
Interpretation:
Solid: Solid is a sample of matter that retains its shape and density when not confined. Stronger force of attraction exists between atom/ions/ molecules.
Liquid: A liquid is a sample of matter that conforms to shape of container in which aquires a defined surface in the presence of gravity. In this state weaker force exist between atoms/ ions/ molecules.
Gas: A gas is a sample of matter that conforms to the shape of container in which it is placed and acquires whole volume of container.
Negligible force of attraction exists between atoms/ions/molecules.
Supercritical fluid: Fluid over its critical temperature and pressure exhibiting good solvent power.
Concept used introduction:
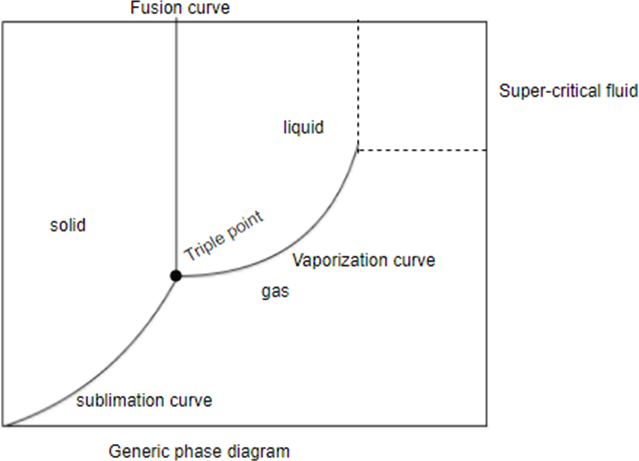
A generic diagram which shows that state of general matter with change in pressure or temperature or both. At a particular temperature or pressure you can find out the state of matter with the help of phase diagram.
To determine:
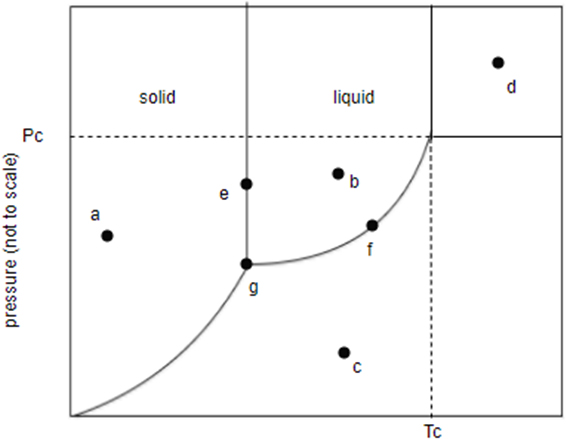
Identify the states present at points through a to g in the phase diagram show here.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
- The velocity distribution function of gas moleculesa) is used to measure their velocity, since the small size of gas molecules means that it cannot be measured in any other wayb) is only used to describe the velocity of particles if their density is very high.c) describes the probability that a gas particle has a velocity in a given interval of velocitiesarrow_forwardExplain why in the representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a particular gas, the maximum occurs for vi = 0 m/s.arrow_forwardExplain why the representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a particular gas becomes flatter as the temperature increases.arrow_forward
- Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following molecules and assign charges where appropriate. The order in which the atoms are connected is given in parentheses. a. CIFCIF b. BrCNBrCN 0 c. SOCI2 × (CISCIO) SOC₁₂ (CISCI) You can draw both an octet and a valence shell expanded structure. Considering the following structural information, which is the better one: The measured S-OS-O bond length in SOC12SOCl2 is 1.43 Å. For comparison, that in SO2SO2 is 1.43 Å [Exercise 1-9, part (b)], that in CHзSOHCH3 SOH d. CH3NH2CH3NH2 (methanesulfenic acid) is 1.66 A. e. CH3OCH3 CH3 OCH3 NH2 f. N2H2× (HNNH) N2 H2 (HNNH) g. CH2COCH₂ CO h. HN3× (HNNN) HN3 (HNNN) i. N20 × (NNO) N2O (NNO)arrow_forwardbre The reaction sequence shown in Scheme 5 demonstrates the synthesis of a substituted benzene derivative Q. wolsd works 2 NH2 NaNO2, HCI (apexe) 13× (1 HNO3, H2SO4 C6H5CIN2 0°C HOTE CHINO₂ N O *O₂H ( PO Q Я Scheme 5 2 bag abouoqmics to sounde odi WEIC (i) Draw the structure of intermediate O. [2 marks] to noitsmot od: tot meinedogm, noit so oft listsb ni zaupaib bas wa (ii) Draw the mechanism for the transformation of aniline N to intermediate O. Spoilage (b) [6 marks] (iii) Identify the reagent X used to convert compound O to the iodinated compound [tom E P. vueimado oilovonsa ni moitos nolisbnolov ayd toes ai tedw nisiqx (iv) Identify the possible structures of compound Q. [2 marks] [2 marks] [shom 2] (v) bus noires goiribbeolovo xnivollot adj to subora sidab Draw the mechanism for the transformation of intermediate P to compound Q. [5 marks] vi (vi) Account for the regiochemical outcome observed in the reaction forming compound Q. [3 marks]arrow_forwardPROBLEM 4 Solved Show how 1-butanol can be converted into the following compounds: a. PROBLEM 5+ b. d. -C= Narrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





