
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
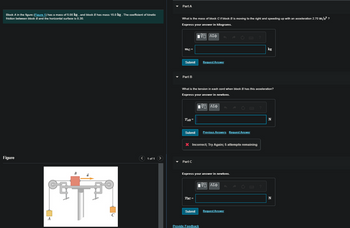
Transcribed Image Text:Block A in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 5.00 kg, and block B has mass 15.0 kg. The coefficient of kinetic
friction between block B and the horizontal surface is 0.30.
Part A
What is the mass of block C if block B is moving to the right and speeding up with an acceleration 2.70 m/s²?
Express your answer in kilograms.
Figure
B
с
A
mc=
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
kg
What is the tension in each cord when block B has this acceleration?
Express your answer in newtons.
TAB
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
1 of 1
Part C
Express your answer in newtons.
TBC =
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
N
N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part A An 88 kg person stands on a uniform ladder 4.0 m long, that weighs 90 N, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The floor is rough; hence, it exerts both a normal force, f1, and a frictional force, f2, on the ladder. The wall, on the other hand, is frictionless; it exerts only a normal force, f3. Using the dimensions given in the figure, find the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is halfway up the ladder. Express your answers using two significant figures separated by commas. ? f1, f2, fa = kN Submit Request Answer Part B Find the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is three-fourths of the way up the ladder. Express your answers using two significant figures separated by commas. να ΑΣΦ ? f1, f2, f3 = kN Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback a-3.8 m mgarrow_forwardQ10. A car travels 15 km in 1 hour, what is its average velocity. A _10misec B-416 m/sec C-2misec D-35misec § Show Answerarrow_forwardp lease just part barrow_forward
- can someone answer part E pleasearrow_forward1. The block in the figure to the right remains motionless against the wall because of an applied force and the force of static friction between the block and the wall. The coefficient of static friction is μs. Which equation correctly describes the magnitude of the frictional force between the wall and the block?a. Ff=(mgcosθ)μsb. Ff= (Fasinθ–mg) μsc. Ff= (Facosθ – mg) μsd. Ff= Facosθμse. Ff= (Facosθ + mg) μsarrow_forwardhe FBD of the block should have looked like this. 1. A contestant in a winter sporting event pushes a block of ice of mass m across a frozen lake as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between the block and ice is μs, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk. θ is the angle the force makes with the x-axis. In this part, we are going to set-up Newton's second Law equations for the cases(1) when the ice block just starts moving, and(2) when it is accelerating to the right with an acceleration a. All answers are symbolic. ALL ANSWERS ARE CASE-SENSITIVE. Subpart 1: Newton's Second Law along the y-axis (i) Write Newton's Second Law along the y-axis by adding all forces in the y-direction taking into account their signs (forces pointing upwards are positive and downward are negative) in terms of the normal force N, weight mg, F and θ. In both scenarios, there is no acceleration along the y-direction, therefore, ay=0.…arrow_forward
- ew T Co Stants Consider the system shown in the figure (Figure 1). Block A weighs 43.7 N and block B weighs 24.2 N. Once block B is set into downward motion, it descends at a constant speed. A cat, also of weight 43.7 N, falls asleep on top of block A. If block B is now set into downward motion, what is its acceleration magnitude? Express your answer in meters per second squared. m/s? a = Submit Request Answer Figure 1 of 1 Part C A cat, also of weight 43.7 N, falls asleep on top of block A. If block B is now set into downward motion, what is its acceleration direction? A upwards downwards Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardHW1.4. 2D Moment resultant Two forces lying in the x-y plane are defined by their magnitudes and direction angles, as shown in the figure below. Force F₁ has a magnitude F₁ = 360 N, an angle 0₁ = 109°, and acts at point A (310, 0) mm. Force F₂ has a magnitude F₂ = 270 N, an angle 02 = 56°, and acts at point B = (0,385) mm. Determine the total moment about point O due to these two forces. Remember to follow the standard sign convention for clockwise (-) and counter-clockwise (+) moments. y B 10 02 F₂ F₁ A 0₁ X TEGINGENarrow_forwardPart A What is the value of Fmax, the maximum value of the contact force during the collision? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Fmax = HÅ Value N www ?arrow_forward
- M Support Cable 37° M As shown in the diagram above, a rigid rod of mass M is hinged at its left end against a wall. A block of mass M hangs on the right edge of the rod. A support cable attached to the right end of the rod forms an angle of 37 degrees with horizontal. The tension in the string is 1,057 N. Calculate the mass M of the rod and the block. Express your answer in kilograms and round to the nearest tenth (1 decimal).arrow_forwardPart A - Finding the Cartesian components of a force described by direction angles Find the Cartesian components of force P acting in the x, y, and z directions given P = 50.0 N, a = 110.0°, B= 29.5°, and y=69.3°. Recall that is the angle between the vector and the x axis, ß is the angle between the vector and the y axis, and y is the angle between the vector and the z axis. Express your answers, separated by commas, to three significant figures.arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON