
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.SE, Problem 60AP
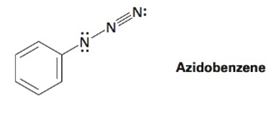
The azide
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
a)
b)
c)
H
NaOH
heat, dehydration
+
KOH
heat, dehydration
NaOH
+
(CH3)3CCHO
heat, dehydration
Ph
show mechanism
Please draw by hand
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 2.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 2.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 2.1 - Use the electronegativity values shown in Figure...Ch. 2.1 - Look at the following electrostatic potential map...Ch. 2.2 - Ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, may look nonpolar...Ch. 2.2 - Make three-dimensional drawings of the following...Ch. 2.3 - Calculate formal charges for the nonhydrogen atoms...Ch. 2.3 - Organic phosphate groups occur commonly in...Ch. 2.6 - Which of the following pairs of structures...Ch. 2.6 - Draw the indicated number of resonance forms for...
Ch. 2.7 - Nitric acid (HNO3) reacts with ammonia (NH3) to...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 12PCh. 2.8 - Amide ion, H2N-, is a much stronger base than...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 14PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 15PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 16PCh. 2.11 - Using curved arrows, show how the species in part...Ch. 2.11 - Prob. 18PCh. 2.12 - Of the two vitamins A and C, one is hydrophilic...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 20VCCh. 2.SE - The following model is a representation of...Ch. 2.SE - cis-l, 2-Dichloroethylene and trans-1,...Ch. 2.SE - The following molecular models are representations...Ch. 2.SE - Predict the product(s) of the acid/base reactions...Ch. 2.SE - Use curved arrows to draw the protonated form of...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 26MPCh. 2.SE - Double bonds can also act like Lewis bases,...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 28APCh. 2.SE - Use the electronegativity table given in Figure...Ch. 2.SE - Which of the following molecules has a dipole...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 31APCh. 2.SE - Phosgene, C12C=O, has a smaller dipole moment than...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 33APCh. 2.SE - Methanethiol, CH3SH, has a substantial dipole...Ch. 2.SE - Calculate the formal charges on the atoms shown in...Ch. 2.SE - Assign formal charges to the atoms in each of the...Ch. 2.SE - Which of the following pairs of structures...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 38APCh. 2.SE - 1, 3-Cyclobutadiene is a rectangular molecule with...Ch. 2.SE - Alcohols can act either as weak acids or as weak...Ch. 2.SE - The O-H hydrogen in acetic acid is more acidic...Ch. 2.SE - Draw electron-dot structures for the following...Ch. 2.SE - Write the products of the following acid-base...Ch. 2.SE - Rank the following substances in order of...Ch. 2.SE - Which, if any, of the substances in Problem 2-44...Ch. 2.SE - The ammonium ion (NH4+, pKa = 9.25) has a lower...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 47APCh. 2.SE - Prob. 48APCh. 2.SE - Calculate Ka values from the following pka’s:...Ch. 2.SE - Calculate pKa values from the following Ka’s:...Ch. 2.SE - What is the pH of a 0.050 M solution of formic...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 52APCh. 2.SE - Maleic acid has a dipole moment, but the closely...Ch. 2.SE - Assume that you have two unlabeled bottles, one of...Ch. 2.SE - Identify the acids and bases in the following...Ch. 2.SE - Which of the following pairs represent resonance...Ch. 2.SE - Draw as many resonance structures as you can for...Ch. 2.SE - Carbocations, which contain a trivalent,...Ch. 2.SE - We’ll see in the next chapter that organic...Ch. 2.SE - The azide functional group, which occurs in...Ch. 2.SE - Phenol, C6H5OH, is a stronger acid than methanol,...Ch. 2.SE - Thiamin diphosphate (TPP), a derivative of vitamin...Ch. 2.SE - Determine if each compound or ion below has a...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 64APCh. 2.SE - Prob. 65APCh. 2.SE - Draw the conjugate base for each compound below...Ch. 2.SE - 1, 1, 1-Trichloroethanol is an acid more than 1000...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Predict the major product and give a mechanism for the following reactions: (CH3)3COH/H₂SO4 a) b) NC CH₂O c) LOCH, (CH3)3COH/H2SO4 H,SO -OHarrow_forwardIndicate if the aldehyde shown reacts with the provided nucleophiles in acid or base conditions. a NaBH4 be Li eli -NH2 P(Ph3) f KCN g OH excess h CH3OH i NaCHCCH3arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forward
- Polar solutes are most likely to dissolve into _____, and _____ are most likely to dissolve into nonpolar solvents. A. nonpolar solutes; polar solvents B. nonpolar solvents; polar solvents C. polar solvents; nonpolar solutes D. polar solutes; nonpolar solventsarrow_forwardDeducing the Peactants Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Xarrow_forwardDraw all 8 stereoisomers, circling each pair of enantiomer(s)/ mirror image compound(s)arrow_forward
- Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help Chemical Formula - Aktiv Che X + → C 11 a app.aktiv.com Google Chrome isn't your default browser Set as default Question 12 of 16 Q Fri Feb 2 Verify it's you New Chrome availabl- Write the balanced molecular chemical equation for the reaction in aqueous solution for mercury(I) nitrate and chromium(VI) sulfate. If no reaction occurs, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. 3 Hg(NO3)2(aq) + Cг2(SO4)3(aq) → 3 Hg₂SO (s) + 2 Cr(NO3), (aq) ean Ui mate co ence an climate bility inc ulnerabili women, main critic CLIMATE-INI ernational + 10 O 2 W FEB 1 + 4- 3- 2- 2 2 ( 3 4 NS 28 2 ty 56 + 2+ 3+ 4+ 7 8 9 0 5 (s) (1) Ch O 8 9 (g) (aq) Hg NR CI Cr x H₂O A 80 Q A DII A F2 F3 FA F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 #3 EA $ do 50 % 6 CO & 7 E R T Y U 8 ( 9 0 F10 34 F11 川 F12 Subr + delete 0 { P }arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction n the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. >arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Some important notes: A ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- if the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY