
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780073511214
Author: Francis A Carey Dr., Robert M. Giuliano
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.5, Problem 11P
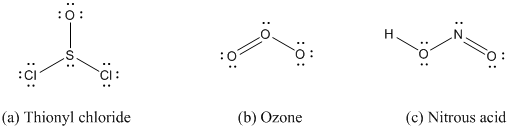
The following inorganic species will be encountered in this text. Calculate the formal charge on each of the atoms in the Lewis formulas given.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Strain Energy for Alkanes
Interaction / Compound kJ/mol kcal/mol
H: H eclipsing
4.0
1.0
H: CH3 eclipsing
5.8
1.4
CH3 CH3 eclipsing
11.0
2.6
gauche butane
3.8
0.9
cyclopropane
115
27.5
cyclobutane
110
26.3
cyclopentane
26.0
6.2
cycloheptane
26.2
6.3
cyclooctane
40.5
9.7
(Calculate your answer to the nearest 0.1 energy unit, and be sure to specify units, kJ/mol or kcal/mol. The answer is case
sensitive.)
H.
H
Previous
Next
A certain half-reaction has a standard reduction potential Ered +1.26 V. An engineer proposes using this half-reaction at the anode of a galvanic cell that
must provide at least 1.10 V of electrical power. The cell will operate under standard conditions.
Note for advanced students: assume the engineer requires this half-reaction to happen at the anode of the cell.
Is there a minimum standard reduction
potential that the half-reaction used at
the cathode of this cell can have?
If so, check the "yes" box and calculate
the minimum. Round your answer to 2
decimal places. If there is no lower
limit, check the "no" box..
Is there a maximum standard reduction
potential that the half-reaction used at
the cathode of this cell can have?
If so, check the "yes" box and calculate
the maximum. Round your answer to 2
decimal places. If there is no upper
limit, check the "no" box.
yes, there is a minimum.
1
red
Πν
no minimum
Oyes, there is a maximum.
0
E
red
Dv
By using the information in the ALEKS…
In statistical thermodynamics, check the
hcv
following equality: ß Aɛ =
KT
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
Ch. 1.1 - How many electrons does carbon have? How many are...Ch. 1.1 - Referring to the periodic table as needed, write...Ch. 1.2 - Species that have the same number of electrons are...Ch. 1.2 - Which of the following ions possess a noble gas...Ch. 1.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 1.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 1.3 - Problem 1.7 All of the hydrogens are bonded to...Ch. 1.4 - Problem 1.8 In which of the compounds...Ch. 1.4 - Indicate the direction of the dipole for the...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 1.5 - The following inorganic species will be...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 1.6 - Problem 1.14 Nitrosomethane and formaldoxime both...Ch. 1.6 - Prob. 15PCh. 1.7 - All of the bonds in the carbonate ion (CO32-) are...Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 17PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 18PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 19PCh. 1.9 - Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, has an ionic bond...Ch. 1.9 - Prob. 21PCh. 1.10 - Which of the following compounds would you expect...Ch. 1.11 - Using the curved arrow to guide your reasoning,...Ch. 1.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 1.11 - Prob. 25PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 26PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 28PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 29PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 30PCh. 1.13 - Which is the stronger acid, H2O or H2S? Which is...Ch. 1.13 - Prob. 32PCh. 1.13 - Prob. 33PCh. 1.13 - Hypochlorous and hypobromous acid (HOClandHOBr)...Ch. 1.13 - Prob. 35PCh. 1.13 - Prob. 36PCh. 1.14 - What is the equilibrium constant for the following...Ch. 1.14 - Prob. 38PCh. 1.14 - Prob. 39PCh. 1.15 - Write an equation for the Lewis acid/Lewis base...Ch. 1 - Write a Lewis formula for each of the following...Ch. 1 - Prob. 42PCh. 1 - Write structural formulas for all the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 44PCh. 1 - Expand the following structural representations so...Ch. 1 - Each of the following species will be encountered...Ch. 1 - Consider Lewis formulas A, B, and C: H2 C -NN:...Ch. 1 - Prob. 48PCh. 1 - Prob. 49PCh. 1 - Prob. 50PCh. 1 - Prob. 51PCh. 1 - Prob. 52PCh. 1 - Prob. 53PCh. 1 - Prob. 54PCh. 1 - Which compound in each of the following pairs...Ch. 1 - With a pKa of 11.6, hydrogen peroxide is a...Ch. 1 - The structure of montelukast, an antiasthma drug,...Ch. 1 - One acid has a pKa of 2, the other has a pKa of 8....Ch. 1 - Calculate Ka for each of the following acids,...Ch. 1 - Rank the following in order of decreasing acidity....Ch. 1 - Rank the following in order of decreasing...Ch. 1 - Consider 1.0 M aqueous solutions of each of the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 63PCh. 1 - Prob. 64PCh. 1 - Prob. 65PCh. 1 - Prob. 66PCh. 1 - Prob. 67PCh. 1 - Prob. 68PCh. 1 - Amide Lewis Structural Formulas Lewis formulas are...Ch. 1 - Amide Lewis Structural Formulas Lewis formulas are...Ch. 1 - Amide Lewis Structural Formulas Lewis formulas are...Ch. 1 - Prob. 72DSPCh. 1 - Amide Lewis Structural Formulas Lewis formulas are...Ch. 1 - Amide Lewis Structural Formulas Lewis formulas are...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward(11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B Bond A Bond C a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest Bond Strongest Bond b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. c. (5pts) Use principles discussed in lecture, supported by relevant structures, to succinctly explain the why your part b (i) radical is more stable than your part b(ii) radical. Written explanation can be no more than one-two succinct sentence(s)!arrow_forward
- . 3°C with TH 12. (10pts total) Provide the major product for each reaction depicted below. If no reaction occurs write NR. Assume heat dissipation is carefully controlled in the fluorine reaction. 3H 24 total (30) 24 21 2h • 6H total ● 8H total 34 래 Br2 hv major product will be most Substituted 12 hv Br NR I too weak of a participate in P-1 F₂ hv Statistically most favored product will be major = most subst = thermo favored hydrogen atom abstractor to LL Farrow_forwardFive chemistry project topic that does not involve practicalarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Q2. Consider the hydrogenation of ethylene C2H4 + H2 = C2H6 The heats of combustion and molar entropies for the three gases at 298 K are given by: C2H4 C2H6 H2 AH comb/kJ mol¹ -1395 -1550 -243 Sº / J K¹ mol-1 220.7 230.4 131.1 The average heat capacity change, ACP, for the reaction over the temperature range 298-1000 K is 10.9 J K¹ mol¹. Using these data, determine: (a) the standard enthalpy change at 800 K (b) the standard entropy change at 800 K (c) the equilibrium constant at 800 K.arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B Bond A Bond C a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest Bond Strongest Bond b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. c. (5pts) Use principles discussed in lecture, supported by relevant structures, to succinctly explain the why your part b (i) radical is more stable than your part b(ii) radical. Written explanation can be no more than one-two succinct sentence(s)! Googlearrow_forwardPrint Last Name, First Name Initial Statifically more chances to abstract one of these 6H 11. (10pts total) Consider the radical chlorination of 1,3-diethylcyclohexane depicted below. 4 4th total • 6H total 래 • 4H total 21 total ZH 2H Statistical H < 3° C-H weakest - product abstraction here bund leads to thermo favored a) (6pts) How many unique mono-chlorinated products can be formed and what are the structures for the thermodynamically and statistically favored products? Product 6 Number of Unique Mono-Chlorinated Products Thermodynamically Favored Product Statistically Favored Product b) (4pts) Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for the FIRST propagation step (p-1) for the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. Only draw the p-1 step. You do not need to include lone pairs of electrons. No enthalpy calculation necessary H H-Cl Waterfoxarrow_forward
- 10. (5pts) Provide the complete arrow pushing mechanism for the chemical transformation → depicted below Use proper curved arrow notation that explicitly illustrates all bonds being broken, and all bonds formed in the transformation. Also, be sure to include all lone pairs and formal charges on all atoms involved in the flow of electrons. CH3O II HA H CH3O-H H ①arrow_forwardDo the Lone Pairs get added bc its valence e's are a total of 6 for oxygen and that completes it or due to other reasons. How do we know the particular indication of such.arrow_forwardNGLISH b) Identify the bonds present in the molecule drawn (s) above. (break) State the function of the following equipments found in laboratory. Omka) a) Gas mask b) Fire extinguisher c) Safety glasses 4. 60cm³ of oxygen gas diffused through a porous hole in 50 seconds. How long w 80cm³ of sulphur(IV) oxide to diffuse through the same hole under the same conditions (S-32.0.0-16.0) (3 m 5. In an experiment, a piece of magnesium ribbon was cleaned with steel w clean magnesium ribbon was placed in a crucible and completely burnt in oxy cooling the product weighed 4.0g a) Explain why it is necessary to clean magnesium ribbon. Masterclass Holiday assignmen PB 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY