
Concept explainers
a)
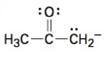
Interpretation:
To draw the maximum resonance structures possible for the species

Concept introduction:
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. For writing different resonance forms in the structure given, first a three atom groupings with a multiple bond and a p orbital with pair of electrons is to be identified. Then the exchange of position of double bond and electrons in p orbital will give another resonance form. The shift is represented by a curved arrow.
To draw:
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species

Answer to Problem 38AP
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  is two.
is two.
Explanation of Solution
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and their nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. The anion has a carbon atom doubly bonded to an oxygen and singly bonded to an adjacent carbon atom bearing negative charge. Using the nonbonding electrons on the negatively charged carbon atom and the π bond one more structure can be drawn, as shown, without change in position or hybridization of any atom. Hence the species given has two resonance forms.
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  are two.
are two.
b)
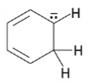
Interpretation:
To draw the maximum resonance structures possible for the species

Concept introduction:
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. For writing different resonance forms in the structure given, first a three atom groupings with a multiple bond and a p orbital with pair of electrons is to be identified. Then the exchange of position of double bond and electrons in p orbital will give another resonance form. The shift is represented by a curved arrow.
To draw:
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species

Answer to Problem 38AP
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  is three.
is three.
Explanation of Solution
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and their nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. The anion given has a carbon atom doubly bonded to another carbon and singly bonded to an adjacent carbon atom bearing negative charge. Another double bond also is present. Using the nonbonding electrons on the negatively charged carbon atom and the π bonds two more structures can be drawn as shown, without change in position or hybridization of any atom. Hence the species given has three resonance forms.
Conclusion:
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  are three.
are three.
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  are three.
are three.
c)
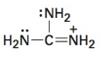
Interpretation:
To draw the maximum resonance structures possible for the species

Concept introduction:
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. For writing different resonance forms in the structure given, first a three atom groupings with a multiple bond and a p orbital with pair of electrons is to be identified. Then the exchange of position of double bond and electrons in p orbital will give another resonance form. The shift is represented by a curved arrow.
To draw:
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species

Answer to Problem 38AP
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  is three.
is three.
Explanation of Solution
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and their nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. The cation given has a carbon doubly bonded to positively charged nitrogen and singly bonded to two more nitrogens each with a pair of nonbonding electrons. Using the nonbonding electrons on the nitrogens and the π bond in C=N, two more structures, as shown, can be drawn without change in position or hybridization of any atom. Hence the species given has three resonance forms.
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species  are three.
are three.
d)
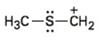
Interpretation:
To draw the maximum resonance structures possible for the species
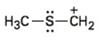
Concept introduction:
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. For writing different resonance forms in the structure given, first a three atom groupings with a multiple bond and a p orbital with pair of electrons is to be identified. Then the exchange of position of double bond and electrons in p orbital will give another resonance form. The shift is represented by a curved arrow.
To draw:
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species
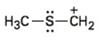
Answer to Problem 38AP
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species 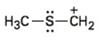 is two
is two
Explanation of Solution
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and their nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. The cation given has a carbon atom singly bonded to a sulfur atom which has two lone pairs of electrons. Using the nonbonding electrons on the sulfur atom one more structure can be drawn, as shown, without change in position or hybridization of any atom. Hence the species given has two resonance forms.
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species 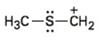 are two.
are two.
e)
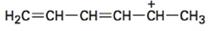
Interpretation:
To draw the maximum resonance structures possible for the species
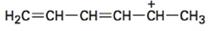
Concept introduction:
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. For writing different resonance forms in the structure given, first a three atom groupings with a multiple bond and a p orbital with pair of electrons is to be identified. Then the exchange of position of double bond and electrons in p orbital will give another resonance form. The shift is represented by a curved arrow.
To draw:
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species
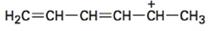
Answer to Problem 38AP
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species 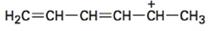 is three.
is three.
Explanation of Solution
Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and their nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. In the cation given, the positively charged carbon is attached a carbon chain that contains two conjugated double bonds. Using the two π bonds two more structures can be drawn, as shown, without change in position or hybridization of any atom. Hence the species given has three resonance forms.
The maximum resonance structures possible for the species 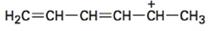 are three.
are three.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Synthetic natural gas (SNG) is a methane-containing mixture produced from the gasification of coal or oil shale directly at the site of the mine or oil field. One reaction for the production of SNG is: 4 CO (g) + 8 H2 (g) → 3 CH4 (g) + CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)Use the following thermochemical equations to determine ΔHo for the reaction as written. C(graphite) + 2 H2 (g) → CH4 (g) H2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) → H2O (g) C(graphite) + 1/2 O2 (g) → CO (g) CO(g) + 1/2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ΔHo = -74.8 kJ ΔHo = -285.8 kJ ΔHo = -110.5 kJ ΔHo = -283.0 kJ 5b. For the previous SNG reaction, how much energy would be released/gained if 200.0 g of CO were allowed to react with 400.0 g of H2?arrow_forwardThe PCC (1-piperidinocyclohexane carbonitrile) content of a clandestinely synthesized PCP (phencyclidine) sample can be determined by precipitating and weighing the product: PCC + Phenylmagnesium Bromide → PCP MW = 186.258 g/mole MW = 181.31 g/mole MW 243.387 g/mole In one analysis, 0.702 g of sample was dissolved in 25 mL of cylcohexanone and 1 g of phenylmagnesium bromide was added. After 25 minutes, the precipitate was filtered, washed with acetone, dried at 110°C, and found to weigh 0.869 3 grams. Find the recovery in wt% of PCC in the sample. In another analysis, the same sample was found to contain 5.17% of another impurity. What is the separation factor of this impurity in relation to PCC?arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Click on all of the atoms that make up the largest coplanar unit in the molecule below. H H N-H CIN C. C H H HHarrow_forwardClassify each of the following as either a substitution, elimination, or addition reaction. آمر +H₂O H+ + HNO3 H+ مر O OH NO2 + HO +H₂O O substitution O elimination ◇ addition O substitution O elimination O addition Br OH + HBr Explanation Check +2H2 + HBr Pt/C Br O substitution O elimination O addition O substitution O elimination O addition O substitution O elimination O additionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forward
- Would this align with acetone 2 ว 10 20 STUDENT LAB NOTE 26 3133 30 42 41 44 96 56 60 40 50 50 8-8-8 70 70 74 7375 80 60 90arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardPick 1 sets of two molecules from the list in the picture and provide a simulation of 2D NMR (H-H COSY and HSQC). I dont fully understand how to do it, so I would like to see how you do itarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardUse the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals 2P 2P 02p 015 B, C, Narrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand rating and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

