
Wet limestone is used to scrub SO2 gas from the exhaust gases of power plants. One possible reaction gives hydrated calcium sulfite:
CaCO3(s) + SO2(g) + ½ H2O(ℓ) ⇄ CaSO3 · ½ H2O(s) + CO2(g)
Another reaction gives hydrated calcium sulfate:
CaCO3(s) + SO2(g) + ½ H2O(ℓ) + ½ O2(g) ⇄ CaSO4 · ½H2O(s) + CO2(g)
(a) Which reaction is more product-favored at equilibrium? Use the data in the table below and any other information needed in Appendix L to calculate ΔrG° for each reaction at 25 °C.
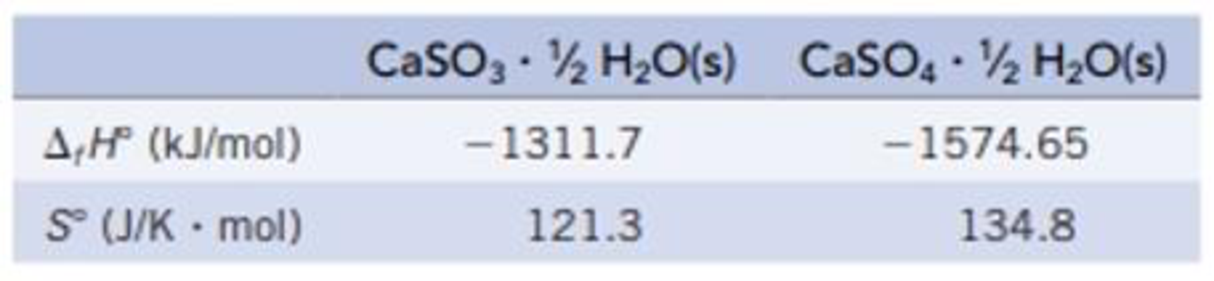
(b) Calculate ΔrG° for the reaction
CaSO3 · ½ H2O(s) + ½ O2(g) ⇄ CaSO4 · ½ H2O(s)
Is this reaction product- or reactant-favored at equilibrium?
(a)
Interpretation:
Among the given reactions the reactions that is more favoured at product side should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The Gibbs free energy or the free energy change is a thermodynamic quantity represented by
Here,
Answer to Problem 58GQ
The reaction which is more product-favored at equilibrium is reaction
Explanation of Solution
The value of
Given:
The Appendix L referred for the values of standard entropies and enthalpies.
For reaction
The standard enthalpy change is expressed as,
Substituting the respective values
Also,
Substituting the respective values
Now,
Substituting the value of
For reaction
The standard enthalpy change is expressed as,
Substituting the respective values
Also,
Substituting the respective values
Now,
Substituting the value of
(b)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The Gibbs free energy or the free energy change is a thermodynamic quantity represented by
Here,
Answer to Problem 58GQ
The
Thus, the reaction is product-favored at equilibrium.
Explanation of Solution
The value of
Given:
The Appendix L referred for the values of standard entropies and enthalpies.
The standard enthalpy change is expressed as,
Substituting the respective values
Also,
Substituting the values,
Now,
Substitute the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Pleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardThe Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





