
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Three blocks A, B, and C stand next to each other as shown in the figure. A force F is applied to push block C directly and sends the blocks accelerating to the right with acceleration of 10 m/s2. Let's assume there is no friction between the blocks and the ground. The mass of A, B, and C are 12.300, 89.200, and 154.100 kg, respectively. What is the force applied on block C by block B (in unit of N)?
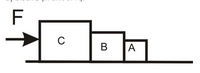
Transcribed Image Text:F
C
В
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In Figure 1, we depict two boxes and an applied force of magnitude 100.0N. The horizontal floor is frictionless, and box A is more massive thanbox B. Which of the following is correct? (Before you answer this question, draw FBDs and sum forces.)a. Box A pushes on box B with a force of 100 N, and box B pusheson box A with a force of 100 N.b. Box A pushes on box B harder than box B pushes on box A.c. Boxes A and B push on each other with equal forces of less than 100.0N.d. The boxes will not begin to move unless the total weight of the twoboxes is less than 100.0 N.arrow_forwardBoxes A and B are connected to each end of a light vertical rope, as shown in the following figure. A constant upward force 80.0 N is applied to box A. Starting from rest, box B descends 11.5 m in 4.50 s. The tension in the rope connecting the two boxes is 32.0 N (Figure 1). Figure F A B 1 of 1 Part A What is the mass of box B? Express your answer with the appropriate units. MB = Submit Part B mA = Submit μA Provide Feedback Value Request Answer What is the mass of box A? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μA Value → Request Answer Units Units ? ?arrow_forwardThe horizontal wire shown on the right in the figure below will break when the tension in it exceeds the value Tmax. What is the maximum mass M that the hanging object can have without the horizontal wire breaking? (Assume the wire on the left does not break prior to the horizontal wire breaking.) a Tmax/g sinθ b Tmax/g c Tmax/g tanθ d Tmax tanθ/g e Tmax/g cosθarrow_forward
- Block A in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 5.00 kg, and block B has mass 15.0 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the horizontal surface is 0.30. Part A What is the mass of block C if block B is moving to the right and speeding up with an acceleration 2.70 m/s²? Express your answer in kilograms. Figure B с A mc= ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part B kg What is the tension in each cord when block B has this acceleration? Express your answer in newtons. TAB ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining 1 of 1 Part C Express your answer in newtons. TBC = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback N Narrow_forwardTwo identical 20.0-kg balls, each 25.3 cm in diameter, are suspended by two 35.0-cm wires as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The entire apparatus is supported by a single 18.0-cm wire, and the surfaces of the balls are perfectly smooth. Find the tension in the top wire. Find the tension in each of two bottom wires.arrow_forwardA push and a pull of magnitude F1=3.9 N and F2=5.8 N act on a block of weight 11 N resting and not moving on a rough surface as shown in the figure linked below. The push F1 is horizontal, while the pull F2 acts at angle θ=46 deg with the horizontal How large is the friction force exerted by the surface on the block?arrow_forward
- A block resting on a plane inclined at an angle 36o from the horizontal is being held in place by steel cables a, b, and c as shown in the figure below. The tension in cable b is 75.0 N. Note that cable a is parallel to the surface of the incline and that cable b is perfectly horizontal. a. determine the normal force N and the force due to gravity ??.b. What is the mass of the block in kilograms?arrow_forwardA 2004 Prius with a 150-lb driver and no passengers weighs 3071 lb. The car is initially at rest. Starting at t = 0, a net horizontal force Fx(t) in the +x direction is applied to the car. The force as a function of time is given in (Figure 1). The horizontal parts on the graph correspond to 7500 N and 3500 N. For the time interval t = 0 to t = 4.50 s, what is the impulse applied to the car? What is the speed of the car at t = 4.50 s? At t = 4.50 s, the 3500-N net force is replaced by a constant net braking force Bx = -5240 N . Once the braking force is first applied, how long does it take the car to stop? How much work must be done on the car by the braking force to stop the car? What distance does the car travel from the time the braking force is first applied until the car stops?arrow_forwardA man is attempting to lift a crate using a two part pulley system as shown in the image. The crate has mass m2 = 53 kg, and the man has m1 = 75 kg. He pulls downward on the rope with a force of magnitude F = 659 N. The pulleys are massless and frictionless. 1.) what is the magnitude of the tension force T in newtons? 2.) what is the blocks acceleration in m/s^2?arrow_forward
- A block is pushed up a ramp and is observed to accelerate up the block as is shown in the figure below. The friction coefficient between the block and the ramp is mu. Write an expression for the acceleration of the block in terms of F, theta, m, g and mu.arrow_forwardA stack of two crates is being accelerated upwards by two cables. The cables are directly attached to crate 1 and the tension in each cable is 3248 N. You may assume that the masses of the cables are negligible compared to the masses of the crates. The acceleration of the crates is? bottom crate crate 1 is 109 kg. the top crate is 248 kg.arrow_forwardPart A Make a free-body diagram of the box B. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. Part B Make a free-body diagram of the box A. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON