
(a)
Interpretation: Mechanism for the given type of decarboxylation reaction has to be proposed and it should be compared with the mechanism of decarboxylation of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
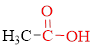
If
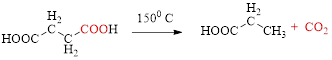
Decarboxylation of
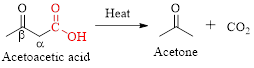
The mechanism of thermal decarboxylation involves two processes,
- (i) Redistribution of electrons in a cyclic transition state.
- (ii) Cyclic transition state possesses keto-enol tautomerism.
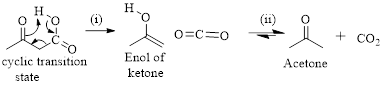
(b)
Interpretation: Mechanism for the given type of decarboxylation reaction has to be proposed and it should be compared with the mechanism of decarboxylation of
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,

If carboxylic acid is heated to a very high temperature then of carbon dioxide will be eliminated from it this reaction is known as decarboxylation. Simple carboxylic acids do not decarboxylate readily.
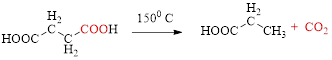
Decarboxylation of
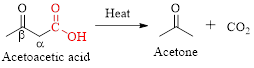
Simply the mechanism of thermal decarboxylation involves two processes,
- (i) Redistribution of electrons in a cyclic transition state.
- (ii) Cyclic transition state possesses keto-enol tautomerism.
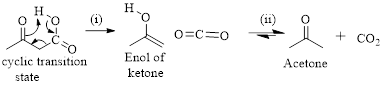
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- -Hydroxyketones and -hydroxyaldehydes are also oxidized by treatment with periodic acid. It is not the -hydroxyketone or aldehyde, however, that undergoes reaction with periodic acid, but the hydrate formed by addition of water to the carbonyl group of the -hydroxyketone or aldehyde. Write a mechanism for the oxidation of this -hydroxyaldehyde by HIO4.arrow_forwardThe ketone shown was prepared in a three-step sequence from ethyl trifluoroacetate. The first step in the sequence involved treating ethyl trifluoroacetate with ammonia to give compound A. Compound A was in turn converted to the desired ketone by way of compound B. Fill in the missing reagents in the sequence shown, and give the structures of compounds A and B.arrow_forwardThe following substances can be prepared by a nucleophilic addition reaction between an aldehyde or ketoneand a nucleophile. Identify the reactants from which they were prepared. If the substance is an acetal, identifythe carbonyl compound and the alcohol; if it is an imine or enamine, identify the carbonyl compound and theamine. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. In cases where there is more than one answer, just giveone. Use Grignard reagents when an organometallic reagent is required. Draw the Grignard reagent as acovalent magnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- Hemiacetals are formed by nucleophilic addition of a hydroxyl group to a carbonyl group. In the same way, cyclic hemiacetals can be formed by treating aldehyde with a catalytic amount of an acid. For the reaction below, draw the structure of the hemiacetal and write the possible mechanism for the transformation. H2SO4 но Harrow_forwardFischer esterification cannot be used to prepare tert-butyl esters. Instead, carboxylic acids are treated with 2-methyIpropene in the presence of an acid catalyst to generate them. REFER IMAGE (a) Why does the Fischer esterification fail for the synthesis of tert-butyl esters?(b) Propose a mechanism for the 2-methylpropene method.arrow_forwardCan you help me understand how to approach this question and explain the mechanism?arrow_forward
- b) Clopirac has been used as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drug. The synthesis of clopirac involves reaction of 4-chloroaniline with hexan-2,5-dione in an initial step. Identify the named reaction that is taking place in this initial step and propose a mechanism for it. -NH₂ + $- Clopirac CO₂Harrow_forwardWrite four examples of the condensation reactions of carbonyl compounds, starting with benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO), with appropriate reagents and appropriate reactions. Write down the mechanism of one you want in detail.arrow_forward4) Show the mechanism for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of the ketal shown below. کارام H+, H₂O HO OHarrow_forward
- N Ph :0: CH3 Primary amines add to aldehydes and ketones to give imines. Imines are formed in a reversible, acid-catalyzed process that begins with nucleophilic addition of the primary amine to the carbonyl group, followed by transfer of the proton to yield a neutral carbinolamine. Protonation of the hydroxyl group converts it into a good leaving group and an E1-like loss of water yields an iminium ion. Deprotonation yields the product imine and regenerates the acid catalyst. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 NH₂OH NH₂OH Ph- :0: OH CH3 CH3 36arrow_forward3 Treatment of 1-aminoadamantane, C„H„N, with methyl 2,4-dibromobutanoate in the presence of a nonnucleophilic base, R,N, involves two successive S,2 reactions and gives compound A. Propose a structural formula for compound A. R&N NH, + Br. C15H93NO, + 2 R,NH Br OCH Br 1-Aminoadamantane Methyl 2,4-dibromobutanoate Aarrow_forwardGive the product of the following transformation:arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


