
College Physics
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134601823
Author: ETKINA, Eugenia, Planinšič, G. (gorazd), Van Heuvelen, Alan
Publisher: Pearson,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 23, Problem 89RPP
To determine
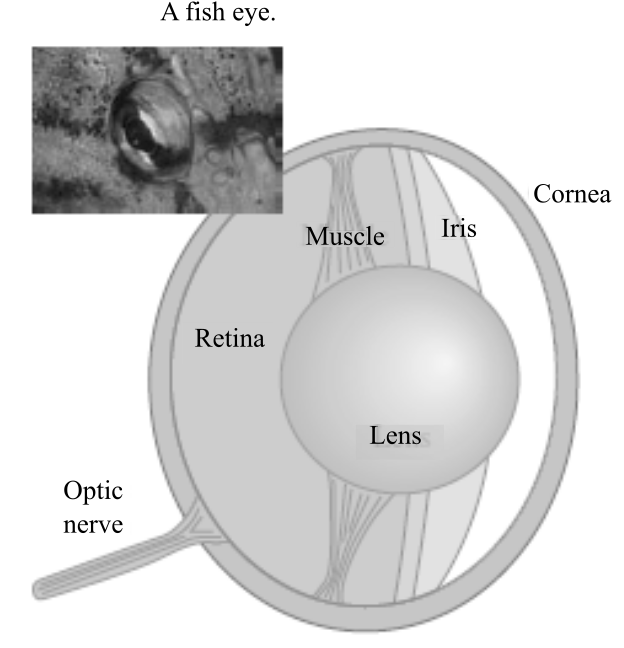
The reason for the black color of a fish’s eye from the following options.
a. The lens is black.
b. No light reflects out from behind the lens.
c. The fluid behind the lens is black.
d. The retina is black.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.1 A mirror is hanging on a...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.2 You've found a concave...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.3 You place a concave mirror on...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.5 Where should you place an...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.6 If we have a mathematical...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.7 What is the main difference...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.8 If a person with normal...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.9 Why is saying that a...Ch. 23 - Where does the image of an object in a plane...Ch. 23 - Where does the image of an object that is s meters...
Ch. 23 - 3. A plane mirror produces an image of an object...Ch. 23 - A concave mirror can produce an image that is...Ch. 23 - 5. A convex mirror can produce an image that is...Ch. 23 - 6. A virtual image is the image produced
a. on as...Ch. 23 - 7. To see an image of an object that is enlarged,...Ch. 23 - To see an image of an object that is enlarged,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 23 - 10. When drawing images of objects produced by...Ch. 23 - 11. The focal length of a glass lens is 10 cm....Ch. 23 - 12. A microbiologist uses a microscope to look at...Ch. 23 - 13. The human eye works in a similar way to which...Ch. 23 - Which of the following changes will result in a...Ch. 23 - When we draw a ray passing through the center of a...Ch. 23 - 16. You run toward a building with walls of a...Ch. 23 - 17. A tiny plane mirror can produce an image...Ch. 23 - Explain how we derived the mirror equation.Ch. 23 - 19. Explain how we derived the thin lens...Ch. 23 - Explain the difference between a real and a...Ch. 23 - You stand in front of a fun house mirror. You see...Ch. 23 - 22. A bubble of air is suspended underwater. Draw...Ch. 23 - 23. A bubble of oil is suspended in water. Draw...Ch. 23 - A typical person underwater cannot focus clearly...Ch. 23 - In a video projector, the picture that appears on...Ch. 23 - The retina has a blind spot at the place where the...Ch. 23 - You need to teach your friend how to draw rays to...Ch. 23 - Place a pencil in front of a plane mirror so that...Ch. 23 - 3.* Use geometry to prove that the virtual image...Ch. 23 - * You are 1.8 m tall. Where should you place the...Ch. 23 - 5. * Two people are standing in front of a...Ch. 23 - 6. * Test an idea Describe an experiment that you...Ch. 23 - * Describe in detail an experiment to find the...Ch. 23 - * Explain with a ray diagram how (a) a concave...Ch. 23 - 9. * Test an idea Describe an experiment to test...Ch. 23 - * Test an idea Describe an experiment to test the...Ch. 23 - 11. * Tablespoon mirror You look at yourself in...Ch. 23 - * Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to...Ch. 23 - Repeat Problem 23.12 for a convex mirror of focal...Ch. 23 - 14. Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to...Ch. 23 - 15. * Sinking ships A legend says that Archimedes...Ch. 23 - 16. * EST Fortune-teller A fortune-teller looks...Ch. 23 - * You view yourself in a large convex mirror of...Ch. 23 - * Seeing the Moon in a mirror The Moons diameter...Ch. 23 - 19. * You view your face in a +20-cm focal length...Ch. 23 - 20. * Buying a dental mirror A dentist wants to...Ch. 23 - * Using a dental mirror A dentist examines a tooth...Ch. 23 - * If you place a point-like light source on the...Ch. 23 - 24. * You have a convex lens and a candle....Ch. 23 - 25. * Explain how to draw ray diagrams to locate...Ch. 23 - * Draw ray diagrams to show how a convex lens can...Ch. 23 - 27. * Use a ruler to draw ray diagrams to locate...Ch. 23 - 28. * Repeat the procedure described in Problem...Ch. 23 - 29. * Repeat the procedure described in Problem...Ch. 23 - 30 * Repeat the procedure in Problem 23.27 for the...Ch. 23 - * Partially covering lens Your friend thinks that...Ch. 23 - * Use ray diagrams to locate the images of the...Ch. 23 - 33. *Use ray diagrams to locate the images of the...Ch. 23 - Light passes through a narrow slit, and then...Ch. 23 - * Describe two experiments that you can perform to...Ch. 23 - * Shaving/makeup mirror You wish to order a mirror...Ch. 23 - 37. Dentist lamps Dentists use special lamps that...Ch. 23 - 38. * A large concave mirror of focal length 3.0m...Ch. 23 - 39 * EST Two convex mirrors on the side of a van...Ch. 23 - Camera You are using a camera with a lens of focal...Ch. 23 - 42. * Camera A camera with an 8.0-cm focal length...Ch. 23 - Video projector An LCD video projector (LCD stands...Ch. 23 - Photo of carpenter ant You take a picture of a...Ch. 23 - * Photo of secret document A secret agent uses a...Ch. 23 - 46. * Photo of landscape To photograph a landscape...Ch. 23 - * Make a rough graph of image distance versus...Ch. 23 - * Make a rough graph of linear magnification...Ch. 23 - * Repeat Problem 23.48 for a concave lens of...Ch. 23 - BIO Eye The image distance for the lens of a...Ch. 23 - BIO Lens-retina distance Fish and amphibians...Ch. 23 - BIO Nearsighted and farsighted (a) A woman can...Ch. 23 - * BIO Prescribe glasses A man who can produce...Ch. 23 - 54. * BIO Correcting vision A woman who produces...Ch. 23 - 55. * BIO Where are the far and near points? (a) A...Ch. 23 - * BIO Age-related vision changes A 35-year-old...Ch. 23 - 5.7 Looking at an aphid You examine an aphid on a...Ch. 23 - 58. * Reading with a magnifying glass You examine...Ch. 23 - 59. * Seeing an image with a magnifying glass A...Ch. 23 - * Stamp collector A stamp collector is viewing a...Ch. 23 - * You place a +20-cm focal length convex lens at a...Ch. 23 - 62. * You place a +25-cm focal length convex lens...Ch. 23 - * EST You place a candle 10 cm in front of a...Ch. 23 - 64. * EST Repeat Problem 23.63 for an object...Ch. 23 - ** You measure the focal length of a concave lens...Ch. 23 - 66.** Telescope A telescope consists of a +4.0-cm...Ch. 23 - 67. ** Yerkes telescope The world’s largest...Ch. 23 - * Telescope A telescope consisting of a +3.0-cm...Ch. 23 - 69. *** Design a telescope You are marooned on a...Ch. 23 - * Microscope A microscope has a +0.50-cm objective...Ch. 23 - 71. ** BIO Dissecting microscope A dissecting...Ch. 23 - *** Microscope A microscope has an objective lens...Ch. 23 - 73. ** Microscope Determine the lens separation...Ch. 23 - * Figure P23.75 shows three cases of the primary...Ch. 23 - Prob. 78GPCh. 23 - ** Two-lens camera A two-lens camera (see Figure...Ch. 23 - **You have a small spherically shaped bottle made...Ch. 23 - BIO Find a farsighted person. Design an experiment...Ch. 23 - 82. BIO Find a nearsighted person. Design an...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - Prob. 89RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 90RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 91RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 92RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 93RPP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax
Laws of Refraction of Light | Don't Memorise; Author: Don't Memorise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4l2thi5_84o;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY