
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The structures of
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
A chiral carbon is the carbon atom which is substituted to four different groups. Due to presence of chiral carbon a molecule become chiral and it gives optical isomers also that is
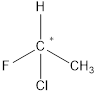
All the substituents are different hence it is a chiral carbon and so molecule.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Using the given IUPAC name 4-chloro-3,4-dimethylnonan-1-amine Please help with the following: One a page titled Stereoisomers print/draw the expanded structure of your molecule.o Calculate the maximum number of possible stereoisomers of your molecule usingthe following formula:▪ Maximum number of possible stereoisomers = 2n(where n= the number ofchiral carbons in your molecule). This calculation does not include E- or Zisomers for any compounds containing double bondso Draw the possible stereoisomers of the molecule.▪ Note that E-, Z- isomers of each stereoisomer are also possible andwould not be accounted for by the formula above; draw any E- or Zisomers. On a page titled Polarity and Solubility Predictions draw/print the structural formula ofyour molecule (expanded or condensed)o Circle or highlight all polar portions of the moleculeo Make predictions whether your molecule will be soluble in water or not and explainyour rational. Note that there may be no correct answer as often…arrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry HW: CANNOT BE HAND DRAWN 2,6-dimethyloct-2-ene Provide a detailed typed explanation of Stereoisomers show the expanded structure of your molecule. Calculate the maximum number of possible stereoisomers of your molecule using the following formula: Maximum number of possible stereoisomers = 2n (where n= the number of chiral carbons in your molecule). This calculation does not include E- or Z- isomers for any compounds containing double bonds Type or using a computer program "draw" the possible stereoisomers of the molecule. Note that E-, Z- isomers of each stereoisomer are also possible and would not be accounted for by the formula above; draw any E- or Z- isomers.arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are present in the structural formula for the open-chain form of d-mannose? Draw the structure of the six-member-ring form of this molecule.arrow_forward
- Drawing optical isomers 1. Locate the chiral centre- look for the carbon atom with four different groups attached. 2. Draw one enantiomer in a tetrahedral shape -chlo 1. Loca - put the chiral carbon atom at the centre and the four different groups in a tetrahedral shape around it. Don't try to draw the full structure of each group -it gets confusing, Just use the structural formulas. 3. Draw the mirror image of the enantiomer-put in a mirror line next to the enantiomer and then draw the mirror image of the enantiomer on the other side of it. Example Draw the two enantiomers of 2-hydroxybutanoic acid. The structure of 2-butanoic acid is shown below. 1. Locate the chiral centre 2. Draw one 3. Draw its mirror image beside it. enantiomer in a 1. La tetrahedral shape H H H C.CH,CH ICOOH C*COOH chiral centre H H. OH H;CH,C I HOOC H;CH,C ОН OH ОНarrow_forwardConsider the molecule N-ethyl-N-methyl-3-iodo-4-methyl hexanamide. Draw it and give the two reactants that would produce this product. Name them and draw their skeletal structures.arrow_forwardGive three different examples of chiral compounds that do not have an asymmetrically substituted carbon atom.arrow_forward
- Indicate the chiral centers in the molecules.arrow_forward1. Draw the structure and write the IUPAC name of Acetaminophen 2. Mention its two most important medicinal uses. 3. Identify and name all the functional groups present in the molecule. 4. Label Chiral carbon atoms, if any.arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure (like the structure in Question 1) for CH3OCOCH2C6H5.arrow_forward
- 4. Draw the structural formulas for the two isomers of C2H60. Identify the class of compound for each isomer. 5. Draw the structural formulas for the two isomers of C2HO2. Identify the class of compound for each isomer. 6. (optional) The structural formula for artificial sweetener aspartame (NutraSweet®) is shown below. Identify the class of compound represented by each of the circled functional groups. HO-C- CH2 CH-c-NH7 CH-C NH2 CH2 284 Experiment 23 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.arrow_forward1. Name the substance, name the group(s) of substances to which this substance belongs. 2. Does this substance contain a functional group or a heteroatom?arrow_forward2-brokopentane is an optically active compound, draw the two possible structure of optical isomer and label the chiral center with an asterisk(*) in each of the optical isomer structurearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





