
Concept explainers
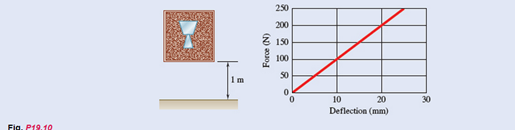
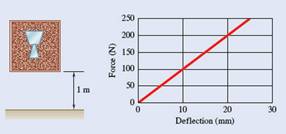
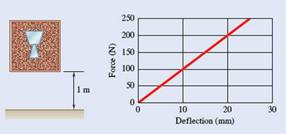
A 5-kg fragile glass vase is surrounded by packing material in a cardboard box of negligible weight. The packing material has negligible damping and a force-deflection relationship as shown. Knowing that the box is dropped from a height of 1 m and the impact with the ground is perfectly plastic, determine (a) the amplitude of vibration for the vase, (b) the maximum acceleration the vase experiences in g' s.
(a)
The amplitude of vibration for the vase.
Answer to Problem 19.10P
Amplitude
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass of vase
Height
Velocity at the end of free fall
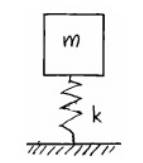
Assume that the spring is unstretched during the free fall. To better understand we use a simple spring mass model for the motion of the vase and the packing material.
Now, taking slope from the graph.
Calculation:
Now, consider simple harmonic motion:
We can obtain the velocity (v) at any time (t) by differentiating (x) with respect to (t),
When the box hits the ground, let
Then, at
And, velocity,
So, velocity of the vase = velocity at the end of free fall
Now, Natural frequency:
Thus, amplitude of the vase
Conclusion:
The amplitude of the vase is
(b)
The maximum acceleration the vase experiences.
Answer to Problem 19.10P
Acceleration
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Mass of vase
Height
Velocity at the end of free fall
Assume that the spring is unstretched during the free fall. To better understand we use a simple spring mass model for the motion of the vase and the packing material.
Now, taking slope from the graph.
Calculation:
Now, consider simple harmonic motion:
We can obtain the velocity (v) at any time (t) by differentiating (x) with respect to (t),
When the box hits the ground, let
Then, at
And, velocity,
So, velocity of the vase = velocity at the end of free fall
Now, Natural frequency:
Thus, amplitude of the vase
And, maximum acceleration of the vase,
Conclusion:
Maximum acceleration of the vase is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- A 2-kg block is supported by a spring with a constant of k= 128 N/m and a dashpot with a coefficient of viscous damping of c=0.6 N.s/m. The block is in equilibrium when it is struck from below by a hammer that imparts to the block an upward velocity of 0.4 m/s. Determine (a) the logarithmic decrement,(b) the maximum upward displacement of the block from equilibrium after two cycles.arrow_forwardA sensitive electronic system, of mass 25 kg, is supported by a spring-damper isolator that rests on the floor of a manufacturing plant. The operation of nearby rotating equipment causes the floor to vibrate with an amplitude of 8 mm at a frequency of 35 Hz. The electronic system can only operate effectively if the amplitude of its acceleration is less than 40 m/s2. It is known that the damping ratio of the isolator is 0.1. i. Determine the maximum stiffness of the isolator needed for the transmitted acceleration level to be acceptable and hence facilitate effective operation of the electronic system. Using the calculated stiffness value, also determine the largest deformation of the spring in millimetres when the system is in motion. ii. If the damping ratio is allowed to increase by only increasing the equivalent damping coefficient (c) of the isolator, discuss the effect this change would have on the response of the electronic system when operating in the same environment. In your…arrow_forwardThe mass of a single degree damped vibrating system is 7.5 kg and makes 24 free oscillations in 14 seconds when disturbed from its equilibrium position. The amplitude of vibration reduces to 0.25 of its initial value after five oscillations. Determine : 1. stiffness of the spring, 2. logarithmic decrement, and 3. damping factor, i.e. the ratio of the system damping to critical damping.arrow_forward
- A 25-kg mass is suspended from a spring with a constant of 2 N/mm, which is in turn suspended at the end of a steel cantilever beam with a thickness of 3mm, a width of 20 mm, and a length of 250 mm. Determine the natural frequency of the motion of the weight. + Hints: Please use stainless steel for the cantilever beam in this problem. Table 5 attached at the end of this assignment may come in handy. m The natural frequency w₂ can be found as wn = where k is the spring stiffness of the system and m is the mass.arrow_forwardA body of mass of 50 kg is supported by an elastic structure of stiffness 10 kN/m. The motion of the body is controlled by a dashpot such that the amplitude of vibration decreases to one-tenth of its original value after two complete vibrations. Determine: the damping force at 1 m/s, the damping ratio and the natural frequency of vibration.arrow_forwardAn automobile is modeled as a single-degree-of-freedom system vibrating in the vertical direction. It is driven along a road whose elevation varies sinusoidally. The distance from peak to valley () is 0.2 m and the distance along the road between the peaks is 35 m. If the natural frequency of the automobile is 2 Hz and the damping ratio of the shock absorbers is 0.15, determine the amplitude of vibration of the automobile at a speed of 60 km/hour. If the speed of the automobile is varied, find the most unfavorable speed for the passengers.arrow_forward
- Determine the velocity and frequency of vibration of a rope 6 m long with a mass of 2 kg and stretched with tension of 192 N.arrow_forwardA machine of mass 75 kg is mounted on springs and is fitted with a dashpot to damp out vibrations. There are three springs each of stiffness 10 N/mm and it is found that the amplitude of vibration diminishes from 38.4 mm to 6.4 mm in two complete oscillations. Assuming that the damping force varies as the velocity, determine : 1. the resistance of the dash-pot at unit velocity ; 2. the ratio of the frequency of the damped vibration to the frequency of the undamped vibration ; and 3. the periodic time of the damped vibration.arrow_forwardQ.6 The mass of an automobile is 1800 kg, vibrates in a vertical direction while traveling on a rough road having a sinusoidal wave form with an amplitude Y = 0.01 m. Assuming that the automobile can be modeled as a single degree of freedom system with stiffness 250 kN/m and damping ratio š, determine (a) the amplitude of vibration of the automobile and (b) the force transmitted when it is traveling at a speed causing resonance vibration. damping ratio=0.37arrow_forward
-  A helical spring, of negligible mass, and which is found to extend 0.25 mm under a mass of 1.5 kg, is made to support a mass of 60 kg. The spring and the mass system is displaced vertically through 12.5 mm and released. Determine the frequency of natural vibration of the system. Find also the velocity of the mass, when it is 5 mm below its rest position.arrow_forwardA spring extends by 5 centimeters when loaded vertically with 2.5kg of weight. A new weight of 1.75kg was attached to it and was displaced 6cm from its new equilibrium position and was released from rest. Determine the frequency of vibration in rad per second?arrow_forwardA car with a mass of 1000 kg, has 4 suspensions, and has an un-damped natural frequency of vertical vibration of 5 Hz. Calculate: The stiffness of each spring The un-damped natural circular frequency of vertical vibration when the car is carrying five people each with a mass of 95 kg. The un-damped natural frequency of vertical vibration when the car is carrying five people each with a mass of 95 kgarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





