
Life: The Science of Biology
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781319010164
Author: David E. Sadava, David M. Hillis, H. Craig Heller, Sally D. Hacker
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 22.4, Problem 3R
Summary Introduction
To review:
The reason behind the fact that narrow hybrid zones between Bombina bombina and B.variegata do not get wider over time.
Given:
The figure given below shows hybrid zone between B. bombina and B. variegata, which is shown in red.
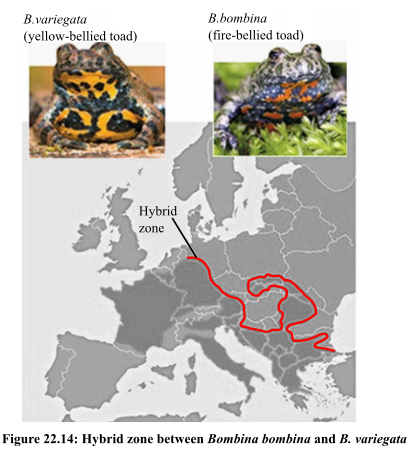
Introduction:
B. bombina (fire-bellied toad) inhabits eastern Europe and B. variegata (yellow-bellied toad) inhabits western and southern Europe. The ranges of two species do overlaps in a narrow zone where these species hybridize forming a hybrid zone.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Does the red tilapia a production of hybridization?
corn id
purple smooth
Purple wrinkled
yellow smooth
yellow wrinkled
W20-AB1-D-A13
486
152
162
54
W21-BB1-A-19
445
152
154
94
W20-BB1-D-19
501
153
167
88
W20-AB1-C-16
489
153
94
56
W20-BB1-H-11
480
153
94
56
MONOHYBRID CROSS1. Present the data as monohybrids (Xx, XX, xx) for all five corn cobs andfor the plant. Present the colour and texture phenotypes with their associatedgenotypes in separate tables. Your first table should include the corn ID, the number of purple kernels, thenumber of yellow kernels, and the phenotypic ratio between the two kernelcolours. Present the texture results in the same format to a separate table.2. What is the dominant phenotype for kernel colour in your assigned cornplant? What is the dominant phenotype for kernel texture in your assigned cornplant?3. What are the probable phenotypes for the previous generation of cornplants with regard to kernel coloration?4. What are the probable phenotypes of the previous generation of cornplants with…
Use two different colors to depict the unduplicated chromosomes of species C with larger chromosomes (2n = 8) and species D with slightly smaller chromosomes (2n =10), and of their F1 hybrid. Is the hybrid likely to befertile?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please draw a Volvox and label it with the following terms: Volvox, Clade Viridiplantae, Daughter colony. Please be sure to include all the terms provided in the illustration. Thank you.arrow_forwardWhat is interspecification hybridisation?arrow_forwardWhy was hybridization carried out between species of Sugarcane in North India & that grown in south India?arrow_forward
- corn id purple smooth Purple wrinkled yellow smooth yellow wrinkled W20-AB1-D-13 486 152 162 54 W21-BB1-A-19 445 152 154 94 W20-BB1-D-19 501 153 167 88 W20-AB1-C-16 489 153 94 56 W20-BB1-H-11 480 153 94 56 DIHYBRID CROSS1. ) Consider the possibility that your observational data are of plantsresulting from a dihybrid cross, where the previous generation were heterozygousfor both traits (RrSs x RrSs). Create a Punnett square for this cross and presentthe expected phenotypic ratio.2.) Present your results in a table as dihybrids and determine the observedphenotypic ratio of purple/smooth to purple/shrunken to yellow/smooth toyellow/shrunken. Consider the plant as a whole rather than the individual cobs.arrow_forwardThere are two genetic loci determiningthe mating type, locus A with 288 alleles and locus B with 81 alleles.(2 points) List a cross of two Schizophyllum commune strains that could successfully mate and across that could not succeed.Successful cross:Unsuccessful crossarrow_forwardCorn id W20-AB1-D-13 486 152 162 54 W21-BB1-A-19 445 152 154 94 W20-BB1-D-19 501 153 167 88 W20-AB1-C-16 489 153 94 56 W20-BB1-H-11 480 153 94 56 MONOHYBRID CROSS1. Present the data as monohybrids (Xx, XX, xx) for all five corn cobs andfor the plant. Present the colour and texture phenotypes with their associatedgenotypes in separate tables. Your first table should include the corn ID, the number of purple kernels, thenumber of yellow kernels, and the phenotypic ratio between the two kernelcolours. Present the texture results in the same format to a separate table.2. What is the dominant phenotype for kernel colour in your assigned cornplant? What is the dominant phenotype for kernel texture in your assigned corn plant?3. What are the probable phenotypes for the previous generation of cornplants with regard to kernel coloration?4. What are the probable phenotypes of the previous generation of cornplants with regard to kernel texture?arrow_forward
- If the hybrids do not become reproductively isolated from their parent species and form a new species, what are the three possible outcomes for the hybrid zone over time?arrow_forwardOf the three outcomes of hybridization (fusion, stability, and reinforcement), which of them will result in the continued generation of interspecies hybrids? Explain.arrow_forwardWHAT IF If M. cardinalis individuals that had the M. lewisii yup allele wereplanted in an area that housed both monkey flower species, how might theproduction of hybrid offspring be affected?arrow_forward
- 3. 3 I bbtal) Let's take a ślightly different look at the blue-eyed Mary Plants again. To remind you, the populations are dimorphic for dark blotches on the leaves --- some plants have blotches, and others don't. You have already determined earlier in the semester that Blotched is the dominant allele for this trait (use p for the dominant allele), and blotchless (no dark blotches on leaves) is the recessive allele for this trait (use g for the recessive allele). Leaves were sampled from each individual in a population of these plants, representing population in its entirety. The results are shown below: Remember our Hardy-Weinberg formulas: p² + 2pq +q² = 1 and p + q =1. Based solely on the phenotypic information given in the figure above, determine the following information (round to 2 decimal nlaces, please): :de d£h: q = 2pq- 2pqs What percentage of the plants are homozygous for the dominant allele?arrow_forwardRev. 67 6. What do the letters on the axes of the Punnett square represent? 7. Using the Punnett square below, what would be the resulting genotypes of offspring from an FF x ff monohybrid cross? 8. What is the difference between a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross? 9. If two heterozygous plants are crossed, what is the chance that the offspring will be FF? Use a Punnett square to support your answer.arrow_forwardans these complete fast pleassarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

The Human Reproductive System; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TucxiIB76bo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY