
Concept explainers
Draw the product formed when phenylacetic acid
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
k.
l.
(a)
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
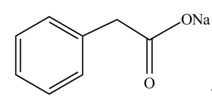
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
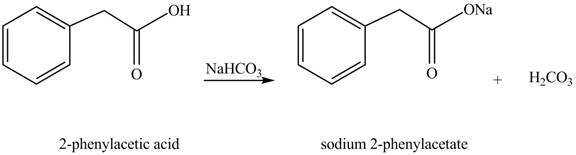
Figure 1
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
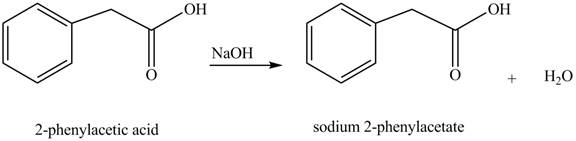
Figure 2
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
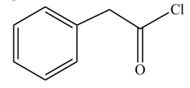
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
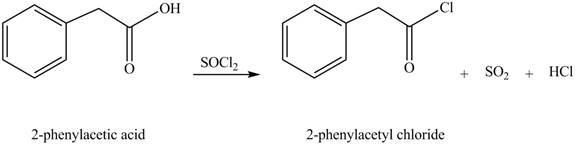
Figure 3
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(d)
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids does not react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
No product is formed when phenylacetic acid
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids does not react with
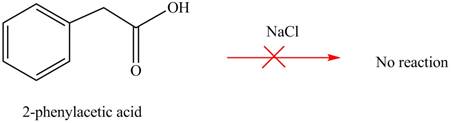
Figure 4
No product is formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(e)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
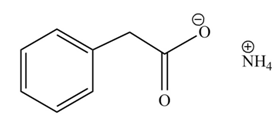
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
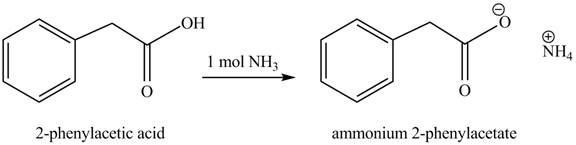
Figure 5
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(f)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
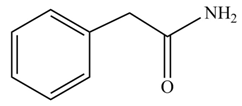
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
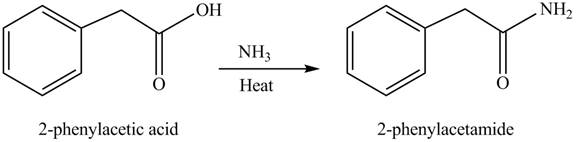
Figure 6
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(g)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with alcohols in acidic medium to form esters.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
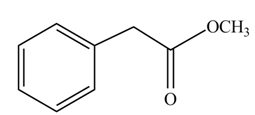
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
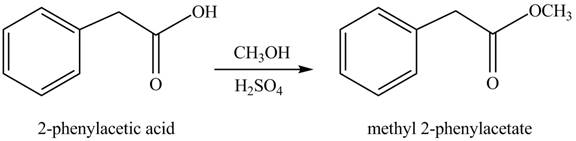
Figure 7
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(h)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with alcohols in basic medium to form carboxylate ions.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
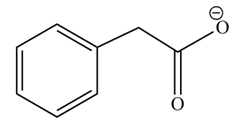
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
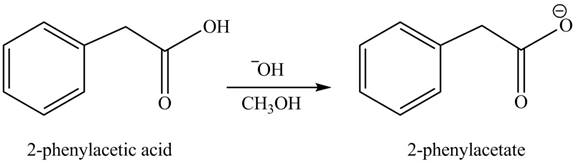
Figure 8
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(i)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with acid chlorides in presence of strong base to form anhydrides.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
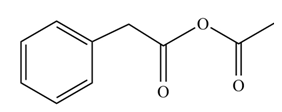
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
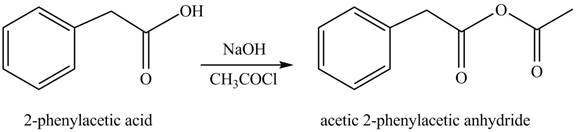
Figure 9
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(j)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
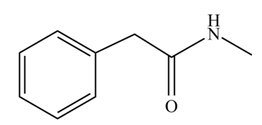
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
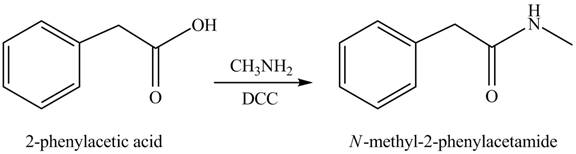
Figure 10
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(k)
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
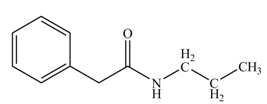
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
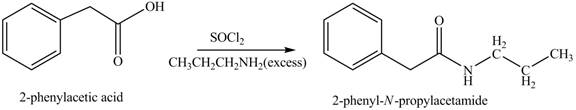
Figure 11
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
(l)
Interpretation: The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Concept introduction: Carboxylic acids react with
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
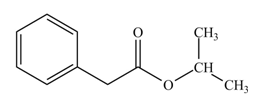
Explanation of Solution
Carboxylic acids react with
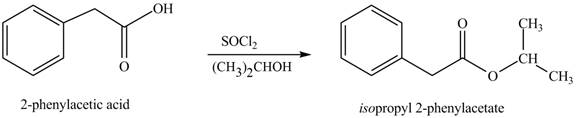
Figure 12
The product formed when phenylacetic acid
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- this is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures on a paper please hand drawn and post, please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardA mixture of 0.412 M C12, 0.544 M F2, and 0.843 M CIF is enclosed in a vessel and heated to 2500 K. C12(g) + F2(g )2CIF(g) Kc = 20.0 at 2500 K Calculate the equilibrium concentration of each gas at 2500 K. [C12] = M [F2] = M [ CIF] =arrow_forwardShow reaction mechanism with explanation. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardthis is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures and post, answer the question in a very simple and straight forward manner thanks!!!!! please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures or diagrams, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this kindly solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

