
A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket A. The coefficients of friction are μs = 0.30 and μk = 0.25 between block B and bracket A, and there is no friction in the pulley or between the bracket and the horizontal surface. (a) Determine the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A. (b) If the weight of block C is 10 percent larger than the answer found in a, determine the accelerations of A, B, and C.
Fig. P12.31
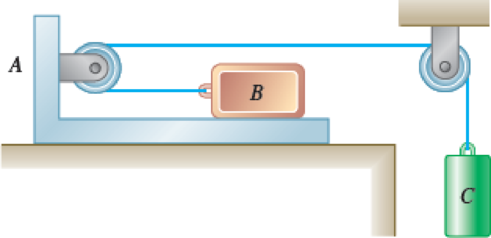
(a)
Find the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A.
Answer to Problem 12.31P
The maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of block B
The weight of bracket A
The coefficient of static friction between block B and bracket A
The coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and bracket A
Calculation:
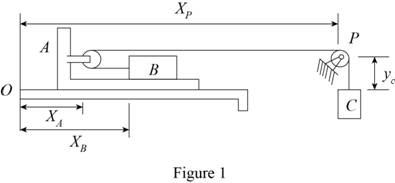
Let as consider the horizontal coordinate of A is
left of A.
Let as consider the horizontal coordinate of B is
left of A.
Let as consider
Sketch the system with coordinates points as shown in Figure (1).
Write the general equation of mass (m):
Here, W is the weight, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Consider the constraint of cord.
Write the total length of cable length (L).
Here,
Differentiate Equation (1) with respect to t to write velocity of the blocks.
Here,
Differentiate Equation (2) with respect to t to write acceleration of the blocks.
Here,
No slip between bracket A and block B. Therefore, the acceleration of bracket A is equal to acceleration of block B.
Substitute
From Equation (4) and (5), consider
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of bracket A as shown in Figure (2).
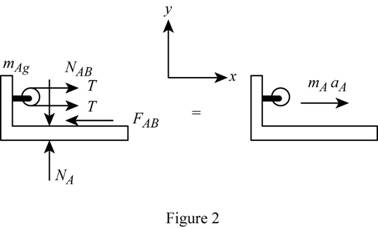
Refer Figure (2).
Apply Newton’s law of equation along x-axis.
Here, T is the tension in the cable,
Substitute
Here,
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of block B as shown in Figure (3).
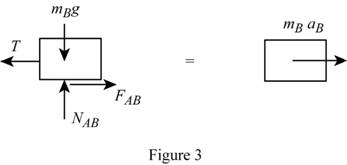
Refer Figure (3).
Apply Newton’s law of equation along x-axis.
Substitute
Here,
Apply Newton’s law of equation along y-axis.
Here,
Write the equation of frictional force
Substitute
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of block C as shown in Figure (4).
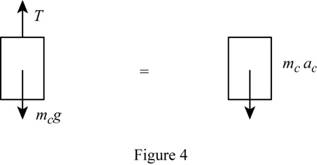
Refer Figure (4).
Apply Newton’s law of equation along y-axis.
Substitute
Here,
Adding Equation (5), (6), and (9).
Substitute Equation (6) in Equation (12).
Subtract Equation (6) and (9).
Substitute Equation (6) and (10) in Equation (14).
Subtracting Equation (13) and (9).
Substitute 0.30 for
Thus, the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A is
(b)
Find the accelerations of bracket A, block B and block C.
Answer to Problem 12.31P
The accelerations of bracket A is
The accelerations of block B is
The accelerations of block C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of block C is 10 % larger than the answer found in part (a).
Calculation:
Find the weight of block C.
The slip is occurring. Therefore consider the kinetic acceleration.
Write the equation of frictional force
Substitute
Subtract Equation (6) and (9).
Substitute Equation (17) in Equation (18).
Substitute 0.25 for
Rewrite the Equation (5).
Substitute 10 lb for
Find the accelerations of bracket A, block B and block C.
Solve Equation (3), (20), and (21).
Thus, the accelerations of bracket A is
Thus, the accelerations of block B is
Thus, the accelerations of block C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- The hose supplying the cylinder operating the bucket of a large excavator has fluid at 1000 psi flowing at 5 gpm. What is theavailable power in the line?arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forwardGiven the following data for crack rocker mechanism. If θ2 = 4π/3 and ω2 = 1 rad/s, Determine all possible values of ω4 and ω3 analytically. The lengths of links are a = 2, b = 8, c = 7 and d = 9 in cm.arrow_forward
- Q6] (20 Marks) Select the most suitable choice for the following statements: modo digi -1A 10 af5 1 -The copper-based alloy which is responded to age hardening is a) copper-nickel b) aluminum bronze c) copper - beryllium d) brass besincaluy 2- Highly elastic polymers may experience elongations to greater than.... b) 500% bromsia-P c) 1000%. d) 1200% 15m or -2 a)100% 3- The cooling rate of quenching the steel in saltwater will be ......the cooling rate of quenching ir c) faster than sold) none of them a) slower than 4- Adding of a) Cr b) the same as ...... Will lead to stabilize the b) Mo 10 austenite in steel. c) Nimble avolls 1d) Sized loloin nl 5- The adjacent linear chains of crosslinked polymers are joined one to another at various positic DIR... by.........bonds c) covalent noisqo gd) ionic lg 120M 6- For the ceramic with coordination number 6 the cation to anion radius ratio will be a) Van der Waals a) 0.155-0.225 a) linear b) hydrogen (b) 0.225-0.414 c) 0.414 0.732 ..polymers.…arrow_forwardExamine Notes: Attempt Six Questions Only. rever necessa , Q1] (20 Marks) Answer with true (T) or false (F), corrects the wrong phrases, and gives sho reasons for correct and corrected statements: 1- High chromium irons are basically grey cast irons alloyed with 12 to 30 % Cr. yous board-19qgo orT-1 2- The drawbacks of Al- Li alloys are their high young modulus and high density.&M 0) (0 3- Vulcanized rubbers are classified under thermoplastic polymers. 4- Diamond is a stable carbon polymorph at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. ( 5- The metallic ions of ceramic are called anions, and they are positively charged. yldgiH-S 69001(6arrow_forwardH.W 5.4 Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa. The diameters of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 2P- PA 50mm B 200mm 2P 0.9m 1.3marrow_forward
- d₁ = = Two solid cylindrical road AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that 30mm (for AB) and d₂ 50mm (for BC), find the average normal stress in each road and the total deformation of road AB and BC. E=220GPa H.W 5.3 60kN A For the previous example calculate the value of force P so that the point A will not move, and what is the total length of road AB at that force? P◄ A 125kN 125kN 0.9m 125kN 125kN 0.9m B B 1.3m 1.3marrow_forwardClass: B Calculate the load that will make point A move to the left by 6mm, E-228GPa The cross sections of the rods are as shown in fig. below. 183 P- Solution 1.418mm 200mm 80mm 3P- 18.3 A 080mm B 200mm 3P- 0.9m إعدادات العرض 1.3m 4.061mmarrow_forwardH.W6 Determine the largest weight W that can be supported by two wires shown in Fig. P109. The stress in either wire is not to exceed 30 ksi. The cross- sectional areas of wires AB and AC are 0.4 in2 and 0.5 in2, respectively. 50° 30° Warrow_forward
- Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. H.W2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2-Eq.of motion 8wn 4-0 (5) m. Jo marrow_forward2. Read the following Vernier caliper measurements. (The scales have been enlarged for easier reading.) The Vernier caliper is calibrated in metric units. (a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 سلسلسله (b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسل (c) 1 23456 (d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 سلسلسarrow_forwardExplain why on the interval 0<x<1000 mm and 1000<x<2000mm, Mt is equal to positive 160 Nm, but at x= 0mm and x=1000mm Mt is equal to -160 Nm (negative value!). What is the reason for the sign change of Mt?arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
