
A hygrometer, which measures the amount of moisture in a gas stream, is to be calibrated using the apparatus shown here:
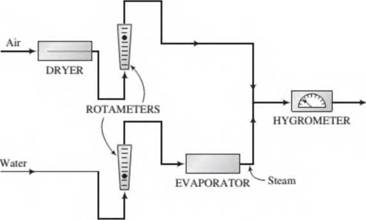
Steam and dry air are fed at known flow rates and mixed to form a gas stream with a known water content, and the hygrometer reading is recorded; the flow rate of either the water or the air is changed to produce a stream with a different water content and the new reading is recorded, and so on. The following data are taken:
| Mass Fraction of Water, y | Hygrometer Reading, R |
| 0.011 | 5 |
| 0.044 | 20 |
| 0.083 | 40 |
| 0.126 | 60 |
| 0.170 | 80 |
- Draw a calibration curse and determine an equation for y(R).
- Suppose a sample of a stack gas is inserted in the sample chamber of the hygrometer and a reading of R = 43 is obtained. If the mass flow rate of the stack gas is 1200 kg/h, what is the mass flow rate of water vapor in the gas?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ELEMENTARY PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Edition) (Prentice Hall International Series in the Physical and Chemical Engineering Sciences)
Process Dynamics and Control, 4e
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (9th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects
Data Structures and Algorithms in Java
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)
- volume reactants gas products Na₂CO3 (s) + 2 HCI (aq) solution mass separate layer gram liquid solid coefficient CO₂ (g) + H₂O (1) + 2 NaCl (aq)|arrow_forwardP1A.6 The molar mass of a newly synthesized fluorocarbon was measured in a gas microbalance. is device consists of a glass bulb forming one end of a beam, the whole surrounded by a closed container. The beam is pivoted, and the balance point is attained by raising the pressure of gas in the container, so increasing the buoyancy of the enclosed bulb. In one experiment, the balance point was reached when the fluorocarbon pressure was 327.10Torr; for the same setting of the pivot, a balance was reached when CHF3 (M = 70.014 g mol−1) was introduced at 423.22 Torr. A repeat of the experiment with a di erent setting of the pivot required a pressure of 293.22 Torr of the uorocarbon and 427.22 Torr of the CHF3. What is the molar mass of the fluorocarbon? Suggest a molecular formula.arrow_forwardA solid fuel, described by the chemical structure below, is combusted in 10% excess air. If necessary, clearly state any assumptions required to develop your solution. H Н —с — N — с — s — н | || 0 = C S H (a) Determine the mass feed rate (g/min) of the fuel such that 10,000 m³/min of total flue gas is generated at 1500 °C and 1 atm. (b) Determine the effluent SO2 concentration (ppm,) at STP and dry conditions.arrow_forward
- You are working in an oil refinery. Where you use hydrocarbon gases like methane (CH4), ethane (C2H), and propane (C3H8) and prepared a mixture, When measured the pressure at 25°C it turns out to be 7.50 atm. This gas mixture was then also used in a mass spectrophotometer and the following data was obtained. Based on this information find the partial pressure of each gas and report respectively as their name appeared in the question 10 30 40 50 Molecular maaNs (amu) اخترأحد الخبارات a. 2.3 atm, 3.8 atm, 1.4 atmO b. 4.0 atm, 1.5 atm, 2.5 atm O 2.1 atm, 4.0 atm, 1.4 atm O d. 3.8 atm, 1.4 atm, 23 atm e. 1.4 atm, 2.3 atm, 3.8 atmO Intensity of peaksarrow_forwardA brine solution of salt flows at a constant rate of 9 L/min into a large tank that initially held 100 L of brine solution in which was dissolved 0.4 kg of salt. The solution inside the tank is kept well stirred and flows out of the tank at the same rate. If the concentration of salt in the brine entering the tank is 0.04 kg/L, determine the mass of salt in the tank after t min. When will the concentration of salt in the tank reach 0.01 kg/L? Determine the mass of salt in the tank after t min, mass = | kgarrow_forwardA given soil sample is subjected for proximate analysis - specifically moisture content and analysis of inorganic matter (or ash) content. A cleaned and tared crucible is weighed in an analytical balance and found to be 4.5015 grams . The soil sample is weighed-in and the crucible, together with the plant sample, measured a total of 6.2525 grams. The set-up is then placed in an oven and dried to 105 degrees Celsius for at least two hours. The setup is cooled to room temperature in a dessicator and then measured to a constant weight of 5.9775 grams. Afterwards, the setup is placed inside the muffle furnace and ignited to 720 degrees Celsius for at least an hour. The set-up is cooled to room temperature again inside the dessicator and then measured to the constant weight of 4.9375 grams. (A) What is the percent moisture in the plant sample? Write the answer in THREE SIGNIFICANT FIGURES. (B) What is the percent volatile (organic) matter in the plant sample? Express answer in THREE…arrow_forward
- P1A.6 The molar mass of a newly synthesized fluorocarbon was measured in a gas microbalance. is device consists of a glass bulb forming one end of a beam, the whole surrounded by a closed container. e beam is pivoted, and the balance point is attained by raising the pressure of gas in the container, so increasing the buoyancy of the enclosed bulb. In one experiment, the balance point was reached when the fluorocarbon pressure was 327.10Torr; for the same setting of the pivot, a balance was reached when CHF3 (M = 70.014 g mol−1) was introduced at 423.22 Torr. A repeat of the experiment with a di erent setting of the pivot required a pressure of 293.22 Torr of the uorocarbon and 427.22 Torr of the CHF3. What is the molar mass of the fluorocarbon? Suggest a molecular formula.arrow_forwardEnter the balanced net ionic equation for HCl(aq)+K2CO3(aq)→H2O(l)+CO2(g)+KCl(aq)HCl(aq)+K2CO3(aq)→H2O(l)+CO2(g)+KCl(aq). Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.arrow_forwardCalculate the pressure at the base of a mercury column 400 mm high. The mercury density at room temperature is 13.5951 g / cm3.Express the result in column, atmosphere, psi, pascal, and bar units. Calculate the pressure exerted on the drum skin of a diver located at a depth of 20 feet below sea level. Assume that the seawater density is: 1 gr / cm3. Calculate the molar volume of Cu2Te. Express this volume in mol/liter and mol/cm 3 units. ( rm=7.270 g/cm3) Use the ideal gas law and the van der Waals equation to calculate the pressure of ammonia gas at a temperature. T = 300 K the molar volume is V = 24 liters / molarrow_forward
- 20. A mixture consisting of 6 kg of O, and 9 kg of N, has a pressure of 3 bar and temperature of 20°C. For the mixture determine the following : (i) The mole fraction of each component ; (iii) The specific gas constant; (v) The partial pressures and partial volumes. (ii) The average molecular weight ; (iv) The volume and density; [Ans. (i) 0.3684, 0.6315 ; (iüi) 29.475 ; (iii) 0.282 kJ/kg K ; (iv) 4.13 m?, 3.629 kg/m² ; (v) 1.1 bar, 1.894 bar ; 1.52 m², 2.61 m²)arrow_forwardA student prepared two beakers with identical sprigs of a water plant as shown in the figure below. She placed one beaker in the shade and the other beaker beside a fluorescent lamp. She then systemalically changed the distance from the beaker to the lamp. She counted the bubbles given off by the plants in each beaker. Showwn here is the graph of the data for the beaker she placed beside the lamp. Al what distance from the light source was the greatest number of bubbles produced? Alr Duee Relessed a Derent Distances From the Light Source 三 no- 45- Air bubbles Water Water plant 810- 10- 10 15 20 2s do Distance From Light S-ource (om) 10cm O B 25cm 5cm 15cmarrow_forwardPart F The third variable (call it v) is v=x1-cx2 + x3, where c is a constant you need to determine so that the equation for v is the SHM equation. Determine v. The solution to the equation for vis v = 2B cos(t + b). Express your answer in terms of some, all, or none of the variables 21, 22, 23, and the appropriate constants. v = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer ?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





