
Concept explainers
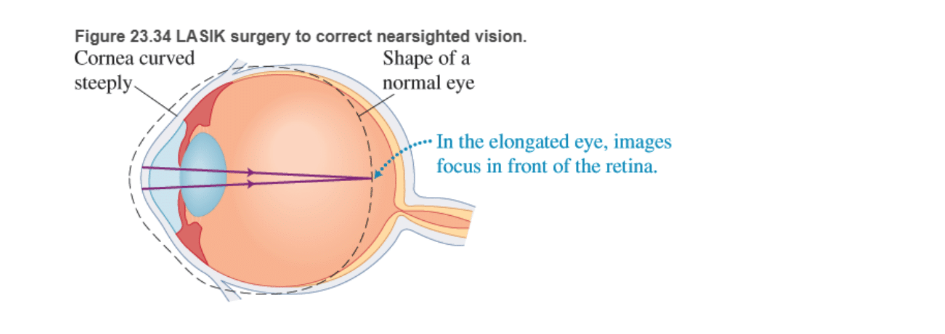
BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis) is a surgical procedure intended to reduce a person's dependency on glasses or contact lenses. Laser eye surgery corrects common vision problems, such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism (blurred vision resulting from corneal irregularities), or some combination of these. In myopia, the cornea, the clear covering at the front of the eye, is often too highly curved, causing rays from distant objects to form sharp images in front of the retina (Figure 23.34). LASIK refractive surgery can flatten the cornea so that images of distant objects form on the retina. A knife cuts a flap in the cornea with a hinge left at one end of this flap. The flap is folded back, exposing the middle section of the cornea Pulses from a computer-controlled laser vaporize a portion of the tissue and the flap is replaced.
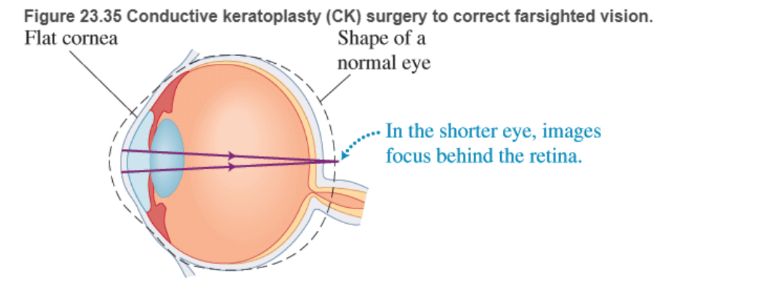
In farsighted people, an object held at the normal near point of the eye (about 25-50 cm from the eye) forms an image behind the retina (Figure 23.35). Increasing the curvature of the cornea causes rays from near objects to produce an image on the retina.
Your eyeball is 2.10 cm from the cornea to the retina You look at a sign on the freeway that is effectively an infinite distance away. The image for the sign is 1.96 cm from the cornea within the eye. What is the focal length of the cornea-lens system?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- Which of the following is true about the eye condition known as myopia? Select one: а. It means the eye can focus at short distance, but not long distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have diverging lenses O b. It means the eye can focus at long distance, but not short distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have converging lenses O c. It means the eye can focus at short distance, but not long distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have converging lenses O d. It means the eye can focus at long distance, but not short distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have diverging lenses Checkarrow_forwardNeed help, please and thanks!arrow_forwardMost animals—humans included—have eyes that use lenses to form images. The eyes of scallops are different. A typical scallop eye forms images largely by reflection from a mirror- like surface at the back of the eye. as shown the important features of a typical scallop eye. The lens causes very little redirection of incoming light rays; it is the spherical surface in the back of the eye that brings rays of light to a focus on the cells of the retina. (For simplicity, we’ve shown no refraction by the lens, although the lens does cause some refraction that seems to help to make the image sharper by correcting for the spherical aberration introduced by the mirror.) The reflection is due to thin-film interference from the front and back faces of 80-nm-thick transparent crystals of guanine, index n = 1.83, that are embedded in cytoplasm with index n = 1.34. The individualeyes are quite small. A typical scallop has 40 to 60 eyes, each with a 450-mm–diameter pupil and a reflecting surface at…arrow_forward
- Which of the following is true about the eye condition known as hyperopia? Select one: а. It means the eye can focus at short distance, but not long distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have diverging lenses O b. It means the eye can focus at short distance, but not long distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have converging lenses It means the eye can focus at long distance, but not short С. distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have converging lenses d. It means the eye can focus at long distance, but not short distance, and is corrected with eye glasses that have diverging lenses Checkarrow_forwardA person with a particularly strong refractive lens is ........... and uses ............ lenses to correct his vision. a) farsighted, concave b) farsighted, convex c) nearsighted, convex d) nearsighted, concavearrow_forwardMost animals—humans included—have eyes that use lenses to form images. The eyes of scallops are different. A typical scallop eye forms images largely by reflection from a mirror- like surface at the back of the eye. as shown the important features of a typical scallop eye. The lens causes very little redirection of incoming light rays; it is the spherical surface in the back of the eye that brings rays of light to a focus on the cells of the retina. (For simplicity, we’ve shown no refraction by the lens, although the lens does cause some refraction that seems to help to make the image sharper by correcting for the spherical aberration introduced by the mirror.) The reflection is due to thin-film interference from the front and back faces of 80-nm-thick transparent crystals of guanine, index n = 1.83, that are embedded in cytoplasm with index n = 1.34. The individualeyes are quite small. A typical scallop has 40 to 60 eyes, each with a 450-mm–diameter pupil and a reflecting surface at…arrow_forward
- Most animals—humans included—have eyes that use lenses to form images. The eyes of scallops are different. A typical scallop eye forms images largely by reflection from a mirror- like surface at the back of the eye. as shown the important features of a typical scallop eye. The lens causes very little redirection of incoming light rays; it is the spherical surface in the back of the eye that brings rays of light to a focus on the cells of the retina. (For simplicity, we’ve shown no refraction by the lens, although the lens does cause some refraction that seems to help to make the image sharper by correcting for the spherical aberration introduced by the mirror.) The reflection is due to thin-film interference from the front and back faces of 80-nm-thick transparent crystals of guanine, index n = 1.83, that are embedded in cytoplasm with index n = 1.34. The individualeyes are quite small. A typical scallop has 40 to 60 eyes, each with a 450-mm–diameter pupil and a reflecting surface at…arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true about an eye that is nearsighted? a) The image is in front of the retina, and this can be corrected by a diverging lens. b) The image is in back of the retina, and this can be corrected by a diverging lens. c) The image is in front of the retina, and this can be corrected by a converging lens. d) The image is in front of the retina, and this can be corrected by a diverging lens.arrow_forwardYou are working in an optical research laboratory. Your supervisor requests that you build her a beam expander with specifications required by her experiment. A beam expander is a series of two lenses on the same principal axis. A beam of laser light covers the total area of the first lens, which focuses the parallel rays at its focal point. A second lens with a longer focal length and a larger radius is placed on the axis so that the rays expanding from the focal point of the first lens cover the area of the second lens. The outgoing rays of the second lens are parallel. The net result is that the diameter of the outgoing laser beam is larger than the original beam. Your supervisor provides you with a lens of focal length f₁ = 1.30 cm. Its diameter matches that of an incoming laser beam of diameter d₁ = 0.150 cm. She wants the beam expanded to a diameter of d₂ = 0.690 cm. She asks you to find the following. (a) the focal length ₂ necessary for the second lens (in cm) cm (b) the…arrow_forward
- Presbyopia is the tendency to gradually become far-sighted (hyperopic) as you age. If you have normal vision when you are young, you have a near point of 25 cm.A. If the distance between your eye's lens and retina is 1.73 cm, what is the focal length of your eye's lens when you look at an object at your near point?f = _____ cmB. As you get older, suppose that the near point of your eye increases to 46 cm. What is the focal length of your eye's lens when you look at an object at your near point now?f = _______ cmC. With your near point at 46 cm, what is the focal length of the corrective lens (placed directly in front of your eye's lens) which you would need to look at an object that is 25 cm in front of your eye?f = _____ cmarrow_forwardA certain eyeglass lens is thin at its center, even thinner at its top and bottom edges, and relatively thick at its left and right edges. What defects of vision is this lens intended to correct? (i) Hyperopia for objects oriented both vertically and horizontally; (ii) myopia for objects oriented both vertically and horizontally; (iii) hyperopia for objects oriented vertically and myopia for objects oriented horizontally; (iv) hyperopia for objects oriented horizontally and myopia for objects oriented vertically.arrow_forwardYou have a thin, diverging lens. If the value of q (the distance from the image to the mirror along the principal axis of the mirror) is -1.63cm and the distance of p (the distance from the object to the mirror along the principal axis of the mirror) is 21.39cm, what is the focal length of the diverging lens? Diverging lens Ray 1 Ray 1 Ray 3 Object Virtual image Ray 2 Principal focal point Secondary focal point -Ifl- 一I- Note: Do not explicitly include units in your answer (it is understood the unit is cm). Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





