
Interpretation: The two possible structures of the compound C5H13N that exhibits three signals in its proton NMR spectrum and no signals above 3000cm−1 in IR spectrum have to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The arrangement of atoms that are bonded together determines its constitution and molecular formula of that particular compound. This concept is referred as structural isomers or in more modern term constitutional isomers. Each atom has a typical valency or valence which is defined as the ability of an atom to form a
If a compound has N−H bond in its structure, it shows a signal above 3000cm−1 in IR spectrum. In proton NMR, the signals are based on the arrangement of hydrogen atoms that are connected to carbon atoms.
To find: Draw the two possible structures of the compound C5H13N that exhibits three signals in its proton NMR spectrum and no signals above 3000cm−1 in IR spectrum
Find the valency for carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and nitrogen (N) in C5H13N
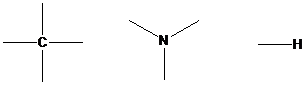
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





