? (a) negative (b) less than 15.0 cm (c) equal to 15.0 cm (d) greater than 15.0 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forward
- Why is the following situation impossible? Consider the lensmirror combination shown in Figure P35.55. The lens has a focal length of fL = 0.200 m, and the mirror has a focal length of fM = 0.500 m. The lens and mirror are placed a distance d = 1.30 m apart, and an object is placed at p = 0.300 m from the lens. By moving a screen to various positions to the left of the lens, a student finds two different positions of the screen that produce a sharp image of the object. One of these positions corresponds to light leaving the object and traveling to the left through the lens. The other position corresponds to light traveling to the right from the object, reflecting from the mirror and then passing through the lens. Figure P35.55 Problem 55 and 57.arrow_forwardIn Figure P26.38, a thin converging lens of focal length 14.0 cm forms an image of the square abcd, which is hc = hb = 10.0 cm high and lies between distances of pd = 20.0 cm and pa = 30.0 cm from the lens. Let a, b, c, and d represent the respective corners of the image. Let qa represent the image distance for points a and b, qd represent the image distance for points c and d, hb represent the distance from point b to the axis, and hc represent the height of c. (a) Find qa, qd, hb, and hc. (b) Make a sketch of the image. (c) The area of the object is 100 cm2. By carrying out the following steps, you will evaluate the area of the image. Let q represent the image distance of any point between a and d, for which the object distance is p. Let h represent the distance from the axis to the point at the edge of the image between b and c at image distance q. Demonstrate that h=10.0q(114.01q) where h and q are in centimeters. (d) Explain why the geometric area of the image is given by qaqdhdq (e) Carry out the integration to find the area of the image. Figure P26.38arrow_forwardA lamp of height S cm is placed 40 cm in front of a converging lens of focal length 20 cm. There is a plane mirror 15 cm behind the lens. Where would you find the image when you look in the mirror?arrow_forward
- The left face of a biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 12.0 cm, and the right face has a radius of curvature of magnitude 18.0 cm. The index of refraction of the glass is 1.44. (a) Calculate the focal length of the lens for light incident from the left. (b) What If? After the lens is turned around to interchange the radii of curvature of the two faces, calculate the focal length of the lens for light incident from the left.arrow_forwardA floating strawberry illusion is achieved with two parabolic mirrors, each having a focal length 7.50 cm, facing each other as shown in Figure P33.58. If a strawberry is placed on the lower mirror, an image of the strawberry is formed at the small opening at the center of the top mirror, 7.50 cm above the lowest point of the bottom mirror. The position of the eye in Figure P35.58a corresponds to the view of the apparatus in Figure P35.58b. Consider the light path marked A. Notice that this light path is blocked by the upper mirror so that the strawberry itself is not directly observable. The light path marked B corresponds to the eye viewing the image of the strawberry that is formed at the opening at the top of the apparatus. (a) Show that the final image is formed at that location and describe its characteristics. (b) A very startling effect is to shine a flashlight beam on this image. Even al a glancing angle, the incoming light beam is seemingly reflected from the image! Explain. Figure P35.58arrow_forwardTwo converging lenses having focal length of f1 = 10.0 cm and f2 = 20.0 cm are placed d = 50.0 cm apart, as shown in Figure P23.44. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position x = 31.0 cm indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magnification of the system? (c) Is the final image uptight or inserted? Figure P23.44arrow_forward
- An observer to the right of the mirror-lens combination shown in Figure P36.89 (not to scale) sees two real images that are the same size and in the same location. One image is upright, and the other is inverted. Both images are 1.50 times larger than the object. The lens has a focal length of 10.0 cm. The lens and mirror are separated by 40.0 cm. Determine the focal length of the mirror.arrow_forwardHow far should you hold a 2.1 cm-focal length magnifying glass from an object to obtain a magnification of 10 x ? Assume you place your eye 5.0 cm from the magnifying glass.arrow_forwardA leaf of length h is positioned 71.0 cm in front of a converging lens with a focal length of 39.0 cm. An observer views the image of the leaf from a position 1.26 in behind the lens, as shown in Figure P25.25. (a) What is the magnitude of the lateral magnification (the ratio of the image size to the object size) produced by the lens? (b) What angular magnification is achieved by viewing the image of the leaf rather than viewing the loaf directly? Figure P25.25arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





