
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
What is the likely function of the cytosolic cAMP in this transduction pathway?
Question 16 options:
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Transcribed Image Text:H
H₁ H
ATP synthase
UCP1
Beta-3 adrenergic receptor-
H₁
H₁
H
Cytosol
H' H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Mitochondria
inner-membrane
-Norepinephrine
G-protein
Fatty acids
Mitochondria
outer-membrane
CAMP
Protein
kinase A
Lipase
ATP
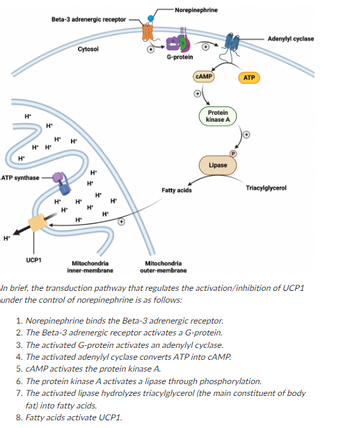
1. Norepinephrine binds the Beta-3 adrenergic receptor.
2. The Beta-3 adrenergic receptor activates a G-protein.
3. The activated G-protein activates an adenylyl cyclase.
4. The activated adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into CAMP.
5. CAMP activates the protein kinase A.
Adenylyl cyclase
Triacylglycerol
In brief, the transduction pathway that regulates the activation/inhibition of UCP1
under the control of norepinephrine is as follows:
6. The protein kinase A activates a lipase through phosphorylation.
7. The activated lipase hydrolyzes triacylglycerol (the main constituent of body
fat) into fatty acids.
8. Fatty acids activate UCP1.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How are H^3 peptides used to study intracellular pathways?arrow_forwardResearchers use a technique call RNA interference to knock down (i.e. not completely gone) the Bcl-2 gene in the amygdala of lab animals. What cellular response would you expect to occur? Question 1 options: A) An increase in apoptosis; many cells in the area would die B) An increase in axon regrowth after injury C) A decrease in cytochrome c levels released from the mitochondria D) A decrease in glial cell infiltration after injuryarrow_forwardATR is a protein kinase that is activated by double stranded DNA breaks. a) True Ob) Falsearrow_forward
- When regulatory protein binds to a mature mRNA in the cytoplasm and prevents it from binding to a ribosome, this is an example of: A) transcriptional control B) post-transcriptional control C) post-translational control D) epigenetic control E) translational controlarrow_forwardCytopathic effects (CPE) are visible changes in cells due to: A)viral infection B)mutations C)bacterial infections D)the cell's genes are being expressedarrow_forwardWhy do Receptor Tyrosine Kinases have to form a dimer?arrow_forward
- a) b) d) You, a Jojo's Bizzare Adventures fan, hear about the upcoming part 6 as an anime. You get very excited to the point where your heart just stops beating and you almost die. You are taken into the hospital and the doctor tells you that Ca2+ is not being released intracellularly, causing your heart to stop contracting. This may be due to which protein? Adenylyl Cyclase Intracellular Docking protein Protein Kinase A Phospholipase Carrow_forwardWhat are the two components that give their nameto the signal transduction system in prokaryotic cells?What is the function of each of the components?arrow_forwardAnswer these two multiple choice questionsarrow_forward
- What event is common to ALL signal transduction pathways? A) Calcium ions bind to/ activate proteins. B) Cyclic nucleotides are formed. C) Proteins change in shape. D) Phosphates are transferred between molecules. E) Protons are transferred between molecules.arrow_forwardHow does the loss of the Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) protein lead to the deregulation of Beta-catenin functions in FAP patients?arrow_forwardSome cancer researchers have proposed using a-amanitin in cancer therapy. How might a-amanitin be used in the treatment of cancer?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education