
(a)
Interpretation:
Write a structural formula for the principal organic product formed by treating the following compound with NaBH4 followed by H2O
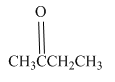
Concept Introduction:
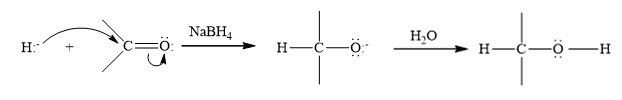
Reduction is the process in which hydrogen is added to the compound.
NaBH4 is a reducing agent, it behave rich source of H- ions during the reduction. The hydride ion is added to a carbonyl carbon and an alkoxide ion is formed as an intermediate which on hydrolysis forms an alcohol.
(b)
Interpretation:
Write a structural formula for the principal organic product formed by treating with following compound with NaBH4 followed by H2O
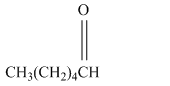
Concept Introduction:
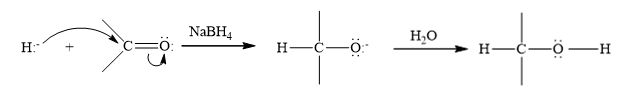
Reduction is the process in which hydrogen is added to the compound.
NaBH4 is a reducing agent, it behave rich source of H- ions during the reduction. The hydride ion is added to a carbonyl carbon and an alkoxide ion is formed as an intermediate which on hydrolysis forms an alcohol.
(c)
Interpretation:
Write a structural formula for the principal organic product formed by treating with following compound with NaBH4 followed by H2O
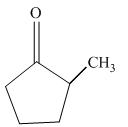
Concept Introduction:
Reduction is the process in which hydrogen is added to the compound.
NaBH4 is a reducing agent, it behave rich source of H- ions during the reduction. The hydride ion is added to a carbonyl carbon and an alkoxide ion is formed as an intermediate which on hydrolysis forms an alcohol.
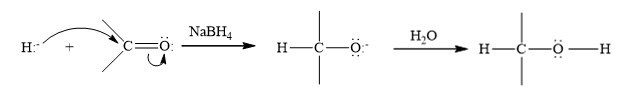
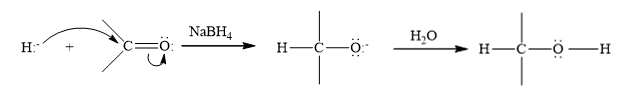
(d)
Interpretation:
Write a structural formula for the principal organic product formed by treating with following compound with NaBH4 followed by H2O
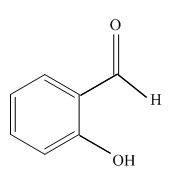
Concept Introduction:
Reduction is the process in which hydrogen is added to the compound.
NaBH4 is a reducing agent, it behave rich source of H- ions during the reduction. The hydride ion is added to a carbonyl carbon and an alkoxide ion is formed as an intermediate which on hydrolysis forms an alcohol.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

