
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
a. Determine the principal stresses at point A on the cross section of the wrench at section a-a. Also Specify the orientation for this state of stress.
b. Determine maximum in-plane shear stress at point A on the cross section of the wrench at section a-a. Also Specify the orientation for this state of stress.
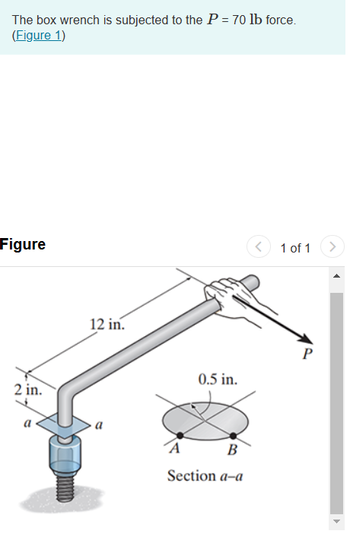
Transcribed Image Text:The box wrench is subjected to the P = 70 lb force.
(Figure 1)
Figure
2 in.
12 in.
0.5 in.
B
Section a-a
<
1 of 1
P
>
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. State of efforts in the coordinate axis marked in the problem. 2. Principal maximum and minimum forces and maximum shear force in the plane. 3. Angle at which the principal stresses meet. 4. Drawing of Mohr's circle, marking the line that corresponds to the stress state of point 1.arrow_forwardIn each case, the state of stress sx, sy, txy produces normal and shear stress components along section AB of the element that have values of sx = -5 kPa and tx y = 8 kPa when calculated using the stress transformation equations.Establish the x and y axes for each segment and specify the angle u, then show these results acting on each segment.arrow_forwardThe solid rod is subjected to the loading shown. Determine the state of stress at point B, and show the results on a differential volume element at this point.arrow_forward
- only HANDWRITTEN answer needed ( NOT TYPED)arrow_forward1. The box beam is subjected to the loading shown. Determine the principal stresses in the beam at point A. 6 in. 800 lb AH 6 in. 8 in. '8 in. A -3 ft--2.5 1200 lb +-2.5 ft---2.5 ft-|- -5 ft-arrow_forwardanswer letters D, E, and F onlyarrow_forward
- draw fbd and show solutionarrow_forward2) A 150 lb horizontal force, P, is applied to end D of handle ABD in the direction shown. Section AB has a diameter of 1.2 in. a. Determine the stress state at point H (H has sides parallel to the x and y axes). b. Draw a Mohr's circle representation for the point. What are the principal stresses at point H. 10 in. 4 in. y B 18 in. 1.2 in. P xarrow_forwardThe following shaft consists of a tube AB and a solid rod BC. The tube has an inner diameter of 25 mm and an outer diameter of 30 mm. The rod has a diameter of 15 mm. Determine the average normal stress at point D. The average normal stress at point D isarrow_forward
- 5. Two forces act on the solid circular rod (r=.005 m) as shown. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal stresses and the absolute maximum in plane shear stress at point A. 100 mm 150 mm 500 N V 300 N -•64- o (M Pa) 6.l12 -64 T (MPa) Taug = 6.l12 R=Vo2037+ 3.0562 =3.062 M Pa O; = R+ Jarg; 0,=60119MPQ t 3.0 0056 M Pa T,= Oava - R; 2 0068 MPaa Therefore Tabs =R= 3.062MPaa maxarrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress The solid 1.35-in.-diameter rod is subjected to a uniform axial distributed loading along its length of w =775 lb/ft. Two concentrated loads also act on the rod: P= 2500 lb and Q = 800 lb. Assume a = 11 in. and b = 22 in. Determine the normal stress in the rod at the following locations: (a) x = 7 in. (b) x = 21 in. w a Answer: Ox=7in. = i psi Ox=21in. i psiarrow_forwardDetermine the principal stresses in the beam at point A. Specify the orientation of the element representing the principal stresses. 150 kN 60 kN 50 mm A A [150 150 mm 60 mm 0.5 m -0.25 m-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY