
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The inorganic product formed when butanal undergoes Tollen’s test has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
In
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Tollen’s test:
This is also known as silver mirror test. The reagent that is used in Tollen’s test is silver nitrate and ammonia in water. Aldehyde reacts with Tollen’s reagent, where the silver ion is reduced to silver metal and the aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
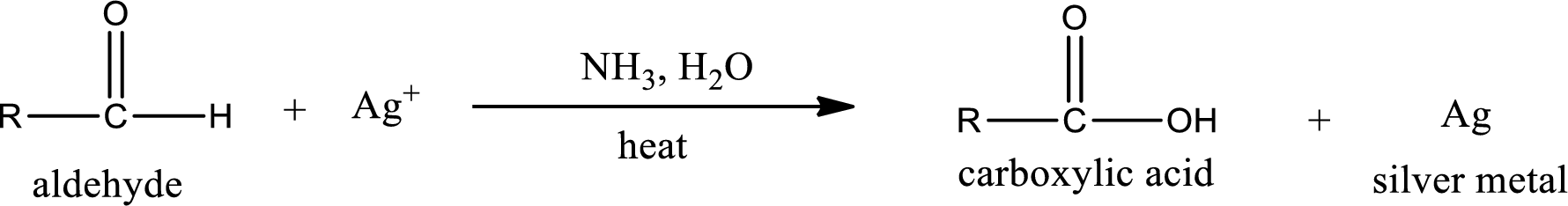
Ketone does not undergo Tollen’s test to deposit silver metal.
Benedict’s test:
This test is also similar to Tollen’s test. In this test,
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.79EP
The inorganic product formed is silver metal.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes undergo Tollen’s test. The product formed when aldehyde undergo oxidation is a carboxylic acid. The general oxidation reaction for aldehyde can be given as,
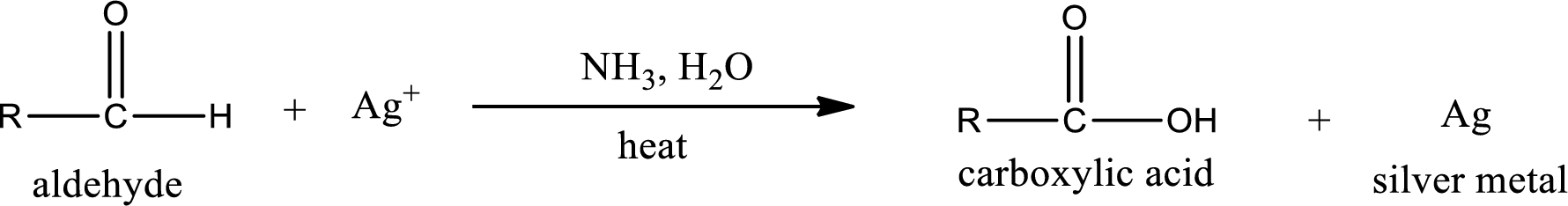
Given aldehyde is butanal and the structure can be given as shown below,
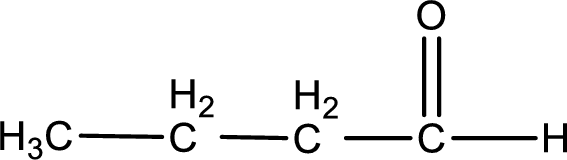
This on reaction with Tollen’s reagent gives carboxylic acid and silver metal as the product. The structure of the inorganic product formed and the complete reaction can be given as shown below,
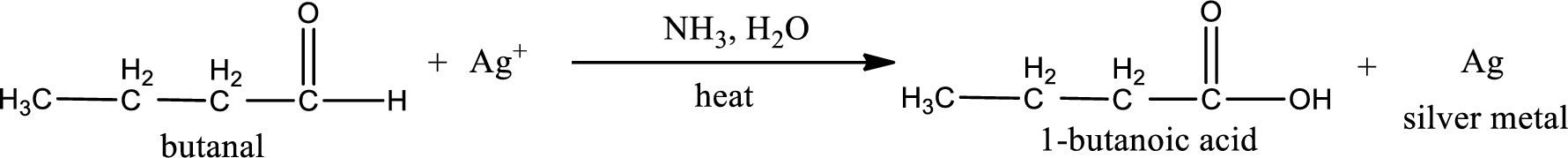
Silver metal is formed as the inorganic product when butanal undergoes Tollen’s test.
The inorganic product formed is given.
(b)
Interpretation:
The inorganic product formed when 2-butanone undergoes Tollen’s test has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Tollen’s test:
This is also known as silver mirror test. The reagent that is used in Tollen’s test is silver nitrate and ammonia in water. Aldehyde reacts with Tollen’s reagent, where the silver ion is reduced to silver metal and the aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
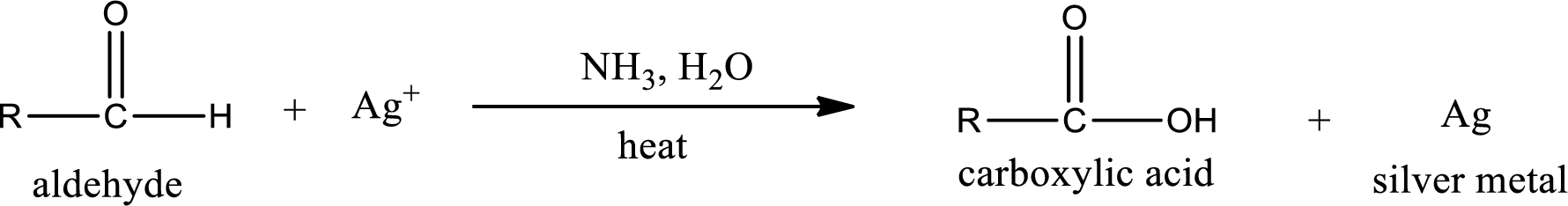
Ketone does not undergo Tollen’s test to deposit silver metal.
Benedict’s test:
This test is also similar to Tollen’s test. In this test,
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.79EP
No inorganic product is obtained as 2-butanone does not undergo Tollen’s test.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes undergo Tollen’s test. The product formed when aldehyde undergo oxidation is a carboxylic acid. The general oxidation reaction for aldehyde can be given as,
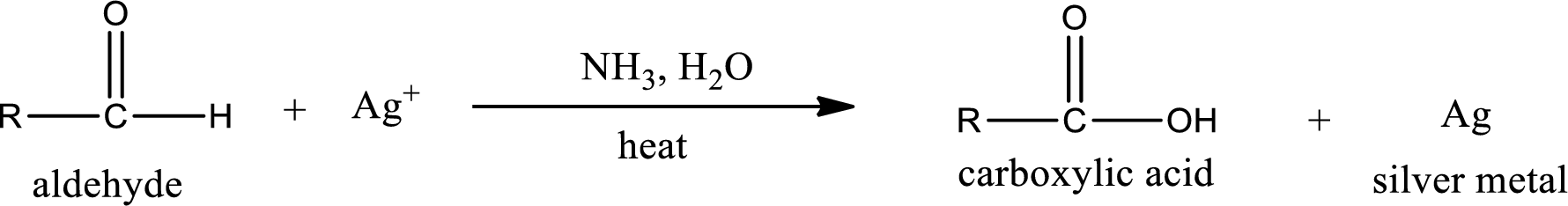
Given compound is a ketone that is 2-butanone and the structure can be given as shown below,
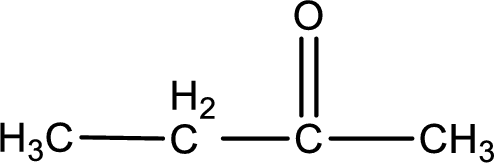
This on reaction with Tollen’s reagent does not give oxidized product. Therefore, no reaction takes place when 2-butanone reacts with Tollen’s reagent.
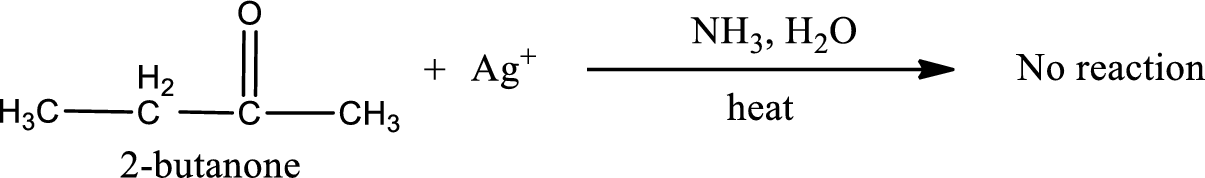
No inorganic product is formed when 2-butanone undergoes Tollen’s test.
No reaction takes place when 2-butanone undergoes Tollen’s test.
(c)
Interpretation:
The inorganic product formed when 3-methylpentanal undergoes Benedict’s test has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Tollen’s test:
This is also known as silver mirror test. The reagent that is used in Tollen’s test is silver nitrate and ammonia in water. Aldehyde reacts with Tollen’s reagent, where the silver ion is reduced to silver metal and the aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
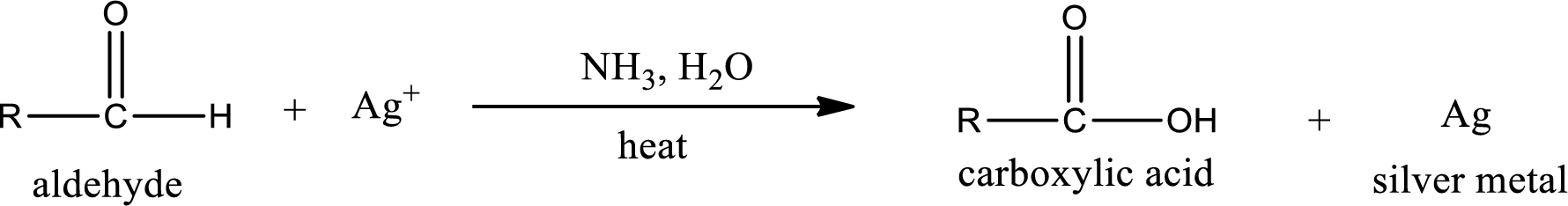
Ketone does not undergo Tollen’s test to deposit silver metal.
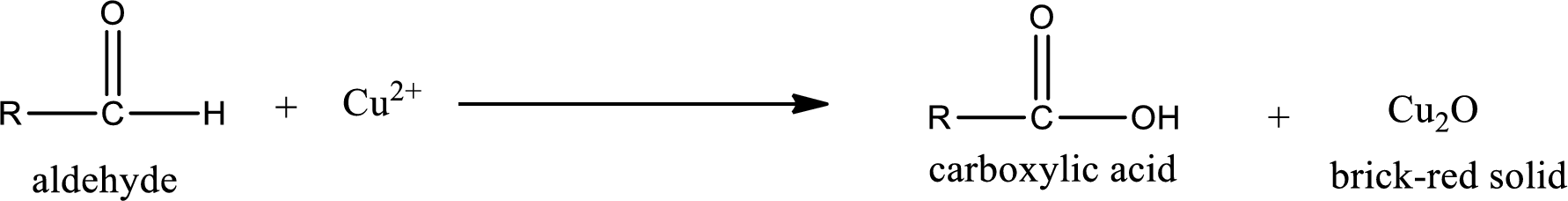
Benedict’s test:
This test is also similar to Tollen’s test. In this test,
(c)
Answer to Problem 15.79EP
The inorganic product formed is
Explanation of Solution
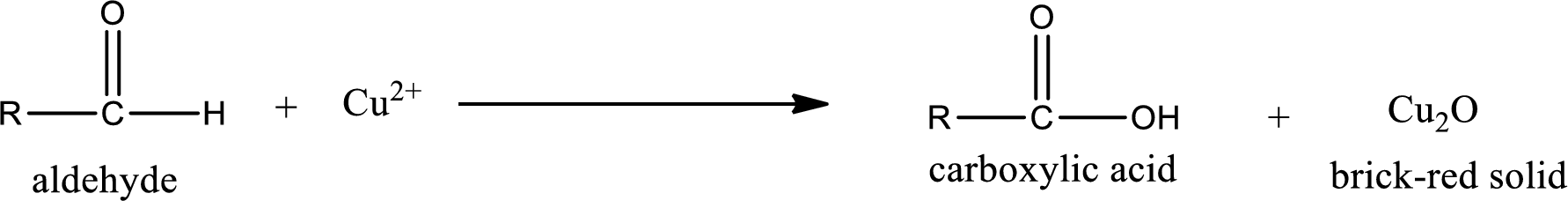
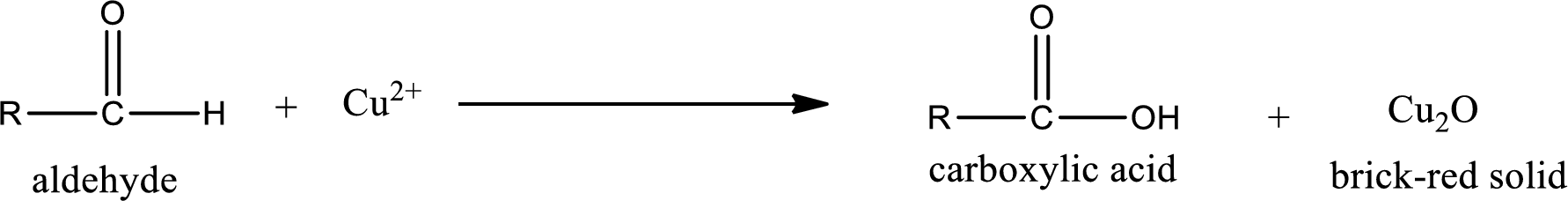
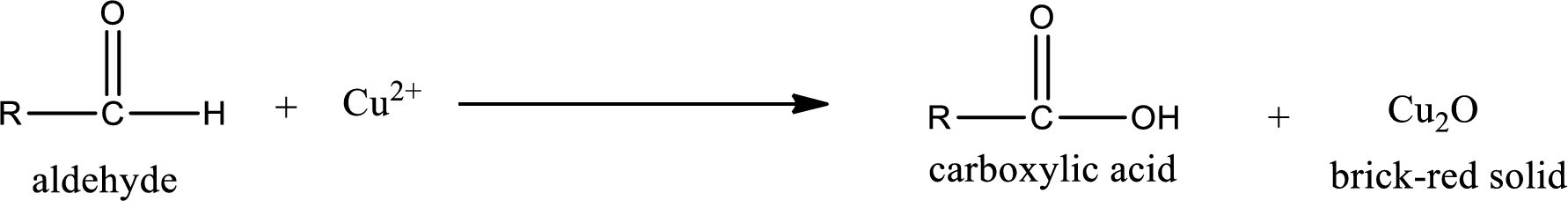
Aldehydes undergo Benedicts’s test. The product formed when aldehyde undergo oxidation is a carboxylic acid. The general oxidation reaction for aldehyde can be given as,
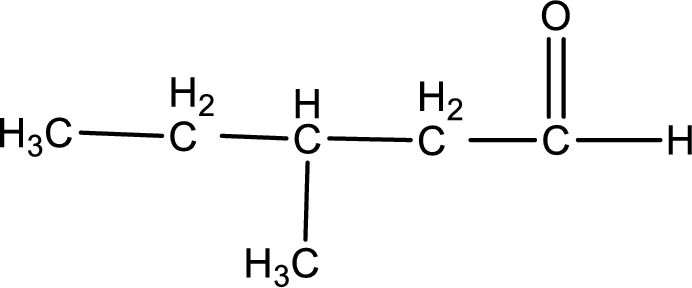
Given aldehyde is 3-methylpentanal and the structure can be given as shown below,
This on reaction with Tollen’s reagent gives carboxylic acid and Copper(I) oxide as the product. The inorganic product formed and the complete reaction can be given as shown below,
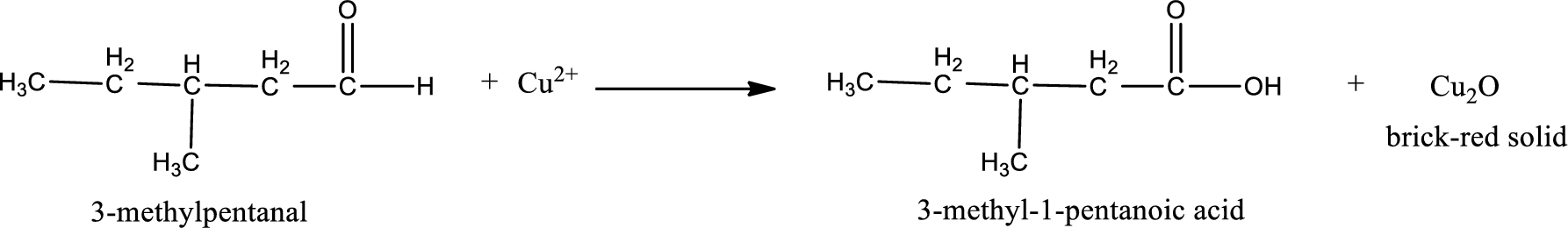
The inorganic product formed when 3-methylpropanal undergoes Benedict’s test is given.
(d)
Interpretation:
The inorganic product formed when 3-pentanone undergoes Benedict’s test has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Tollen’s test:
This is also known as silver mirror test. The reagent that is used in Tollen’s test is silver nitrate and ammonia in water. Aldehyde reacts with Tollen’s reagent, where the silver ion is reduced to silver metal and the aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid.
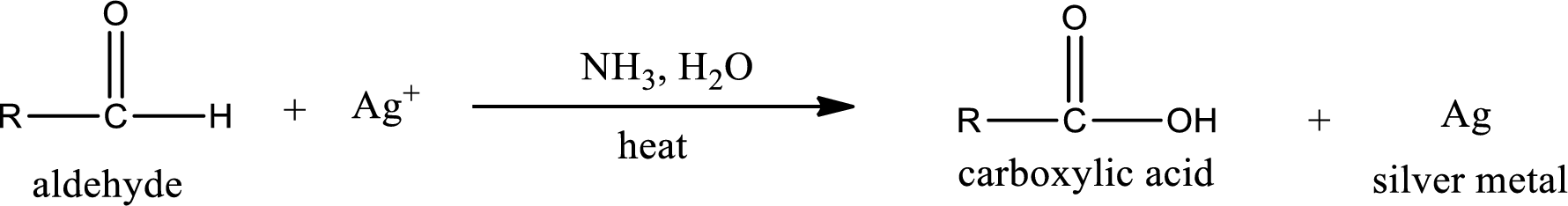
Ketone does not undergo Tollen’s test to deposit silver metal.
Benedict’s test:
This test is also similar to Tollen’s test. In this test,
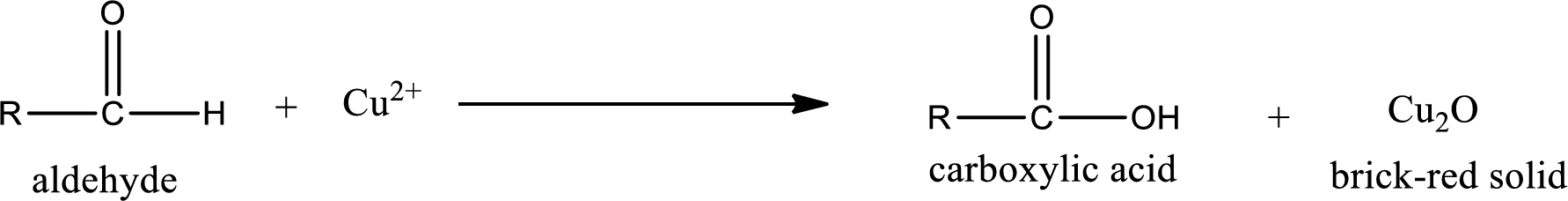
(d)
Answer to Problem 15.79EP
No inorganic product is formed when 3-pentanone undergoes Benedict’s test.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes undergo Benedict’s test. The product formed when aldehyde undergo oxidation is a carboxylic acid. The general oxidation reaction for aldehyde can be given as,
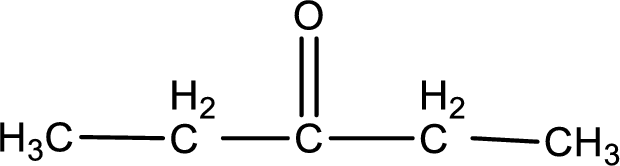
Given compound is a ketone. The name of ketone is 3-pentanone and the structure can be given as shown below,
This on reaction with Benedict’s reagent does not give oxidized product. Therefore, no reaction takes place when 3-pentanone undergoes Benedict’s test.
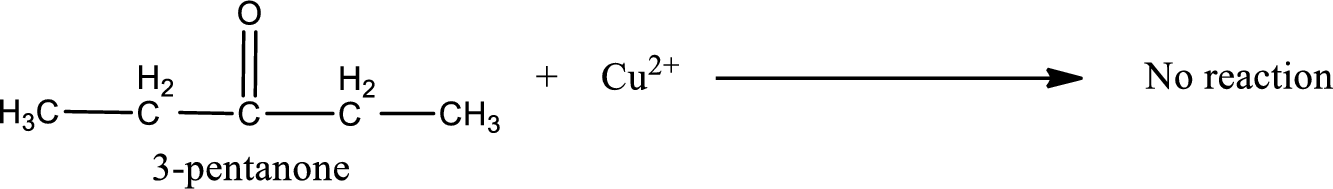
No inorganic product is formed when 3-pentanone undergo Benedict’s test.
No reaction takes place when 3-pentanone undergoes Benedict’s test.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- The Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





