
Concept explainers
Draw one valid Lewis structure for each compound. Assume the atoms are arranged as drawn.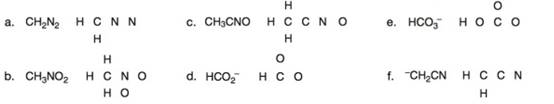
(a)
Interpretation: A valid Lewis structure for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms present in a molecule is represented by the Lewis structure of that molecule. The electron pairs in the molecule are considered to be delocalized.
Answer to Problem 1.43P
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is,
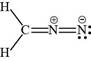
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
![]()
Figure 1
The valence electrons are counted as,
The bonds and lone pairs are added in the given arrangement of atoms. The valid Lewis structure is,

Figure 2
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation: A valid Lewis structure for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms present in a molecule is represented by the Lewis structure of that molecule. The electron pairs in the molecule are considered to be delocalized.
Answer to Problem 1.43P
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is,
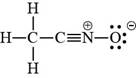
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
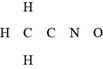
Figure 3
The valence electrons are counted as,
The bonds and lone pairs are added in the given arrangement of atoms. The valid Lewis structure is,

Figure 4
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation: A valid Lewis structure for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms present in a molecule is represented by the Lewis structure of that molecule. The electron pairs in the molecule are considered to be delocalized.
Answer to Problem 1.43P
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is,
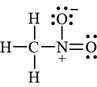
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
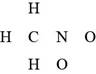
Figure 5
The valence electrons are counted as,
The bonds and lone pairs are added in the given arrangement of atoms. The valid Lewis structure is,
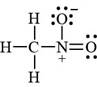
Figure 6
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation: A valid Lewis structure for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms present in a molecule is represented by the Lewis structure of that molecule. The electron pairs in the molecule are considered to be delocalized.
Answer to Problem 1.43P
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is,
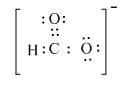
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
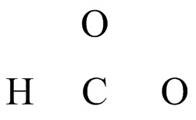
Figure 7
The valence electrons are counted as,
The bonds and lone pairs are added in the given arrangement of atoms. The valid Lewis structure is,
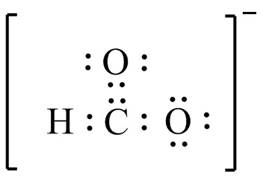
Figure 8
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation: A valid Lewis structure for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms present in a molecule is represented by the Lewis structure of that molecule. The electron pairs in the molecule are considered to be delocalized.
Answer to Problem 1.43P
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is,
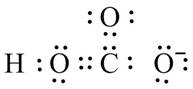
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
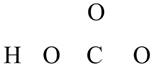
Figure 9
The valence electrons are counted as,
The bonds and lone pairs are added in the given arrangement of atoms. The valid Lewis structure is,
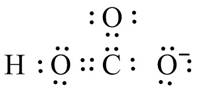
Figure 10
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is shown in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation: A valid Lewis structure for the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms present in a molecule is represented by the Lewis structure of that molecule. The electron pairs in the molecule are considered to be delocalized.
Answer to Problem 1.43P
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is,
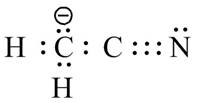
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
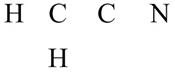
Figure 11
The valence electrons are counted as,
The bonds and lone pairs are added in the given arrangement of atoms. The valid Lewis structure is,
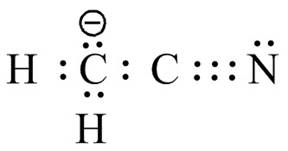
Figure 12
The valid Lewis structure for the given compound is shown in Figure 12.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please don't use Ai solutionarrow_forwardUse the periodic table below to answer the question that follows. The Periodic Table of Elements 2 1 Nonmetals Noble Gases H 1.008 Hydrogen 4 11 19 6.94 Lithium Na 22.990 Sodium Be 9.012 Beryllium 12 Mg 24.305 Magnesium 20 Ca 40.08 Calcium 21 Sc 44.956 Scandium Transition Metals Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Lanthanides Actinides 22 Ti 47.867 Titanium 23 V 50.942 Vanadium Post-Transition Metals Metalloids 40 Zr 91.224 Zirconium 88.906 Yttrium 57-71 72 K 39.098 Potassium 37 Rb 85.468 Rubidium 55 87 Cs 132.905 Cesium Fr 223.020 Francium 38 39 Sr 87.62 Strontium 56 88 Ba 137.328 Barium Ra 226.025 Radium Hf 178.49 Hafnium 89-103 104 Rf [261] Rutherfordium 41 Nb 92.906 Niobium 73 Ta 180.948 Tantalum 105 Db 24 Halogens Cr 51.996 Chromium 42 25 Mn 54.938 Manganese 43 TC Mo 95.95 Molybdenum Technetium 98.907 26 44 Fe 55.845 Iron Ru 101.07 Ruthenium 74 75 76 W Re 183.84 Tungsten 106 Sg 186.207 Rhenium 107 Bh 27 45 Co 58.933 Cobalt Rh 102.906 Rhodium 28 46 Ni 58.693 Nickel Pd 106.42…arrow_forwardUse the periodic table below to answer the question that follows. The Periodic Table of Elements 1 5 13 B 10.811 Boron Al 26.982 Aluminum 31 49 Ga 69.723 Gallium 26 Fe 55.845 Iron Ru 101.07 Ruthenium Os 192.217 Osmium Hs 27 45 Co 58.933 Cobalt Rh 102.906 Rhodium 77 Ir 192.217 Iridium 109 Mt 28 46 Ni 58.693 Nickel Pd 106.42 Palladium 78 Pt 195.085 Platinum 110 29 47 79 30 Cu Zn 63.546 Copper Ag 107.868 Silver Au 196.967 Gold 48 65.38 Zinc Cd 112.411 Cadmium 80 Hg 81 114.818 Indium Tl 6 14 32 C 12.011 Carbon Si 28.086 Silicon Ge 72.631 Germanium 50 Sn 118.711 Tin 7 8 9 N FL 14.007 Nitrogen 15.999 Oxygen 18.998 Fluorine 16 17 15 30.974 Phosphorus 33 51 As 74.922 Arsenic Sb 121.760 Antimony Bi 34 32.066 Sulfur Se 78.972 Selenium 52 Te 127.6 Tellurium 84 Po [208.982] Polonium 35.453 Chlorine 35 53 85 Br 79.904 Bromine 126.904 lodine At 209.987 Astatine 10 18 He 4.003 Helium Ne 20.180 Neon 36 54 86 Ar 39.948 Argon Kr 84.798 Krypton Xe 131.294 Xenon Rn 222.018 82 83 Pb 200.592 Mercury 204.383…arrow_forward
- m Given that the freezing point of water is 0.0 °C at 1 atm and the freezing point depression constant is 1.86, what is the freezing point of a 0.05 m solution of a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte solute in water? • Your answer should have one significant figure. Provide your answer below: degrees Carrow_forwardmol Malate dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate with a standard Gibbs free energy of AG° = +29.7*. What is the equilibrium constant (Keq) for this reaction at 298 K and pH 7? Under physiological conditions at 310 K and pH 7, this reaction is at equilibrium. In the mitochondrial matrix, the ratio NAD+/NADH is 8 and the concentration of malate is 1.0 mM. What is the concentration of oxaloacetate? Malate dehydrogenase is also present in the cytoplasm where the ratio NAD+/NADH is 700 and malate concentration is 1.0 mM. If this reaction is at equilibrium at 310 K and pH 7, what is the cytosolic concentration of oxaloacetate? malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+arrow_forwardI don't want answer from com AI. No chat gpt ok only sure experts solve it correct complete solutions ok not guidelines okk. Question: Explain the trends in Figure 19.1 and what the f-orbitals got to do with the trends.arrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forward1. Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat several bacterial infections. Bacampicillin is a derivative of ampicillin (a prodrug) that enhances the oral bioavailability of the parent antibiotics. In the body, Bacampicillin decomposes to release Ampicillin and side products. Provide a mechanism for the following reaction. For simplicity, replace the core structure with R. NH2 Bacampicillin N NH2 S H3O+ Ampicillin OH Η CO2 Ηarrow_forward
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





