
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:3. The table on the last page compares for each of four different proteolytic enzymes the
chemical bonding structure of a classical substrate with the structures of two competitive
inhibitors. For each substrate structure an arrow indicates the position of the scissile bond,
i.e., the bond that is cleaved through catalytic action. For each enzyme, one of the inhibitors
is a classical competitive inhibitor while the other is a transition-state inhibitor analog. While
ordinary competitive inhibitors are associated with (dissociation) inhibitor equilibrium con-
stants of ~10-3 to 10-6 M, transition-state analogs exhibit inhibitor constants ≤ 10-⁹ M.
(a)
For each enzyme draw a circle around those parts of the substrate that account
for specificity of substrate recognition.
(b)
For each enzyme identify the transition-state inhibitor analog by drawing a circle
around it and give a brief explanation of why it mimics the structure of the transition-state
species.
(c)
Draw a "generic" Lineweaver-Burk plot that would apply to each enzyme in which
there are only three straight lines that separately represent (1) initial velocity data in the
absence of an inhibitor, (2) initial velocity data in the presence of the classical competitive
inhibitor, and (3) initial velocity data in the presence of the transition-state inhibitor analog.
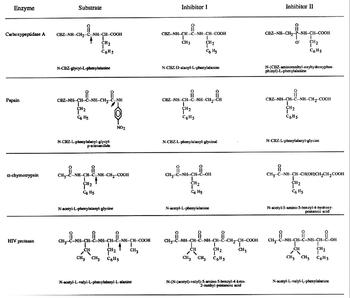
Transcribed Image Text:Enzyme
Carboxypeptidase A
Papain
α-chymotrypsin
HIV protease
Substrate
CBZ-NH-CH,-C--NH-CH-COOH
N-CBZ-glycyl-L-phenylalanine
CH₂
T
C6H5
i
CBZ-NH-CH--C-NH-CH, CẠNH
NHI NH
CH₂
C6 Hz
N-CBZ-L-phenylalanyl-glycyl-
CH₂-
p-nitroanilide
i
CH,-C-NH-CH-C-NH-CH2-COOH
1
CH2
C6 H5
NO2
N-acetyl-L-phenylalanyl-glycine
CHO LINH CHÍNH CH
-NH--
1
CH
CH₂
CH3 CH3 C6H5
NH-CH-C-NH-CH-COOH
I
CH3
N-acetyl-L-valyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-alanine
Inhibitor I
CBZ-NH-CH-C-NH-CH-COOH
CH3
N-CBZ-D-alanyl-L-phenylalanine
CH3-C
i
CBZ-NH-CH-C--NH-CH,CH
1-C₁₂-1
T
CH₂
C Hs
T
CH₂
C6H5
N-CBZ-L-phenylalanyl-glycinal
ů
NH--CH--C--OH
CH₂
C6H5
N-acetyl-L-phenylalanine
CH,--C--NH-CH-C-NH-CH-C-CH2-CH-COOH
CH
CH2
CH3 CH3 C6H5
CH 3
N-(N-(acetyl)-valyl)-5-amino-5-benzyl-4-keto-
2-methyl-pentanoic acid
CBZ--NH-CH₂--P--NH-CH--COOH
O
Inhibitor II
N-(CBZ-aminomethyl-oxyhydroxyphos-
phinyl)-L-phenylalanine
i
CBZ--NH--CH--C--NH-CH2-COOH
8
1
CH2
C6H5
CH 2
C6H5
N-CBZ-L-phenylalanyl-glycine
요
CH3--C--NH--CH--CH(OH)CH₂CH₂COOH
CH2
C6H5
N-acetyl-5-amino-5-benzyl-4-hydroxy-
pentanoic acid
요
CH,--C--NH--CH--C-NH--CH--C--OH
CH
CH
11E0
CH₂
CH3 CH3 C6H5
N-acetyl-L-valyl-L-phenylalanine
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
For answer (a) regarding the last row of compounds, why is the -CH-(CH3)2 not also responsible for the substrate specificity given it is also identical across the substrate and the inhibitors?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
For answer (a) regarding the last row of compounds, why is the -CH-(CH3)2 not also responsible for the substrate specificity given it is also identical across the substrate and the inhibitors?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 40. Which of the following statements about transition state analog inhibitors are true? MARK ALL THAT APPLY. Group of answer choices Provide insight into catalytic mechanisms. Very potent and specific inhibitors. They have difficulty binding to the active site because they resemble the energetically unstable transition state of the substrate. Can be used as immunogens to generate catalytic antibodies.arrow_forwardi am so confused with this onearrow_forward1E. Please help me in detailarrow_forward
- I am a bit confused about this PPT slide explanation. Why would a high energy transition state be favored when it requires more activation energy in an enzyme-substrate binding scenario?arrow_forward24. Consider the figure below, which is an alternate way to depict the energy changes occurring during a reaction from Substrate (S) to Product (P), when uncatalyzed (curve A) and when catalyzed by an enzyme (curve B). Note that curve B is not the same way we modeled an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in class; this model is a different, perhaps slightly more realistic, way of conceptualizing the energy changes over the course of a reaction than what we did in class. S and ES represent the transition states for reaction of the free substrate (S) or the enzyme-substrate complex (ES). T T activation energy for uncatalyzed reaction EST S edhosob nohtum od bluo woH abiow yedio 2 wwolaixa-y odi no vaigin oroda dapng odt ni o nfog) r gibadhoa P B ES EP progress of reaction activation energy for catalyzed reaction a) Explain briefly why, in curve B, the energy state of the enzyme-substrate complex is less than the energy state of the substrate alone. b) Suppose the enzyme in the diagram was mutated…arrow_forward1. Provide the best coenzyme(s) for each step shown below. Give a 1–2 sentence rationale for your choice. 2. Reaction (C) can require multiple coenzymes, or the enzyme may only require one. Briefly describe how the reaction that uses only one coenzyme works. Be specific about the mechanism.arrow_forward
- 1. For enzymatic reaction, a mechanism was proposed by Michaelis and Menten as follows: ES k, and k,' ES à E and P k,. E + S a. Use steady state assumption, derive expression for the reaction rate. Where E is concentration of enzyme, S substrate, ES complex of E and S, E = E, – ES. (If you have difficulty in doing it, please consult lecture note) b. Assume K = 0.038 mol.L' at 25 °C, when the substrate concentration is 0.156 Mol.L', the rate of the reaction is 1.21 m mol/L.s. The maximum rate of conversion reaction is reached at high substrate concentrations. Calculate the maximum rate of this enzyme catalyzed reaction.arrow_forward1. If a molecule is interating with its side chains of an enzymes active site but it is not the substrate of the enzyme what kind of enzyme regulation is this? 2. What is the change in thetype of bond between Ser 80 -> Arg. 3. Will this change cause the complex to be more or less stable. Explainarrow_forward6. Examine the plot of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction below: Wheat-germ acid phosphatase shows Michaelis-Menten kinetics when acting on para-nitrophenol phosphate 16 14 12 10 8 4 2 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 (S] / mM a) Is this reaction better characterized by Michaelis-Menten kinetics or simple mass action? b) What is the approximate value of Vmax? Km? c) Assuming that this plot was made at 100 nM enzyme, draw the curve, including axis labels, for 300 nM enzyme. d) Imagine that this enzyme is inhibited by a competitive inhibitor with Ki (for inhibitor) = Km (for substrate). Note that v = (kcat [E] tot [S]/Km) / (1 + [S]/Km + [I]/Ki). Draw the curve of reaction velocity (v) versus [S] for [I] = 1 mM. e) Now consider an experiment where you simultaneously introduce substrate and competitive inhibitor at equal concentrations. Make a plot of v versus concentration of [S] = [I], i.e. the X-axis should be the concentration of both I and S, which are equal. v/ uM min-arrow_forward
- 1. - - Substrate Enzyme - 1 2 3 BOO - Look at the above diagram and understand what is being shown. Explain AND draw a graph depicting how the rate of the reaction depicted here is changing. ☐ L 2. How will the rate of the reaction change with time after 3? How can we increase the rate of the reaction after 3? I 100 B Larrow_forward7. An enzyme-catalyzed reaction proceeds by the mechanism below: E+S1ES --2E+P E+A 3 EA EA+S4→ EAS --5→ EA + P E+I6 → EI EAS +17→ EAIS -8 EIS + P A. B. C. E = enzyme, S = substrate, I = inhibitor, P = product and A = activator Rate constants (k's) for the forward reactions are: K1, K2, k3, K4, k5, k6, k7, and k8 Rate constants (k's) for the reverse reactions are: k-1, k-3, K.4, k.6, and k.7 Write the enzyme balance for this mechanism. How many total equations will result from applying the RAPID EQUILIBRIUM ASSUMPTION? Using any concentrations of species in the mechanism and any of the rate constants (k's), write ONE of the equations that would result from applying the QUASI STEADY STATE ASSUMPTION. (ONLY ONE EQUATION; ANY OF THEM ARE FINE)arrow_forward1. The enzyme you are studying uses the substrate pictured at right. An inhibitor box in the freezer contains two tubes labeled Inhibitor #1 and Inhibitor #2, along with the structures of the compounds contained within them and their respective Ki. Which one is more likely to be the non-competitive inhibitor? Inhibitor #1 K₁ = 10 μM m CH₂OH OH -0, $ OH OH Inhibitor #2 K₁ = 50 μM Briefly Justify: OH CH₂OH OH OH OH Substratearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON