
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 1.2, Problem 1.30P
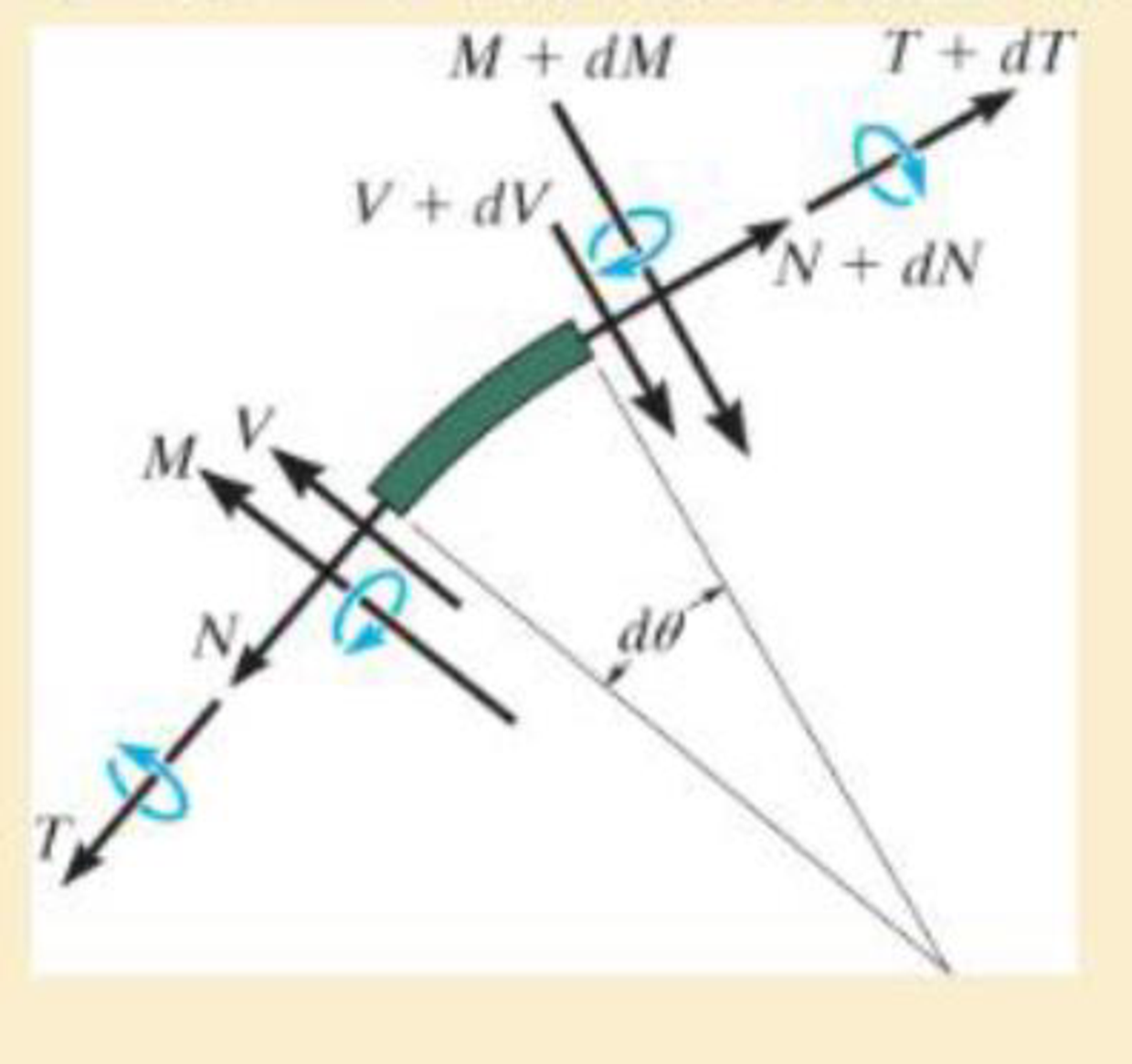
A differential element taken from a curved bar is shown in the figure. Show that dN/dθ = V, dV/dθ = −N, dM/dθ = −T, and dT/dθ = M.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A direct extrusion operation produces the cross section shown in Fig. (2) from an aluminum
billet whose diameter 160 mm and length - 700 mm. Determine the length of the extruded
section at the end of the operation if the die angle -14°
60
X
Fig. (2) Note: all dimensions in mm.
For hot rolling processes, show that the average strain rate can be given as:
=
(1+5)√RdIn(+1)
: +0
usão
العنوان
on
to
A vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm
long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500
rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2R. Take:
-9.81 mis
۲/۱
ostrar
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 1.2 - In each case, explain how to find the resultant...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal and shear...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...
Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The boom DF of the jib crane and the column DE...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The hand crank that is used in a press has the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The pipe has a mass of 12 kg/m. If it is fixed to...Ch. 1.2 - If the drill bit jams when the brace is subjected...Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod AD of radius r has a weight per...Ch. 1.2 - A differential element taken from a curved bar is...Ch. 1.5 - In each case, determine the largest internal shear...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest internal normal force in the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the internal normal force at section A...Ch. 1.5 - The lever is held to the fixed shaft using the pin...Ch. 1.5 - The single-V butt joint transmits the force of 5...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform beam is supported by two rods AB and...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - If the 600-kN force acts through the centroid of...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress at points A,...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in rod AB if...Ch. 1.5 - The supporting wheel on a scaffold is held in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest intensity w of the uniform...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area A and is...Ch. 1.5 - The small block has a thickness of 0.5 in. If the...Ch. 1.5 - If the material fails when the average normal...Ch. 1.5 - If the block is subjected to a centrally applied...Ch. 1.5 - The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress...Ch. 1.5 - The board is subjected to a tensile force of 200...Ch. 1.5 - The boom has a uniform weight of 600 lb and is...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin...Ch. 1.5 - If P=5 kN, determine the average shear stress in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads the...Ch. 1.5 - The column is made of concrete having a density of...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - If P = 15 kN, determine the average shear stress...Ch. 1.5 - The railcar docklight is supported by the...Ch. 1.5 - The plastic block is subjected to an axial...Ch. 1.5 - The two steel members are joined together using a...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The two members used in the construction of an...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The pier is made of material having a specific...Ch. 1.5 - Rods AB and BC have diameters of 4 mm and 6 mm,...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform bar, having a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the greatest constant angular velocity ...Ch. 1.5 - The radius of the pedestal is defined by r =...Ch. 1.7 - Rods AC and BC are used to suspend the 200-kg...Ch. 1.7 - If it is subjected to double shear, determine the...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If each of the three nails has a diameter of 4 mm...Ch. 1.7 - The strut is glued to the horizontal member at...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If the eyebolt is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - If the bar assembly is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - The pin is made of a material having a failure...Ch. 1.7 - If the bolt head and the supporting bracket are...Ch. 1.7 - Six nails are used to hold the hanger at A against...Ch. 1.7 - If A and B are both made of wood and are 38 in....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 1.70PCh. 1.7 - The connection is made using a bolt and nut and...Ch. 1.7 - The tension member is fastened together using two...Ch. 1.7 - The steel swivel bushing in the elevator control...Ch. 1.7 - The spring mechanism is used as a shock absorber...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the size of square bearing plates A and...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - The cotter is used to hold the two rods together....Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - The steel pipe is supported on the circular base...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The assembly consists of three disks A, B, and C...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods support the vertical force...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods AB and AC have diameters of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required minimum thickness t of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum allowable load P that can be...Ch. 1.7 - The compound wooden beam is connected together by...Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The rods AB and CD are made of steel. Determine...Ch. 1.7 - The aluminum bracket A is used to support the...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is...Ch. 1.7 - The bar is connected to the support using a pin...Ch. 1 - The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by...Ch. 1 - The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick...Ch. 1 - Determine the required thickness of member BC to...Ch. 1 - The circular punch B exerts a force of 2 kN on the...Ch. 1 - Determine the average punching shear stress the...Ch. 1 - The 150 mm by 150 mm block of aluminum supports a...Ch. 1 - The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a...Ch. 1 - The cable has a specific weight (weight/volume)...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- : +0 العنوان use only In conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D.-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process. онarrow_forwardIn non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forwardA vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forward
- In conventional drawing of a stainless steel wire, the original diameter D.-3mm, the area reduction at each die stand r-40%, and the proposed final diameter D₁-0.5mm, how many die stands are required to complete this process.arrow_forwardA vertical true centrifugal casting process is used to produce bushings that are 250 mm long and 200 mm in outside diameter. If the rotational speed during solidification is 500 rev/min, determine the inside radii at the top and bottom of the bushing if R-2Rb. Take: 8-9.81 m/sarrow_forwardIn non-continuous dieless drawing process for copper tube as shown in Fig. (1), take the following data: Do-20mm, to=3mm, D=12mm, ti/to=0.6 and vo-15mm/s. Calculate: (1) area reduction RA, (2) drawing velocity v. Knowing that: t₁: final thickness D₁ V. Fig. (1) Darrow_forward
- -6- 8 من 8 Mechanical vibration HW-prob-1 lecture 8 By: Lecturer Mohammed O. attea The 8-lb body is released from rest a distance xo to the right of the equilibrium position. Determine the displacement x as a function of time t, where t = 0 is the time of release. c=2.5 lb-sec/ft wwwww k-3 lb/in. 8 lb Prob. -2 Find the value of (c) if the system is critically damping. Prob-3 Find Meq and Ceq at point B, Drive eq. of motion for the system below. Ш H -7~ + 目 T T & T тт +arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forwardW PE 2 43 R² 80 + 10 + kr³ Ø8=0 +0 R²+J+ kr200 R² + J-) + k r² = 0 kr20 kr20 8+ W₁ = = 0 R²+1) R²+J+) 4 lec 8.pdf Mechanical vibration lecture 6 By: Lecturer Mohammed C. Attea HW1 (Energy method) Find equation of motion and natural frequency for the system shown in fig. by energy method. m. Jo 000 HW2// For the system Fig below find 1-F.B.D 2Eq.of motion 8 wn 4-0 (1) -5- marrow_forward
- The hose supplying the cylinder operating the bucket of a large excavator has fluid at 1000 psi flowing at 5 gpm. What is theavailable power in the line?arrow_forwardQ For the following plan of building foundation, Determine immediate settlement at points (A) and (B) knowing that: E,-25MPa, u=0.3, Depth of foundation (D) =1m, Depth of layer below base level of foundation (H)=10m. 3m 2m 100kPa A 2m 150kPa 5m 200kPa Barrow_forwardGiven the following data for crack rocker mechanism. If θ2 = 4π/3 and ω2 = 1 rad/s, Determine all possible values of ω4 and ω3 analytically. The lengths of links are a = 2, b = 8, c = 7 and d = 9 in cm.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY