
Interpretation:
The proper reactant and the proper coupling reaction pathway have to be suggested for the given
Concept Introduction:
Cross coupling:
A cross coupling reaction is defined as a reaction that creates a
In the case of palladium catalysed cross-coupling reactions the other metal or metalloids are commonly
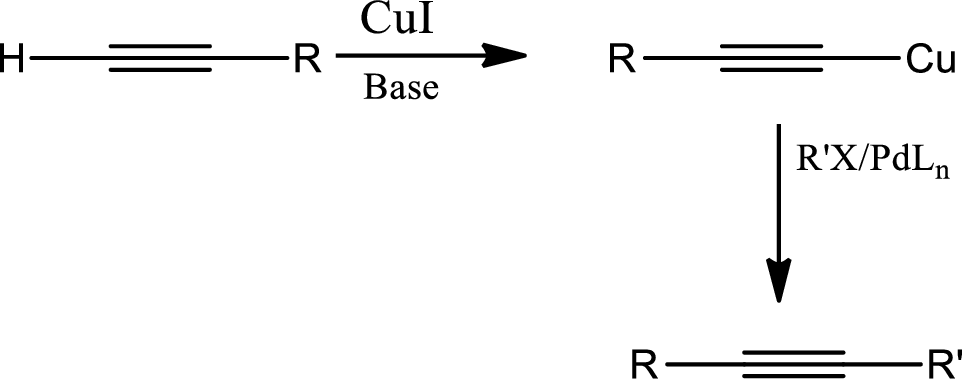
Sonogashira coupling:
The
Generalized reaction,
Suzuki coupling:
The Suzuki coupling uses a boron compound and an alkenyl, aryl or alkyl halide or triflate as the carbon sources with a palladium salt as a catalyst. The reaction is mainly used to form biaryls. The mechanism of the reaction starts with an oxidative addition followed by transmetallation in which the substituent on the borane replaces the ligand on the palladium concluding with the reductive elimination of the palladium to form the new carbon-carbon bond. The base may serve as a new labile ligand to palladium or it may activate the borane by coordination.
Generalized reaction,
Oxidative addition and ligand exchange,
Borane activation
Reaction,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- It is typically very difficult to do a substitution reaction on an aromatic ring when the leaving group is flanked by two other bulky substituents. Moreover, in Section 22.3, we found that nucleophilic aromatic substitution requires strongly electron-withdrawing groups on the benzene ring. However, Pd-catalyzed coupling allows entry into such products. As examples, write the products of the following reactions and state which coupling reaction is being utilized.arrow_forwardFollowing are the steps in the industrial synthesis of glycerin. Provide structures for all intermediate compounds (AD) and describe the type of mechanism by which each is formed.arrow_forwardAn organic compound A of unknown structure was found to have a molecular formula C8H16. When A was poured in water and heated, compound B having a molecular formula C8H18O was formed. B upon heating with sulfuric acid was converted to C as the major product which is identical to A. Ozonolysis of C gave one molecule each of two different products D and E, both having a molecular formula C4H8O. Write the reactions involved and determine the structure of A,B,C,D and E.arrow_forward
- Complete the reactions given below.arrow_forwardEnamines can serve as enolate surrogates in reactions at the a-carbon. In the reaction sequence, the structures of the enamine addition product – the initial iminium and its neutral tautomer – are shown. Draw the structures of the enamine and alkyl bromide reactants that would combine to form these intermediates, and draw the structure of the final product, obtained via hydrolysis of the neutral intermediate. iminium intermediate neutral intermediate tautomerization N. Reactants H20 hydrolysis product Draw the enamine and alkyl bromide reactants. Draw the hydrolysis product. ZIarrow_forwardThe formation of the following cyclic compound has been observed in the hydration of the following alkene, write a mechanism that explains the product.arrow_forward
- Answer the following questions regarding the nucleophilic substitution reaction shown below: CH3CH2CH2-Br + I- ------> CH3CH2CH2I + Br- (a) Write the rate law for this reaction assuming that it is a one step reaction that is first order in each of the reactants. (b) Holding the concentration of the iodide ion constant, what change would be observed in the rate if the concentration of the n- propyl bromide was tripled? (b) Assume that this is an exothermic reaction, draw the energy profile and identify the location of the transition state. (c) Draw the transition state for this reaction. (d) What change is observed for the entropy of the system during this reaction? (e) Show the likely mechanism of this reaction using the proper curved arrowsarrow_forwardGive the name and mechanism of this reaction asaparrow_forward4) Aromatic compounds are among the most abundant and versatile in nature. From a synthetic point of view, these compounds, despite their stabilities, are quite useful and can undergo reactions under special conditions and by specific mechanisms, such as the Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (SAE) and the Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (SNAr). Based on this, please answer the following items: (a) What are the possible isomeric products for the following reaction? Which structure, A or B, do you expect to predominate? Justify your choice. Write down the detailed mechanism of formation of compounds A and B. What would be the bromination product of each (compounds C and D)?arrow_forward
- Give the organic product(s) formed in each of the following reactions. When necessary, draw a 3D representation for the product molecule showing its correct configuration.arrow_forward(b) Consider the reaction of 1-bromobutane with a large excess of ammonia (NH3). Draw the reactants, the transition state, andthe products. Note that the initial product is the salt of an amine (RNH3+ Br - ), which is deprotonated by the excess ammonia to give the amine.arrow_forwardWhat is the suzuki coupling reaction mechanism of the figure below. Explain each step pleasearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

