
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977305
Author: BEER, Ferdinand P. (ferdinand Pierre), Johnston, E. Russell (elwood Russell), Cornwell, Phillip J., SELF, Brian P.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.1, Problem 12.65P
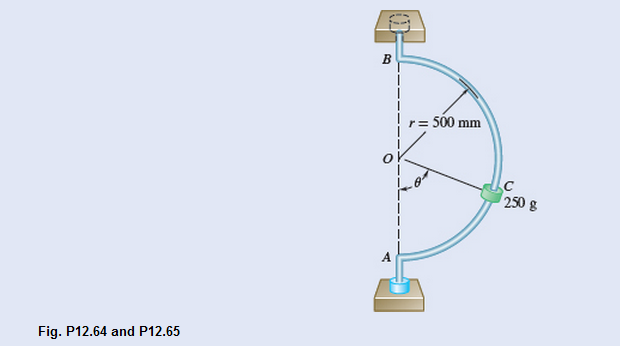
A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular rod which is made to rotate about the vertical AB at a constant rate of 7.5 rad/s. Knowing that the coefficients of friction are us μs=0.25 and μk=0.20 , indicate whether the collar will slide on the rod if it is released in the position corresponding to (a) θ=75° (b) θ=40° . Also, determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted on the collar immediately after release.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need help with a MATLAB code. This code just keeps running and does not give me any plots. I even reduced the tolerance from 1e-9 to 1e-6. Can you help me fix this? Please make sure your solution runs.
% Initial Conditions
rev = 0:0.001:2;
g1 = deg2rad(1);
g2 = deg2rad(3);
g3 = deg2rad(6);
g4 = deg2rad(30);
g0 = deg2rad(0);
Z0 = 0;
w0 = [0; Z0*cos(g0); -Z0*sin(g0)];
Z1 = 5;
w1 = [0; Z1*cos(g1); -Z1*sin(g1)];
Z2 = 11;
w2 = [0; Z2*cos(g2); -Z2*sin(g2)];
[v3, psi3, eta3] = Nut_angle(Z2, g2, w2);
plot(v3, psi3)
function dwedt = K_DDE(~, w_en)
% Extracting the initial condtions to a variable
% Extracting the initial condtions to a variable
w = w_en(1:3);
e = w_en(4:7);
Z = w_en(8);
I = 0.060214;
J = 0.015707;
x = (J/I) - 1;
y = Z - 1;
s = Z;
% Kinematic Differential Equations
dedt = zeros(4,1);
dedt(1) = pi*(e(3)*(s-w(2)-1) + e(2)*w(3) + e(4)*w(1));
dedt(2) = pi*(e(4)*(w(2)-1-s) + e(3)*w(1) - e(1)*w(3));
dedt(3) = pi*(-e(1)*(s-w(2)-1) - e(2)*w(1) + e(4)*w(3));…
alpha 1 is not zero
alpha 1 can equal alpha 2
use velocity triangle to solve for alpha 1
USE MATLAB ONLY
provide typed code
solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer
Turbomachienery .
GIven:
vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, (leaving a stator in axial flow) R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3
Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram
Use this code for plot
% plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4
function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3)
S1L = [0 1];
V1x = [0 0];
V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)];
S2L = [2 3];
V2x = [0 0];
V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)];
W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)];
U2x = [3 3];
U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)];
S3L = [4 5];
V3x = [0 0];
V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)];
W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)];
U3x = [5 5];
U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)];
plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',...
S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',...…
3. Find a basis of eigenvectors and diagonalize.
4
0
-19
7
a.
b.
1-42
16
12-20
[21-61
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 12.1 - A 1000-Ib boulder B is resting on a 200-Ib...Ch. 12.1 - Marble A is placed in a hollow tube, and the tube...Ch. 12.1 - The two systems shown start from rest. On the...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.CQ4PCh. 12.1 - People sit on a Ferris wheel at points A, B, C,...Ch. 12.1 - Crate A is gently placed with zero initial...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.F2PCh. 12.1 - Objects A, B, and C have masses mA, mB, and...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mAand mB, my...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mAand mB, my...
Ch. 12.1 - A pilot of mass m flies a jet in a half-vertical...Ch. 12.1 - Wires AC and BC are attached to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and...Ch. 12.1 - Four pins slide in four separate slots cut in a...Ch. 12.1 - At the instant shown, the length of the boom AB is...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.F11PCh. 12.1 - Pin B has a mass m and slides along the slot in...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.1PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.2PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.3PCh. 12.1 - A spring scale A and a lever scale B having equal...Ch. 12.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-oz model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that may...Ch. 12.1 - A tugboat pulls a small barge through a harbor....Ch. 12.1 - If an automobile's braking distance from 108 km/h...Ch. 12.1 - A 4-kg package is released from rest at point A...Ch. 12.1 - The coefficients of friction the load and the...Ch. 12.1 - A light train made up of two cars is traveling at...Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - Each of the systems shown is initially at rest....Ch. 12.1 - Boxes A and B are at rest on a conveyor belt that...Ch. 12.1 - A 5000-1b truck is being used to lift a 1000-1b...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.20PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.1 - To unload a bound stack of plywood from a truck;...Ch. 12.1 - To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.24PCh. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that a...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.26PCh. 12.1 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to a support...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.1 - An athlete pulls handle A to the left with a...Ch. 12.1 - A 10-Ib block B rests as shown on a 20-1b bracket...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.32PCh. 12.1 - Knowing that k=0.30 , determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - The 30-Ib block B is supported by the 55-Ib block...Ch. 12.1 - Block B of mass 10 kg rests as shown on the upper...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that the swings of an amusement park ride...Ch. 12.1 - During a hammer thrower's practice swings, the...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.38PCh. 12.1 - A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C...Ch. 12.1 - Two wires AC and BC are tied at C to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.42PCh. 12.1 - As part of an outdoor display, a 5-kg model C of...Ch. 12.1 - A 130-ib wrecking ball B is attached to a...Ch. 12.1 - During a high-speed chase, a 2400-Ib sports car...Ch. 12.1 - An airline pilot climbs to a new flight level...Ch. 12.1 - The roller-coaster track shown is contained in a...Ch. 12.1 - A spherical-cap governor is fixed to a vertical...Ch. 12.1 - A series of small packages, each with a mass of...Ch. 12.1 - A 55-kg pilot flies a jet trainer in a half...Ch. 12.1 - A carnival ride is designed to allow the general...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.52PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.53PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.1 - A 3-kg block is at rest relative to a parabolic...Ch. 12.1 - A polisher is started so that the fleece along the...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.57PCh. 12.1 - The carnival ride from Prob. 12.51 is modified so...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.59PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.60PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.61PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.62PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - An advanced spatial disorientation trainer allows...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.67PCh. 12.1 - The 3-kg collar B slides on the frictionless arm...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-kg block B slides without friction inside a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B weighs 4 oz and is free to slide in a...Ch. 12.1 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to let...Ch. 12.1 - A 700-kg horse A lifts a 50-kg hay bale B as...Ch. 12.1 - Slider C has a weight of 0.5 Ib and may move in a...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - For the particle of Prob. 12.74, show (a) that the...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.76PCh. 12.2 - For the particle of Prob. 12.76, determine the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the mass of the earth knowing that the...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.79PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.80PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.2 - The orbit of the planet Venus is nearly circular...Ch. 12.2 - A satellite is placed into a circular orbit about...Ch. 12.2 - The periodic time (see Prob. 12.83) of an earth...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.85PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.86PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.87PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.88PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.89PCh. 12.2 - A 1 -kg collar can slide on a horizontal rod that...Ch. 12.2 - A 1-Ib ball A and a 2-Ib ball B are mounted on a...Ch. 12.2 - Two 2.6-Ib collars A and B can slide without...Ch. 12.2 - A small ball swings in a horizontal circle at the...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m describes the logarithmic...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.96PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.97PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.3 - It was observed that during the Galileo...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.100PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.101PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.102PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.103PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes a circular orbit at an...Ch. 12.3 - A space probe is to be placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.106PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.107PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.108PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.109PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.110PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.111PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.112PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.113PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.114PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.115PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.116PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.117PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.119PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.120PCh. 12.3 - Show that the angular momentum per unit mass h of...Ch. 12 - In the braking test of a sports car, its velocity...Ch. 12 - A bucket is attached to a rope of length L=1.2 m...Ch. 12 - Block A has a weight of 40 Ib, and block B has a...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.125RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.126RPCh. 12 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to pull...Ch. 12 - A robot arm moves in the vertical plane so that...Ch. 12 - Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.130RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.131RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.132RPCh. 12 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Find the eigenvalues. Find the corresponding eigenvectors. 6 2 -21 [0 -3 1 3 31 a. 2 5 0 b. 3 0 -6 C. 1 1 0 -2 0 7 L6 6 0 1 1 2. (Hint: λ = = 3)arrow_forwardUSE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, (leaving a stator in axial flow) R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),...…arrow_forwardUSE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ...…arrow_forward
- The answer should equal to 1157. Please sent me the solution. Thank you!arrow_forwardBONUS: If the volume of the 8cm x 6.5cm x 6cm Block of Aluminum was 312cm3 before machining, find how much material was removed when the fixture below was machined. +2 2.00 cm 6.00 cm 2.50 cm 6.50 cm 1.00 cm 2.50 cm 11.00 cm 8.00 cm 30 CP 9411 FL.4) (m² 1157 Area of triangle = 1/2*B*H Area of circle = лR² Circumference of a circle = 2πR 6.00 cm 6.50 cm 1.50 cm Radius 1.50 cm 1.00 cmarrow_forwardConsider a 5m by 5m wet concret patio with an average water film thickness of .2mm. Now wind at 50 km/h is blowing over the surface. If the air is at 1 atm, 15oC and 35 percent relative humidity, determine how long it will take for the patio to completely dry.arrow_forward
- 70. Compute the number of cubic centimeters of iron required for the cast-iron plate shown. The plate is 3.50 centimeters thick. Round the answer to the nearest cubic centimeter. 50.0 cm 40.0 cm Radius 150° 115.0 cm- 81.0 cmarrow_forwardLaw of Sines Solve the following problems using the Law of Sin 7. Find side x. All dimensions are in inches. -°-67°-37° 81° x Sin A 8.820 X 67°00' 32°00' a sin A b C sin B sin Carrow_forward35. a. Determine B. b. Determine side b. c. Determine side c. 5.330 in.- ZB 73°30'arrow_forward
- Consider a 12 cm internal diameter, 14 m long circular duct whose interior surface is wet. The duct is to be dried by forcing dry air at 1 atm and 15 degrees C throught it at an average velocity of 3m/s. The duct passes through a chilled roo, and it remains at an average temp of 15 degrees C at all time. Determine the mass transfer coeeficient in the duct.arrow_forwardnote n=number of link(dont include the ground link (fixed))arrow_forward6.(单选题) The DOF of the following mechanism is E A F=3x4-2x5-0=2 B F=3x3-2x4-0=1 F=3x3-2x3-2=1 D F=3x4-2x5-1=1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Ch 2 - 2.2.2 Forced Undamped Oscillation; Author: Benjamin Drew;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Tb7Rx-bCWE;License: Standard youtube license