
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
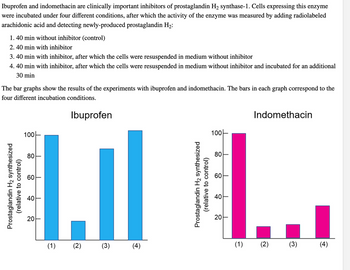
Transcribed Image Text:**Ibuprofen and Indomethacin as Inhibitors of Prostaglandin H₂ Synthase-1: Experimental Analysis**
Ibuprofen and indomethacin are clinically important inhibitors of the enzyme prostaglandin H₂ synthase-1. In this study, cells expressing this enzyme were incubated under four different conditions. The activity level of the enzyme was subsequently measured by adding radiolabeled arachidonic acid and detecting newly-produced prostaglandin H₂. The incubation conditions were as follows:
1. 40 minutes without inhibitor (control).
2. 40 minutes with the inhibitor.
3. 40 minutes with the inhibitor, followed by resuspension in a medium without the inhibitor.
4. 40 minutes with the inhibitor, resuspension in a medium without the inhibitor, followed by an additional 30 minutes of incubation.
**Graphical Analysis:**
*Ibuprofen:*
- The bar graph depicts the results for ibuprofen across the four incubation conditions.
- Condition 1 (control) shows a high level of prostaglandin H₂ synthesis, set as 100% relative to the control.
- Condition 2 exhibits a significant drop in synthesis activity, indicating effective inhibition.
- In condition 3, the synthesis recovers to nearly the same level as the control after resuspension without the inhibitor.
- Condition 4 shows restored synthesis similar to or slightly higher than the control.
*Indomethacin:*
- Similarly, the bar graph for indomethacin reflects synthesis across the four conditions.
- Condition 1 maintains a high synthesis rate (100%), like the control.
- Condition 2 demonstrates a marked decrease in enzyme activity, confirming inhibition by indomethacin.
- Conditions 3 and 4 result in low activity, indicating less recovery of synthesis upon resuspension, compared to ibuprofen.
These graphs illustrate the varying efficacy and reversibility of inhibition by ibuprofen and indomethacin under different experimental conditions.
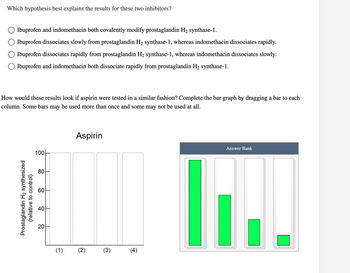
Transcribed Image Text:**Question:**
Which hypothesis best explains the results for these two inhibitors?
- ( ) Ibuprofen and indomethacin both covalently modify prostaglandin H₂ synthase-1.
- ( ) Ibuprofen dissociates slowly from prostaglandin H₂ synthase-1, whereas indomethacin dissociates rapidly.
- ( ) Ibuprofen dissociates rapidly from prostaglandin H₂ synthase-1, whereas indomethacin dissociates slowly.
- ( ) Ibuprofen and indomethacin both dissociate rapidly from prostaglandin H₂ synthase-1.
**Activity:**
How would these results look if aspirin were tested in a similar fashion? Complete the bar graph by dragging a bar to each column. Some bars may be used more than once and some may not be used at all.
**Graph Explanation:**
The bar graph is titled "Aspirin" and measures "Prostaglandin H₂ synthesized (relative to control)" on the vertical axis, with values labeled at intervals: 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100. The horizontal axis features four columns numbered (1), (2), (3), and (4).
To the right, there is an "Answer Bank" consisting of four green bars of varying heights:
1. Tall bar reaching 100.
2. Medium bar reaching about 40.
3. Short bar reaching about 20.
4. Very short bar reaching about 10.
Participants are tasked with placing the bars from the "Answer Bank" into the corresponding numbered columns in a way that reflects potential results for aspirin under similar test conditions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A contributing factor to the development of arthritis is the inappropriate proteolytic destruction of the aggrecan component of cartilage by the proteolytic enzyme aggrecanase. The immune system signal molecule interleukin 2 (IL-2) activates aggrecanase; in fact, IL-2 blockers are sometimes used to treat arthritis. Studies were undertaken to determine whether inhibitors of aggrecanase could counteract the effects of IL-2. Pieces of cartilage were incubated in media with various additions and the amount of aggrecan destruction was measured as a function of time. Aggrecan degradation was measured by the release of glycosaminoglycan. What is the rationale for this assay? Aggrecan is a transferase enzyme that adds glycosaminoglycans to glycoproteins, and these glycosaminoglycans remain free if aggrecan is degraded. Aggrecan is a lectin that binds glycosaminoglycan ligands, and aggrecan releases these glycosaminoglycans as it is degraded. Aggrecan inhibits the removal of glycosaminoglycans…arrow_forwardShown below is a substrate for a Trypsin. Draw the mechanism for this serine protease using the artificial substrate. Be sure to draw the catalytic triad, and show the role of the oxyanion hole. Draw the complete structure of every intermediate and product and PUSH ARROWS!!!!! Do not abbreviate structures using R and R' H₂N _N_CH. сно CH₂ CH₂ CH₂ NH d=19H₂ NH₂ O CH- H₂C HN O CHarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements inaccurately describes glutamate dehydrogenase? Glutamate dehydrogenase uses either NAD+ or NADP+ in a redox reaction Glutamate dehydrogenase catalyzes an oxidative deamination reaction Glutamate dehydrogenase equilibrium lies with the reductive amination of glutamate Glutamate dehydrogenase utilizes hydrolysis to release ammonium from an imine intermediatearrow_forward
- UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes bind the organic compound UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GA) in order to catalyse the transfer of a glucuronic acid group from UDP-GA to a drug molecule, releasing UDP from the active site as a product. UDP is then regenerated by the activity of another enzyme. What terms could be used to describe UDP-GA?arrow_forwardThe phosphorylation and oxidative decarboxylation of oxaloacetate by inorganic phosphate (Pi) to make phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide is endergonic under intracellular conditions. It is characterized by this equation: Oxaloacetate + Pi ←→ Phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O + CO2 ΔG’ = +24.6 kJ/mol The synthesis of GTP from GDP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) in solution is endergonic under intracellular conditions, and it is characterized by this equation: GDP + Pi ←→ GTP + H2O ΔG’ = +30.5 kJ/mol Write a new net thermodynamically coupled reaction equation that describes the synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate from oxaloacetate using the hydrolysis of GTP to power the reaction and calculate the new net ΔG’ of this reaction. Show all of your work.arrow_forward5arrow_forward
- The degradation of CH3 (CH₂ )10 - COOH via the beta-oxidation pathway requires: 6FAD + 6NAD+ + 5C0A-SH + 6H₂O 5FAD + 5NAD+ + 6C0A-SH+ 5H₂O 5FAD + 5NAD + 5C0A-SH + 5H₂0 6FAD + 6NAD+ + 6C0A-SH + 6H₂Oarrow_forwardAnswer the question belowarrow_forward1.Substituents exhibit strong steric repulsion at the GABAA receptor ?what does it means?? 2. Substitutions at C-6, C-8, and C-9 lower the activity?where is C-6, C-8, and C-9 ?can anyone help to lable out?arrow_forward
- Order the cofactors based on their use in the mechanism of the a-etogluterate dehydrogenase complex. 1. Stabilizes a carbanion due to decarboxylation 2. Allows for the splitting of the carbon skeleton from the electron pair generated in a redox reaction 3. Enzyme bond electron carrier that is part of dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase 4. Final electron acceptor in the overall reaction catalyzed by this complex 1 2 3 4 answer choices: lipoamide, biotin, 2 Fe - 2S cluster, TPP, NAD+, FADarrow_forwardThe following diagram shows reaction curves for aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) with carbamoylphosphate and different concentrations of aspartate, in the absence of ATP (curve 1) and presence of ATP (curve 2). What do the shapes of the curves tell us about the ATCase enzyme? 2 جر [aspartate] It binds substrate through a sequential mechanism. It binds substte cooperatively. It obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics. It binds substrate through a concerted mechanism.arrow_forwardFor the following enzymes (3-6) predict how the conditions will most likely affect the enzymes activity with one of the following and provide a 1 sentence explanation: a. increase activity b. decrease activity c. not likely to alter activity 3) alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex binding to AMP when [AMP] is high. 4) phosphohexose isomerase binding NADH when [NADH] is high 5) phosphofructose-1 binding NAD+ when [NAD+] is high 6) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex binding to ATP when [ATP] is higharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON