
Concept explainers
(a)
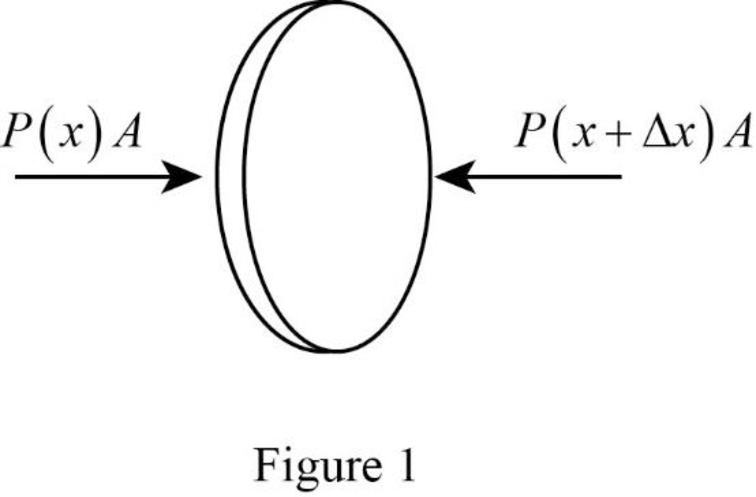
Sketch the force diagram showing that the force exerted due to the pressure of gas on either side of the element.
(a)
Answer to Problem 72CP
The force diagram is given below.
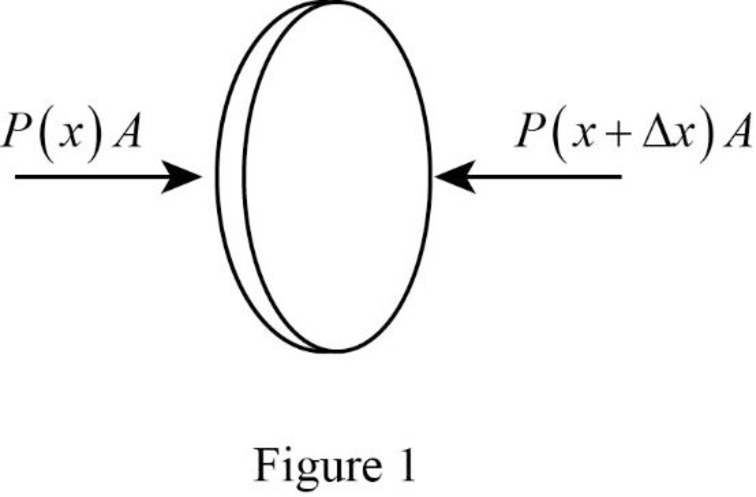
Explanation of Solution
The figure 1 below is the force diagram, which shows that the force exerted on the left and right surface due to the pressure of the gas on either side of the element.
(b)
Show that
(b)
Answer to Problem 72CP
Through calculation it is obtained that
Explanation of Solution
Consider
The net force acting on the element is the difference of the force acting on the either sides due to the pressure of the gas.
The force acting on the surface is.
Here,
Write the expression for mass in terms of volume and density.
Substitute,
Conclusion:
Equate equation (IV) and (I).
Therefore,
(c)
Derive
(c)
Answer to Problem 72CP
It is derived that
Explanation of Solution
Consider equation (V).
Substitute,
Conclusion:
Therefore, it is derived that
(d)
Prove that
(d)
Answer to Problem 72CP
The function
Explanation of Solution
Consider the given function.
Differentiate equation (VIII) with respect to
Differentiate equation (IX) with respect to
Differentiate equation (VIII) with respect to
Differentiate equation (XI) with respect to
Substitute, equation (X) and (XII) in equation (VII).
Equation (XIII) shows that the function
Conclusion:
Therefore, unction
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Technology Update
- Q#3:Why the noisepollution is considered a serious occupational health hazard.How can we prevent and control noise pollution in the workplace.What are the measurement units of noise? How can we measure the sound pressure level of the noise generated by a machine?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a standing sound wave in an 80-cm- long tube. The tube is filled with an unknown gas. Take f = 600 Hz (Figure 1) Figure f 80 cm Molecule : 1 of 1 Part A What is the speed of sound in this gas? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Usound= Submit μA Value Request Answer < Return to Assignment Units Provide Feedback www ?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a standing sound wave in an 80-cm-long tube. The tube is filled with an unknown gas. Take f = 490 Hz (Figure 1) Figure Molecule f : *121* 80 cm What is the speed of sound in this gas? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Usound= μÅ Value Provide Feedback Units Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 7 attempts remaining ?arrow_forward
- What is the length of the shortest tube (tube 7)? Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. What is the length of tube 3?arrow_forwardPhysics 20: SUMMER Assignment 14 9. An ambulance is driving away from you in an area with a speed limit of 50 km/h. You measure the frequency of one of its siren tones to be 737 Hz, when you know the actual frequency of the tone to be 770 Hz. The temperature outside is 13°C. Use the formula below to approximate the speed of sound in that temperature, then determine if the ambulance was speeding. Show all your work, including your rearranging of the Doppler equation. (3) v=331 +0.61T where v is the speed of sound and T is the temperature in °C. 50% = 2. 10. Using the same formula for the speed of sound in question 9, calculate the temperature outside if your friend is dui honki 8arrow_forwardItem 9 Learning Goal: To learn the properties of logarithms and how to manipulate them when solving sound problems. The intensity of sound is the power of the sound waves divided by the area on which they are incident. Intensity is measured in watts per square meter, or W/m². The human ear can detect a remarkable range of sound intensities. The quietest sound that we can hear has an intensity of 10-¹2 W/m², and we begin to feel pain when the intensity reaches 1 W/m². Since the intensities that matter to people in everyday life cover a range of 12 orders of magnitude, intensities are usually converted to a logarithmic scale called the sound intensity level 3, which is measured in decibels (dB). For a given sound intensity I, B is found from the equation ß = (10 dB) log (1). where Io = 1.0 × 10-¹2 W/m². Part A What is the value of log(1,000,000)? Express your answer as an integer. ► View Available Hint(s) The logarithm of x, written log(x), tells you the power to which you would raise 10…arrow_forward
- A vessel of volume V contains 8 gm of H₂ at temperature T = 37°C. 25% of the total molecules get dissociated when the temperature is increased to 207°C. Find the factor f by which the velocity of sound 10 gets changed inside the vessel. Fill farrow_forwardA jogger runs at 7 m/s, and is trailed by a bumblebee moving at 5 m/s and emitting a frequency of 270 Hz. a). What frequency does the jogger hear if the speed of sound in air was 336 m/s? b). Based on the speed of sound, what is the ambient temperature (degrees C)?arrow_forwardProve that the speed of sound in air is given by T v = 331m/s 273K Where y 1.4, M 0.02897 kg/mol, and R 8.31 J/mol and T is the temperature. %3Darrow_forward
- Item 9 Learning Goal: To learn the properties of logarithms and how to manipulate them when solving sound problems. The intensity of sound is the power of the sound waves divided by the area on which they are incident. Intensity is measured in watts per square meter, or W/m². The human ear can detect a remarkable range of sound intensities. The quietest sound that we can hear has an intensity of 10-12 W/m², and we begin to feel pain when the intensity reaches 1 W/m². Since the intensities matter people in everyday life cover a range of 12 orders of magnitude, intensities are usually converted to a logarithmic scale called the sound intensity level 3, which is measured in decibels (dB). For a given sound intensity I, B is found from the equation ß = (10 dB) log (1), where Io = 1.0 × 10-¹2 W/m². ▼ The logarithm of x, written log(x), tells you the power to which you would raise 10 to get æ. So, if y = log(x), then x = 10³. It is easy to take the logarithm of a number such as 10², because…arrow_forwardYour experiments on a particular insulator indicate that at 20°C, the average speed of sound in the insulator is vi = 8500 m/s and its bulk modulus is Bi = 370 GPa. Experimental results from your colleague show that a certain metal alloy has a density of ρm = 6500 kg/m3 and a bulk modulus of Bm = 110 GPa. a. Calculate the density of the insulator ρi in kilograms per cubic meter. b. Calculate the speed of sound vm in the metal alloy in meters per second. c. If the sound traveled as indicated in the structure in figure 1, emerging from the insulator at time ti and the alloy at time tm, determine Δt = tm - ti in seconds. The length of the structure is L = 1.0 m. d. Find the total amount of time t, in seconds, it takes to travel through the structure as indicated in figure 2. The length of the structure is L = 1.0 m.arrow_forwardA girl is playing a trumpet. The sound waves produced are traveling through air to your ear. Which one of the following statements is false concerning this situation? O The sound travels at the speed of light to your ear. O The loudness of the sound wave involves the size of the oscillations in air pressure. O A high-frequency sound that the trumpet produces is interpreted as a high-pitched sound. O Air molecules between the trumpet and your ear vibrate back and forth parallel to the direction the waves are traveling. O The sounds from the trumpet are longitudinal waves.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



