
Concept explainers
Climate Control, Inc. makes expedition-quality rain gear for outdoor enthusiasts. Management prepared a
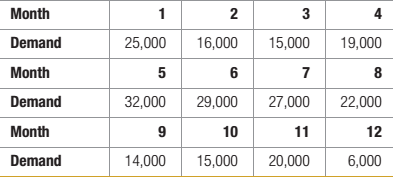
Use the Sales and Operations Planning with Spread sheets Solver in OM Explorer or develop your own spreadsheet models to address the following questions.
- Management is willing to authorize overtime in periods for which regular production and current levels of anticipation inventory do not satisfy demand. However, overtime must be strictly limited to no more than 20 percent of regular-time capacity. Management wants to avoid stockouts and backorders and is not willing to accept a plan that calls for shortages. Is it feasible to hold the workforce constant, assuming that overtime is only used in periods for which shortages would occur?
- Assume that management is not willing to authorize any overtime. Instead, management is will to negotiate with customers so that backorders may be used as a supply option. However, management is not willing to carry more than 5,000 suits from one month to the next in backorder. Is it feasible to hold the work-force constant, assuming that a maximum backorder of 5,000 suits may be maintained from month to month?
- Assume management is willing to authorize the use of overtime over the next 4 months to build additional anticipation inventory. However, overtime must be strictly limited to no more than 20 percent of regular-time capacity. Management wants to avoid stockouts and backorders and is not willing to accept a plan that calls for shortages. Is it feasible to hold the workforce constant, assuming that overtime is only used in months 1 through 4? If not, in which months would additional overtime be required?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN: DECISIONS & CASES (Mcgraw-hill Series Operations and Decision Sciences)
Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (12th Edition)
Business in Action (8th Edition)
- The opening backlog is 800 units. Forecast demand is as shown here. Calculate theweekly production for level production if the backlog is to be reduced to 100 units.arrow_forwardTax Prep Advisers, Inc., has forecasted the following staffingrequirements for tax preparation associates over the next12 months. Management would like three alternative staffingplans to be developed. The company currently has 10 associates. No more than 10new hires can be accommodated in any month because oflimited training facilities. No backorders are allowed, andovertime cannot exceed 25 percent of regular-time capacityon any month. There is no cost for unused overtime capac-ity. Regular-time wages are $1,500 per month, and overtimewages are 150 percent of regular-time wages. Undertime ispaid at the same rate as regular time. The hiring cost is $2,500per person, and the layoff cost is $2.000 per person.a. Prepare a staffing plan utilizing a level workforce strategy,minimizing undertime. The plan may call for a one-timeadjustment of the workforce before month 1.b. Using a chase strategy, prepare a plan that is consistent withthe constraint on hiring and minimizes use of overtime.c.…arrow_forwardDeforrest Marine Motors manufactures engines for the speedboat racing circuit. As part of their annual planning cycle, they forecasted demand for the next four quarters. The number of available days of production and the anticipated demand are given below. Employees Production Rate Production Cost Backorder Cost Overtime Cost Overtime Limit Demand Q1 2,400 6,019,000 They also estimated many of the costs required to conduct operations planning. Some of these key figures are listed below. 30 70 units/employee/quarter Q2 2,200 $1,000/unit $200/unit/quarter $1,500/unit <= 25% of Reg. Production Q3 1,700 Q4 1,800 Hire Cost Fire Cost Subcontracting Cost Subcontracting Limit Inventory Cost Initial Inventory $1,200/employee $800/employee $1,800/unit 400 units maximum $100/unit/quarter 280 units Deforrest Marine Motors wishes to maintain the current number of employees for the entire year to follow a level strategy balanced with inventory and backorders as needed. What is the total cost of this…arrow_forward
- 1. What factors should be considered when selecting the appropriate capacity cushion? Howdoes the choice of capacity cushion relate to other decisions in operations management?To other functional areas? 2. Capacity planning requires a demand forecast for an extended period of time into thefuture. What concerns would you have regarding an extended forecast as a capacityplanner?arrow_forwardDemand for the last four months was: July,20 units; August, 25 units; September, 34 units; October, 36 units. If the naive method was used to forecast the demand, what would MSE be for these months? O 5.33 O 17.34 O 1.25 O Correct answer is not provided. O 55arrow_forwardDetermine the total cost for this plan given the following forecast:Month 1 2 3 4 5 6Forecast 380 400 420 440 460 480Use steady regular output of 400 units per month, use overtime as needed for up to 40 units permonth, and use subcontracting to make up any needed output to match the forecast. Unit costs are:Regular output = $25Overtime = $40Subcontract = $60Average Balance Inventory = $15arrow_forward
- A company evaluate its hiring cost is RM150 per worker and layoff cost is RM200 per worker. Currently the company has 20 workers and based on forecast demand, the actual workers required to meet January demand is 25 workers. Calculate the hiring cost or layoff cost for that month. * O RM750 O RM350 O RM250 O RM1,000arrow_forwardIn reference to an Human Resource Management course 4th year college course at Malone University using the following textbook: Gomez-Mejia, L. R., Balkin, D. B., Cardy, R. L., & Carson, K. P. (2020). Managing human resources. (9th ed.). Boston: Pearson Education. Which one of the following functions is typically not a human resource management responsibility? a. Analysis and design of work b. Demand forecasting c. Performance management and development d. Exit interviewsarrow_forwardA company manufactures a product using two machine cells. Each cell has a design capacity of 250 units per day and an effective capacity of 230 units per day. At present, actual output averages 200 units per cell, but the manager estimates that productivity improvements soon will increase output to 225 units per day. Annual demand is currently 50,000 units. It is forecasted that within two years, annual demand will triple. How many cells should the company plan to produce to satisfy predicted demand under these conditions? Assume 240 workdays per year.arrow_forward
- What do you understand by capacity planning? Explain the decision tree modeling for capacity expansionarrow_forward1. Develop an aggregate plan for the following forecast Period 3 4 5 6 7 Total 1 2 8 Forecast 190 230 260 280 210 170 160 260 180 1,940 There are 20 workers who can produce 10 units per period at a cost of P6.00 per unit. There is no beginning invetory and the cost of carrying inventory is P5.00 per unit per period. Backlog cost is P10.00 per unit per period. Will the present workforce able to produce the forecast? b. What is the total cost of the plan? a.arrow_forwardProblem Answer ALL questions from this section. Write your answers on the supplied answer sheet. Show sufficient work. If necessary, round intermediate calculations and final answers to three decimal places. J 1. The manager of a crew that installs carpeting has tracked the crew's output over the past several we eks, obtaining these figures: Week 10 20 30 43 50 6 Crew Size تمه 30 45 Yards Installed 96- 72- 92- 50, 699 52- 20 39 2₂ Compute the labor productivity for each of the weeks. On the basis of your calculations, what can you conclude about crew size and productivity?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
