
The following data are for the system
(a) How long does it take the system to reach equilibrium?
(b) How does the rate of the forward reaction compare with the rate of the reverse reaction after 30 s? After 90 s?
(a)
Interpretation:
The time required for the system to reach at equilibrium needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The system is said to be in equilibrium if the there is no change in the partial pressure or concentration of reactant and product takes place.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
80 s.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as follows:
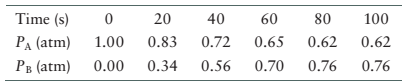
The data for the system is given as follows:
| Time (s) | |
|
| 0 | 1 | 0.000 |
| 20 | 0.83 | 0.34 |
| 40 | 0.72 | 0.56 |
| 60 | 0.65 | 0.70 |
| 80 | 0.62 | 0.76 |
| 100 | 0.62 | 0.76 |
In a system, equilibrium is a stage when the partial pressure or concentration of both reactant and product become constant or no further change in the partial pressure or concentration of reactant and as well as product takes place.
From the data, the partial pressure of reactant, A decreases from 0 s to 80 s and then become constant. In the same way, the partial pressure of product, B increases from 0 s to 90 s and then become constant. Therefore, at 80 s the concentration of both reactant and product become constant therefore, system will reach equilibrium at 80 s.
(b)
Interpretation:
The relation between the rate of forward reaction and that of the reverse reaction needs to determine after 30 s and after 90 s.
Concept introduction:
The rate of the forward reaction depends on the partial pressure of reactant and that of the reverse reaction depends on the partial pressure of the product. At equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of reverse reaction.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
After 30 s, the rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction and after 90 s, the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as follows:
The rate expression for the given system is represented as follows:
This is the rate of the forward reaction.
The same expression for the reverse reaction will be:
At equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction thus,
Also, at equilibrium the partial pressures of reactant and product are 0.62 atm and 0.76 atm respectively, putting the values,
Thus,
Or,
Thus, the expression for the reverse reaction will be:
Now, after 30 s the partial pressure of gas A is 0.72 atm thus, rate of forward reaction will be:
The partial pressure of gas B after 30 s is 0.56 atm thus, the rate of reverse reaction will be:
Dividing equation (1) and (2),
Thus, the rate of forward reaction is 2.12 times the rate of reverse reaction or rate of forward reaction is greater than that of the reverse reaction after 30 s.
Now, after 90 s the partial pressure of gas A is 0.62 atm thus, rate of forward reaction will be:
The partial pressure of gas B after 90 s is 0.76 atm thus, the rate of reverse reaction will be:
Dividing equation (1) and (2),
Thus, the rate of forward reaction is approximately equals to the reverse reaction after 90 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- Indicate the correct answer.a) In boranes, the B-B bonds are the most reactive.b) The B-H-B bonds are the reactive centers in the B2H6 molecule.arrow_forwardIn boranes, the B-B bonds are the most reactive.arrow_forwardThe B-H-B bonds are the reactive centers in the B2H6 molecule. Correct?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





