
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Two identical 20.0-kg balls, each 25.3 cm in diameter, are suspended by two 35.0-cm wires as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The entire apparatus is supported by a single 18.0-cm wire, and the surfaces of the balls are perfectly smooth. Find the tension in the top wire. Find the tension in each of two bottom wires.
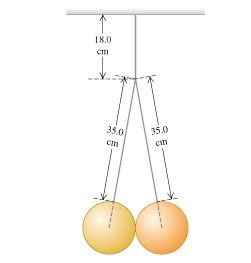
Transcribed Image Text:18.0
cm
35.0
cm
35.0
cm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- no handwritten answers... answer a, b and c...arrow_forwardCreate a slope, with the graph presented. What does the slope represent? How close is your slope to the expected value?arrow_forwardConsider the figure above, where a rigid beam of negligible mass and 10 m long is supported by a cable attached to a spring. When NO block is hung from the beam, the length L (cable-spring) is equal to 5 m. Assume that immediately after block (weight of 260 N) is hung at the end of the beam the spring does not stretch, calculate the tension under this assumption. Using this tension find how much the spring stretches. Express the amount the spring is stretched in cm. k =8275 N/m.arrow_forward
- A bag of cement weighing 525 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in the figure below. Two of the wires make angles ?1 = 61.0° and ?2 = 42.0° with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1, T2, and T3 in the wires. T1 = N T2 = N T3 =.arrow_forwardA 1200-kg car is held in place by a light cable on a very smooth (frictionless) ramp, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The cable makes an angle of 31.0 above the surface of the ramp, and the ramp itself rises at 25.0 above the horizontal. Find the tension in the cable and how hard does the surface of the ramp push on the car?arrow_forwardIf you were performing this experiment in an in-class laboratory, you would be given one or more small iron balls. These would be utilized with a variant of the Free-Fall apparatus shown in the graphic below. (INSERT PICTURE HERE) You would first raise the upper black clamp to the desired height above the middle clamp. Then you would place the ball firmly in the upper clamp. Next, you would turn on the timer and adjust its initial reading to zero. After you release the ball, it falls towards the middle clamp. When it encounters this clamp, the timer stops and you can read the time of fall. Results are usually within 10% of the standard value of g. Here, in this online version, I will supply values of height (h) and time (t). First, calculate the average time (tav) for each height and use it as described next. You will use the third equation above to calculate the value of gravitational acceleration (g) in each case. Then, you will determine the…arrow_forward
- A 3 meter long beam with weight 300 N is supported by a hinge at the wall and a cable as shown. A 300 N block is positioned along the beam at a distance x from the wall. If the breaking strength of the cable is 500 N, what is the maximum value of x? Explain all stepsarrow_forwardYou hang a light in front of your house using an elaborate system to keep the 12-kg object in static equilibrium (Figure 1). What are the magnitudes of the forces that the ropes must exert on the knot connecting the three ropes if θ2 = 63∘ and θ3 = 45∘?arrow_forwardA staging that weighs 390 N supports two painters, one 290 N and the other 340 N. The reading in the left scale is F = 460 N. 460 F, What is the reading F, in the right hand scale? Answer in units of N.arrow_forward
- Consider a pulley system of the type shown in the figure above. Suppose that the upper pulley has no mass and the lower two pulleys have a total mass of 9.1 kg; the block attached to the lower pulleys represents a car engine of mass 115kg . a) What is the tension T in the rope? Assume that all sloped segments of the rope are vertical. b) What force does the ceiling exert on the upper pulley, assuming you pull straight up on the rope?arrow_forwardA cubical box (equal side lengths) of mass 1.7 kg (outline shown in blue in the figure) is supported at an angle = 16 degrees relative to a horizontal surface. The cable supporting the box is at an angle perpendicular to the in-plane diagonal of the box (shown as a dotted line). What is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the box and the horizontal surface such that the box will not slide? cable 0 + 45° Өarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON