
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260265453
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.129RP
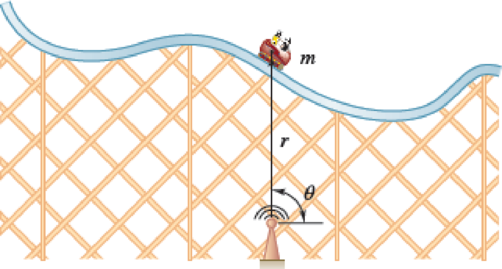
Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic values of a 200-kg roller-coaster cart as it passes overhead. According to the system, r = 25 m, r ˙r=−10 m/s, ¨r=−2 m/s2, θ = 90°, ˙θ=−0.4rad/s, ¨θ=−0.32rad/s2. At this instant, determine (a) the normal force between the cart and the track, (b) the radius of curvature of the track.
Fig. P12.129
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A crate is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A
such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A
is located at a height of h = 121.92 cm above the top of the
crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface.
Use the given dimensions from the table below to perform
the following calculations:
→>
a.) Determine the position vector IAD that describes rope
AD.
b.) Compute the unit vector cд that points from point C to
point A.
c.) If rope AB carries a tension force of magnitude FT = 760
→
N, determine the force vector FT that expresses how this
force acts on point A.
Express each vector in Cartesian components to three
significant figures.
2013 Michael Swanbom
↑z
BY NC SA
b
x
B
У
a
D
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following
table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Be sure to align
your cartesian unit vectors with the coordinate axes shown in
the figure.
Variable Value
a
101.6 cm
b
124.46 cm
с
38.71 cm
a. rдD =
+
b. ÛCA
c. FT=
=…
F3
N<
Ꮎ
2
F2
-Y
F1
There are 3 forces acting on the eye bolt.
Force F1 acts on the XY plane has a magnitude of 536 lbf,
and the angle of 0 = 38°.
Force F2 acts on the YZ plane has a magnitude of 651 lbf,
and the angle = 41°.
Force F3 has a magnitude of 256 lb, and coordinate.
=
f
direction angles of a 71°, B = 115°, and y = 33°.
Determine the resultant force on the eye bolt.
FR = (
+
k) lbf
FR magnitude:
FR coordinate direction angle a:
deg
FR coordinate direction angle ẞ`:
deg
FR coordinate direction angle y:
deg
lbf
Ball joints connect the ends of each of the struts as shown.
The resulting structure supports a force of F = 1925 N which
lies in the xz plane.
a.) Determine the angle (in degrees) between strut AD and
strut AC.
b.) Determine the dimension g such that the force Fis
→>
perpendicular to гAC.
2013 Michael Swanbom
CC
BY NC SA
B
b
C
h/
L
不
g
F
୮
d
y
LLC
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the table
below. Note the figure may not be to scale. Be sure to align
your cartesian unit vectors with the coordinate axes shown in
the figure.
Variable Value
a
4.8 cm
b
13.4 cm
C
11.6 cm
d
10.4 cm
h
4.4 cm
k
14.8 cm
a. The angle between strut AD and strut AC is
b. The dimension g is
deg.
cm.
Chapter 12 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 12.1 - A 1000-lb boulder B is resting on a 200-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Marble A is placed in a hollow tube, and the tube...Ch. 12.1 - The two systems shown start from rest. On the...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B are released from rest in the...Ch. 12.1 - People sit on a Ferris wheel at points A, B, C,...Ch. 12.1 - Crate A is gently placed with zero initial...Ch. 12.1 - Two blocks weighing WA and WB are at rest on a...Ch. 12.1 - Objects A, B, and C have masses mA, mB, and mC,...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4FBPCh. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mA and mB,...
Ch. 12.1 - A pilot of mass m flies a jet in a half-vertical...Ch. 12.1 - Wires AC and BC are attached to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9FBPCh. 12.1 - At the instant shown, the length of the boom AB is...Ch. 12.1 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B has a mass m and slides along the slot in...Ch. 12.1 - The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 3.75...Ch. 12.1 - The value of g at any latitude may be obtained...Ch. 12.1 - A Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite is in...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4PCh. 12.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-oz model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that may...Ch. 12.1 - A tugboat pulls a small barge through a harbor....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9PCh. 12.1 - A 4-kg package is released from rest at point A...Ch. 12.1 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 12.1 - A light train made up of two cars is traveling at...Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12.1 - A 5000-lb truck is being used to lift a 1000-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - The flat-bed trailer carries two 1500-kg beams...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.1 - To unload a bound stack of plywood from a truck,...Ch. 12.1 - To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to...Ch. 12.1 - An airplane has a mass of 25 Mg and its engines...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that a...Ch. 12.1 - A constant force P is applied to a piston and rod...Ch. 12.1 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to a support...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 10 kg, and blocks B and C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.1 - A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - The 30-lb block B is supported by the 55-lb block...Ch. 12.1 - Block B of mass 10 kg rests as shown on the upper...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that the swings of an amusement park ride...Ch. 12.1 - During a hammer throwers practice swings, the...Ch. 12.1 - Human centrifuges are often used to simulate...Ch. 12.1 - A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12.1 - The 0.5-kg flyballs of a centrifugal governor...Ch. 12.1 - As part of an outdoor display, a 5-kg model C of...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.1 - During a high-speed chase, a 2400-lb sports car...Ch. 12.1 - An airline pilot climbs to a new flight level...Ch. 12.1 - The roller-coaster track shown is contained in a...Ch. 12.1 - A spherical-cap governor is fixed to a vertical...Ch. 12.1 - A series of small packages, each with a mass of...Ch. 12.1 - A 55-kg pilot flies a jet trainer in a half...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.51PCh. 12.1 - A curve in a speed track has a radius of 1000 ft...Ch. 12.1 - Tilting trains, such as the Acela Express that...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.1 - A 3-kg block is at rest relative to a parabolic...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.1 - A turntable A is built into a stage for use in a...Ch. 12.1 - The carnival ride from Prob. 12.51 is modified so...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.59PCh. 12.1 - A small 8-oz collar D can slide on portion AB of a...Ch. 12.1 - A small block B fits inside a slot cut in arm OA...Ch. 12.1 - The parallel-link mechanism ABCD is used to...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - An advanced spatial disorientation trainer is...Ch. 12.1 - The 3-kg collar B slides on the frictionless arm...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-kg block B slides without friction inside a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B weighs 4 oz and is free to slide in a...Ch. 12.1 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to let...Ch. 12.1 - A 700-kg horse A lifts a 50-kg hay bale B as...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the mass of the earth knowing that the...Ch. 12.2 - Show that the radius r of the moons orbit can be...Ch. 12.2 - Communication satellites are placed in a...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.2 - The orbit of the planet Venus is nearly circular...Ch. 12.2 - A satellite is placed into a circular orbit about...Ch. 12.2 - The periodic time (see Prob. 12.83) of an earth...Ch. 12.2 - A 500-kg spacecraft first is placed into a...Ch. 12.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit of 2200-km...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.87PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.88PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.89PCh. 12.2 - A 1-kg collar can slide on a horizontal rod that...Ch. 12.2 - Two 2.6-lb collars A and B can slide without...Ch. 12.2 - A small ball swings in a horizontal circle at the...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass mC is being...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.95PCh. 12.3 - A particle with a mass m describes the path...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m describes the parabola y =...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.99PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.100PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.101PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.103PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.104PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.105PCh. 12.3 - Halleys comet travels in an elongated elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.109PCh. 12.3 - A space probe is to be placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 12.3 - The Clementine spacecraft described an elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - A space probe is describing a circular orbit of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.115PCh. 12.3 - A space shuttle is describing a circular orbit at...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.117PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.119PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.120PCh. 12.3 - Show that the angular momentum per unit mass h of...Ch. 12 - In the braking test of a sports car, its velocity...Ch. 12 - A bucket is attached to a rope of length L = 1.2 m...Ch. 12 - A 500-lb crate B is suspended from a cable...Ch. 12 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to pull...Ch. 12 - A robot arm moves in the vertical plane so that...Ch. 12 - Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic...Ch. 12 - The radius of the orbit of a moon of a given...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.131RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.132RPCh. 12 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 13 F1 35 N = 37°. = Determine the resultant force on the eye bolt. FR = ( + FR magnitude: FR coordinate direction angle a: deg FR coordinate direction angle ẞ`: Ꭱ deg FR coordinate direction angle y: deg N k) Narrow_forwardA hollow cylinder with inner radius of 30 mm and outer radius of 50 mm is heated at the inner surface at a rate of 10^5m^2W and dissipated heat by convection from outer surface into a fluid at 80∘C with h=400 m2 KW. There is no energy generation and thermal conductivity of the material is constant at 15mKW. Calculate the temperature of inside and outside surfaces of cylinder.arrow_forwardplease read everything properly... Take 3 4 5 hrs but solve full accurate drawing on bond paper don't use chat gpt etc okkarrow_forward
- An aircraft is flying trim stick-fixed at steady level flight with a speed of 80 m/s and at standard sea level conditions, where the air density is 1.225 kg/m3 . The ratio of the wings' surface area to the tail plane’s surface area is 10, the tail arm is 10 m and the wings’ mean aerodynamic chord length is 2 m. The ratio of the tail plane’s lift to the wings’ lift is -0.01 at that condition. The rest of the known data are given in the two tables at the end of the question. Justify any assumption that you make. a) Calculate the total lift and tail plane lift coefficients, the wings’ load and Calculate the down-wash angle and the tail plane angle of attackarrow_forwardAnswer a and barrow_forwardCơ cấu tạo hình được thiết kế để tạo ra hành trình cắt chậm và quay trở lại nhanh chóng với lưỡi gắn với con trượt tại C. Xác định vận tốc của khối con trượt C tại thời điểm 0=60° nếu liên kết AB đang quay với vận tốc góc 4 rad/s. 45° A. V 1.74(m/s) B. Vc=1.84(m/s) C. Vc = 1.24(m/s) D. Vc=1.64(m/s) 125 mm B = WAB 4 rad/s 300 mm Aarrow_forward
- please help solvearrow_forwardplease help solvearrow_forwardTwo springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m₂ = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and k₂ = 2 N/m. www.m k₁ = 3 (y₁ = 0). m₁ = 1 k2=2 (y₂ = 0) |m₂ = 1 Y2 y 2 System in static equilibrium (Net change in spring length =32-31) System in motion Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system Determine the equations of motion y₁(t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY