
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
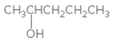
Concept Introduction:
When H2O is lost from a material it is called dehydration. When an alcohol is treated with a strong acid such as H2SO4, a water molecule is lost by breaking two adjacent bonds C-OH and C-H and forming a new double bond, producing an alkene. This is an elimination reaction.
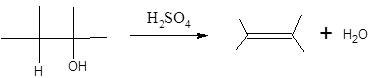
In this reaction more than one type of alkene may produce. But one of them is the major product.
According to Zaitsev rule, the major product alkene formed by elimination, is that which possess more alkyl groups bonded to it
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkene formed when the given alcohol is treated with H2SO4 should be determined. The major product should be predicted using Zaitsev rule.
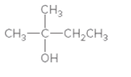
Concept Introduction:
When H2O is lost from a material it is called dehydration. When an alcohol is treated with a strong acid such as H2SO4, a water molecule is lost by breaking two adjacent bonds C-OH and C-H and forming a new double bond, producing an alkene. This is an elimination reaction.
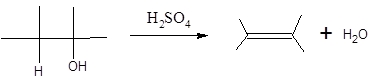
In this reaction more than one type of alkene may produce. But one of them is the major product.
According to Zaitsev rule, the major product alkene formed by elimination, is that which possess more alkyl groups bonded to it
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkene formed when the given alcohol is treated with H2SO4 should be determined. The major product should be predicted using Zaitsev rule.
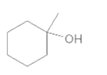
Concept Introduction:
When H2O is lost from a material it is called dehydration. When an alcohol is treated with a strong acid such as H2SO4, a water molecule is lost by breaking two adjacent bonds C-OH and C-H and forming a new double bond, producing an alkene. This is an elimination reaction.
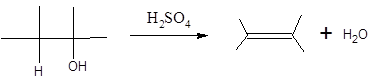
In this reaction more than one type of alkene may produce. But one of them is the major product.
According to Zaitsev rule, the major product alkene formed by elimination, is that which possess more alkyl groups bonded to it
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Draw the structures of the chief product formed when the following alcohols are dehydrated to alkenes: a. b.arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name of the following alcohols and phenols.arrow_forward1: Give at least five (5) uses of Alcohol and Phenol Name Functional Group R-OH Alcohols LOH Phenols Based on the illustration above. What is the difference between alcohol and phenol? Can Phenol react with alcohol?arrow_forward
- Complete the following syntheses – they may be two- or three-step processes. Include any necessary catalysts or reaction conditions. a) Prepare propanone from 1-propanolarrow_forwardGive the common name for NN OH T CH3-CH₂-C-N-CH₂-CH3 Spell out the common name of the compound. Give the IUPAC name for 0 CH₂ || CH₂-C-N-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂, Spell out the IUPAC name of the compound. diethylamine Draw all missing reactants and/or products in the appropriate boxes by placing atoms on the canvas and connecting them with bonds. Add charges where needed. HE CONT HOarrow_forwardName the following alcohol. O2-Bromo-4-ethylcyclopentanol 4-Ethyl-2-bromocyclopentanol O1-Ethyl-3-bromo-4-cyclopentanol O1-Bromo-4-ethyl-2-cyclopentanolarrow_forward
- 4. Complete the following reactions for the preparation of aldehydes and ketones. Draw the structure for the product. Name the reactant and product. a) CH- CH OH Oxidation of 1° alcohol b) CH-CHCH-CH2 CHy dH c) CH-CH-CH Oxidation of 2 alcohol d) Cty-CH-CH-CH e) ->arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the IUPAC name? Draw the structure and give how many carbons are on the parent chain. 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)propane-2-thiolarrow_forwardClassify each molecule as an aldehyde, ketone, or neither. AND Classify each molecule as an ester, ether, or neither.arrow_forward
- Name each aldehyde or ketone. CH, CH, c. CH3-C-CH-CH-CH-C-H ČH,arrow_forwardAn alcohol does not react with aziridine unless an acid is present. Why is the acid necessary?arrow_forwardDraw the structural formula of the products formed when each alkene is treated with one equivalent of NBS in CH2Cl2 in the presence of light.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
