
coli to cause cystitis. Do the same for pyelonephritis. Diagram the pathway taken by Neisseria gonorrhoeae to cause PID.
To draw:
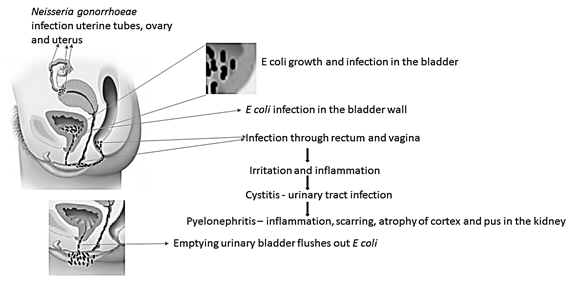
Pathway taken by E. coli to cause cystitis and pyelonephritis. Pathway taken by Neisseria gonorrhoeae to cause PID
Pictorial representation:
Concept introduction:
Cystitis is a urinary tract infection, mostly caused by E coli. Bacterial growth in the urothelium of the bladder through rectum, urethra, perineum and vagina causes cystitis. Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of kidneys, mostly caused by E coli. Bacteria can reach kidney through lower urinary tract and bloodstream. Pelvic inflammatory disease or PID is a severe bacterial infection of pelvic organs of women, mostly caused by N gonorrhoeae.
Explanation of Solution
Cystitis is a common urinary tract infection, caused by Escherichia coli (E coli) bacteria. Nearly 70-95% of the urinary tract infections are caused by E coli. It is a gram-negative, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria. It is commonly found in environment, skin and intestines of animal and human. Mostly they are harmless and help in digestion, and sometimes they can cause serious health problems like diarrhea, cystitis (urinary tract infections), respiratory problem, pneumonia, food poison and others. Cystitis is primarily caused by Escherichia coli and also by Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Klebsiella species, Proteus species and Enterobacter species. E coli covers the lining of the bladder and causes irritation and inflammation which leads to cystitis. Cystitis affects people in all age groups, however, it is more common in women than men due to the short urethra, which is less than 2 inches. The female urethra is very close to anal opening, hence it may lead to intestinal bacterial contamination. It can be prevented by drinking plenty of water which can flush bacteria and also with personal hygiene. Cystitis can be treated with antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim - sulfamethoxazole, fluoroquinolone and ampicillin.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of kidneys, caused by bacterial infection. It is a life-threatening disease which severely damages one or both kidneys and causes renal scarring. More than 70% of pyelonephritis is caused by E coli and rarely by Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella species. Bacteria can reach kidney through lower urinary tract and bloodstream. Initially, it infects bladder and move to kidney and severely damage one or both kidneys. Lower urinary tract infection is very vulnerable for kidney damage and pyelonephritis. Pyelonephritis is more common in women than men due to short urethra, which is less than 2 inches. The female urethra is very close to anal opening, hence it may lead to intestinal bacterial contaminations. Second or third generation cephalosporin is used to treat pyelonephritis.
Pelvic inflammatory disease or PID is a severe bacterial infection of pelvic organs such as uterus, cervix, uterine tubes or ovaries in female. N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis are common microorganisms mostly responsible for PID. Uterine tubes infection or salpingitis by N gonorrhoeae leads to scarring which blocks ovary. The uterine block may cause ectopic pregnancy. Salpingitis causes10-15% infertility in women. PID can be treated with doxycycline and cefoxitin.
Cystitis is a urinary tract infection, majorly caused by E. coli leads to irritation and inflammation of the urinary bladder. Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidney caused by E coli. PID is an inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organ caused by N gonorrhoeae.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physical Universe
HUMAN ANATOMY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
- Explain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardDescribe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- Please help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forwardA 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forwardStandard Concentration (caffeine) mg/L Absorbance Reading 10 0.322 20 0.697 40 1.535 60 2.520 80 3.100arrow_forward
- please draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forwardplease answer all question below with the following answer choice, thank you!arrow_forward
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage- Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:CengageSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:Cengage





