
(a)
Interpretation:
Reasonable precursors have to be suggested for the formation of compound I in the given problem.
Concept introduction:
Amide bond formation:
Amides, commonly known as acid amides are those compounds which have
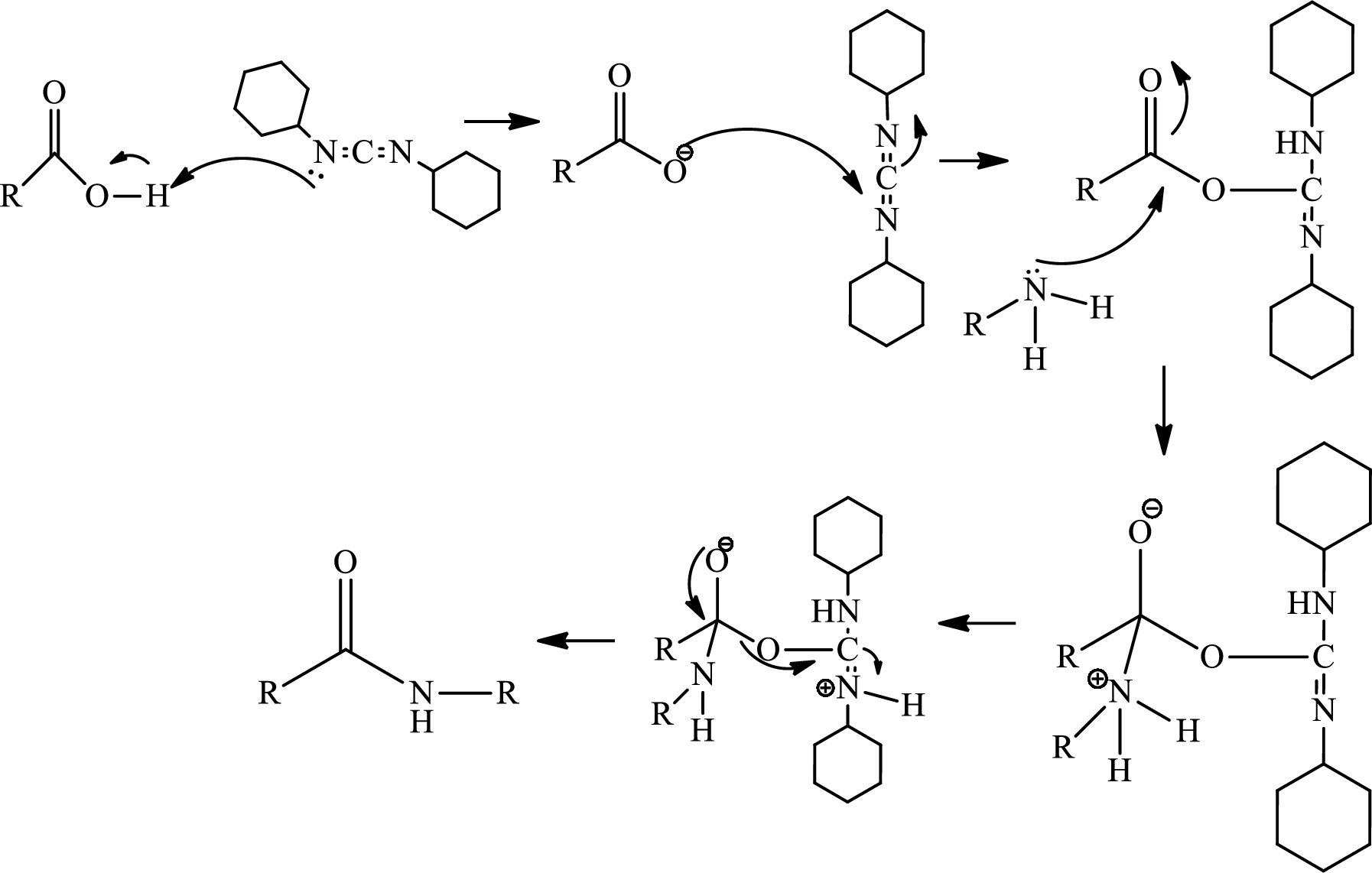
(b)
Interpretation:
Reagents for the reaction along with the mechanism have to be given for the conversion of compound I to II as given in the question.
Concept introduction:
Coupling reaction of aryl halides and phenols catalyzed by palladium and MOP types of ligands:
Palladium catalyzed coupling reactions of aryl halides and phenols are described employing the bulky and electron rich MOP type ligands. When
(c)
Interpretation:
The two isomers of compound II have to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Atropisomers:
Atropisomers are the stereoisomers arising because of the hindered rotation about a single bond where energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual conformers.
(d)
Interpretation:
Suitable reagents have to be given for the transformation of compound II to III in the given problem.
Concept introduction:
Reduction of nitro group:
Reduction of nitro group can be done by various reagents. In industrial scale reduction of nitrobenzene to anniline is a very common reaction. It is done by catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of palladium hydrogen.
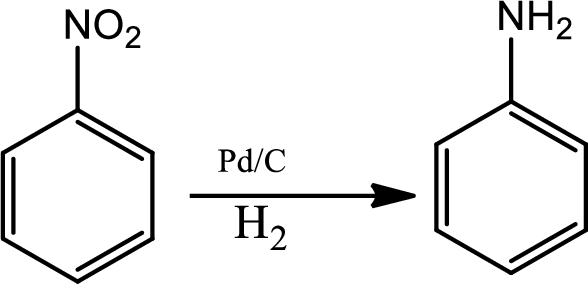
Diazotisation reaction:
Diazonium salta are organic compounds having
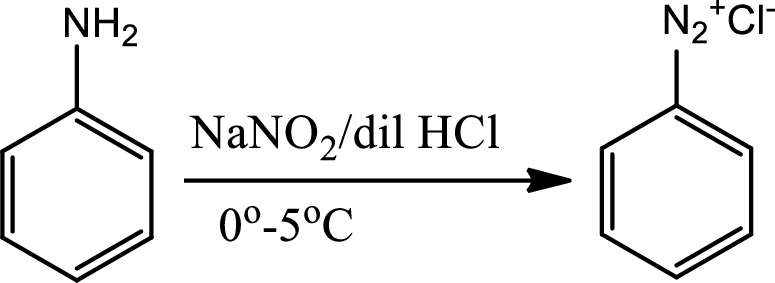
Sandmeyer reaction:
The Sandmeyer reaction is a
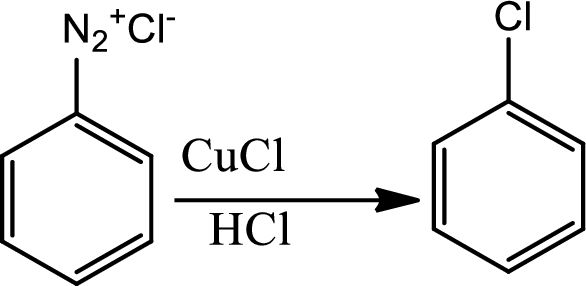
(e)
Interpretation:
The reagents and the fragment of the ring A that is useful for the conversion of compound III to IV have to be given.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reaction:
A grignard reagent is a chemical compound with the formula
(f)
Interpretation:
Ring closure reaction of the deprotected free amino group has to be given along with the mechanism.
Concept introduction:
Amide bond formation:
Amides, commonly known as acid amides are those compounds which have
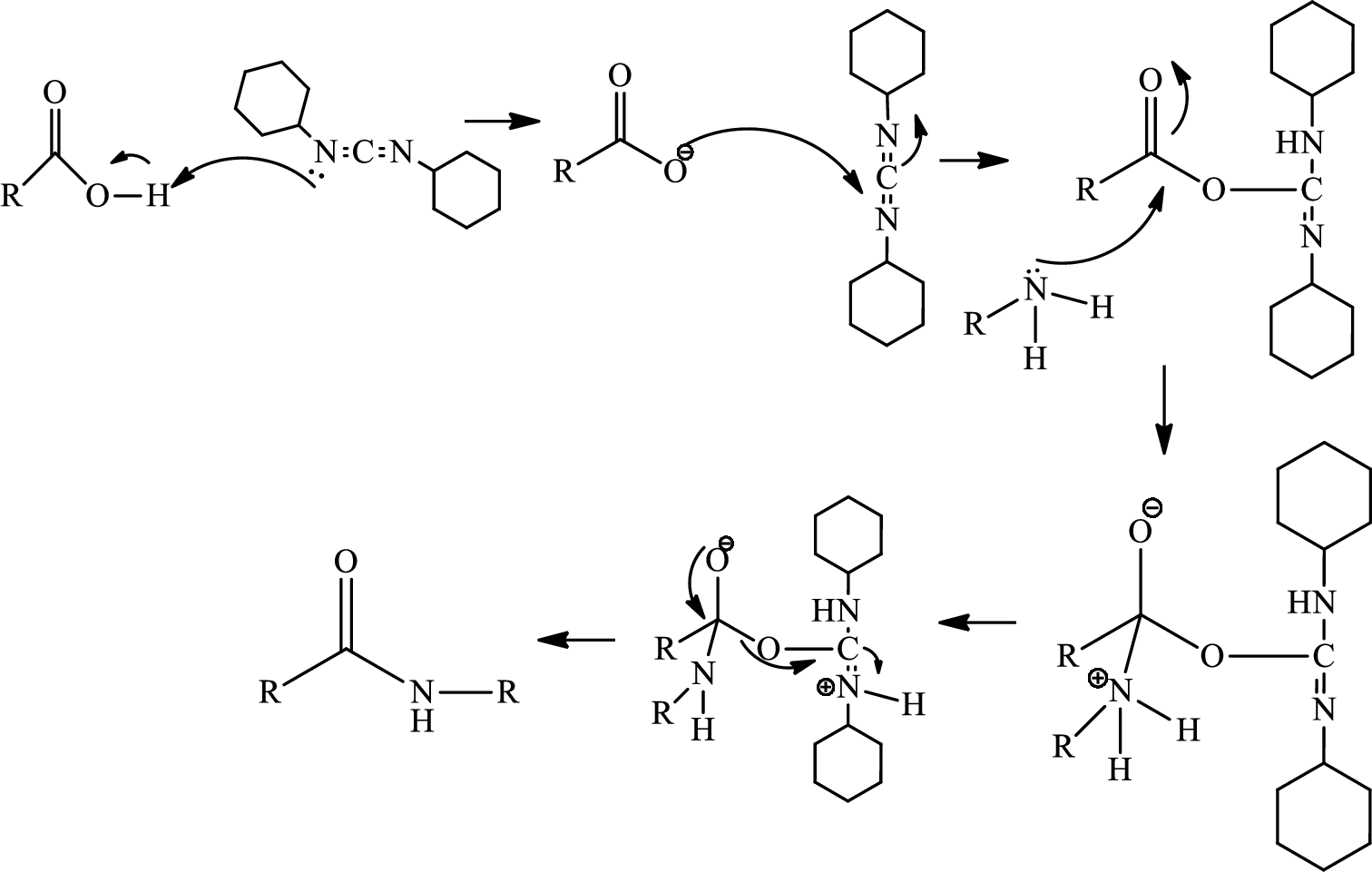
(g)
Interpretation:
The atropisomers have to be drawn and also it has to be shown that only one of them can be converted to vancomycin.
Concept introduction:
Atropisomers:
Atropisomers are the stereoisomers arising because of the hindered rotation about a single bond where energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual conformers.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Given the most probable macrostate: s/k (K) Populations 300 4 200 8 100 16 0 32 Indicate how to demonstrate that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann distribution.arrow_forwardRank the following components in order of decreasing volatility: butane, n-pentane, iso-pentene (e.g., 3-methyl-1-butene), isoprene, pentanol? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forwardViscosity of a liquid related to the activation energy.arrow_forward
- Vibrational contributions to internal energy and heat capacity1) are temperature independent2) are temperature dependentarrow_forwardThe approximation of calculating the partition function by integration instead of the summation of all the energy terms can only be done if the separation of the energy levels is much smaller than the product kT. Explain why.arrow_forwardExplain the meaning of: the electron partition function is equal to the degeneracy of the ground state.arrow_forward
- 28. For each of the following species, add charges wherever required to give a complete, correct Lewis structure. All bonds and nonbonded valence electrons are shown. a. b. H H H H H :0-C-H H H H-C-H C. H H d. H-N-0: e. H H-O H-O H B=0 f. H—Ö—Ñ—Ö—H Norton Private Barrow_forwardAt 0oC and 1 atm, the viscosity of hydrogen (gas) is 8.55x10-5 P. Calculate the viscosity of a gas, if possible, consisting of deuterium. Assume that the molecular sizes are equal.arrow_forwardIndicate the correct option for the velocity distribution function of gas molecules:a) its velocity cannot be measured in any other way due to the small size of the gas moleculesb) it is only used to describe the velocity of particles if their density is very high.c) it describes the probability that a gas particle has a velocity in a given interval of velocitiesd) it describes other magnitudes, such as pressure, energy, etc., but not the velocity of the moleculesarrow_forward
- Indicate the correct option for the velocity distribution function of gas molecules:a) its velocity cannot be measured in any other way due to the small size of the gas moleculesb) it is only used to describe the velocity of particles if their density is very high.c) it describes the probability that a gas particle has a velocity in a given interval of velocitiesd) it describes other magnitudes, such as pressure, energy, etc., but not the velocity of the moleculesarrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure of the alkane 4-ethyl-2, 2, 5, 5- tetramethylnonane. How many primary, secondary, tertiary, and quantenary carbons does it have?arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning




