
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
There are two images, one has the question information and the other is the question.

Transcribed Image Text:**Instructions for Drawing a Free-Body Diagram**
**Task:**
Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on the block.
**Requirements for Full Credit:**
- Correctly labeled axes
- Properly labeled forces
- Accurately indicated angles
Ensure that your diagram is clear and complete to properly represent the physical scenario. This will help you understand the forces involved and how they interact.
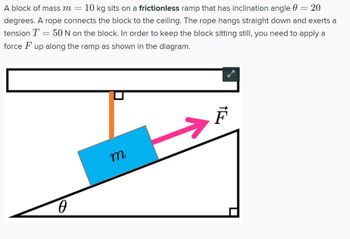
Transcribed Image Text:### Physics Problem: Block on an Inclined Plane with Tension and Applied Force
#### Problem Statement:
A block of mass \( m = 10 \) kg sits on a **frictionless** ramp that has an inclination angle \( \theta = 20 \) degrees. A rope connects the block to the ceiling. The rope hangs straight down and exerts a tension \( T = 50 \) N on the block. In order to keep the block sitting still, you need to apply a force \( \mathbf{F} \) up along the ramp as shown in the diagram.
#### Diagram Explanation:
The diagram shows a block of mass \( m \) placed on an inclined plane (ramp). The following elements are depicted:
1. **Inclined Plane**:
- The plane is inclined at an angle \( \theta = 20 \) degrees from the horizontal.
- The angle \( \theta \) is marked at the lower-left corner of the ramp.
2. **Block**:
- The block is represented as a blue rectangle labeled with mass \( m \).
3. **Rope**:
- An orange rope is attached to the top of the block and connected vertically to the ceiling. This rope exerts a tension \( T = 50 \) N on the block.
4. **Applied Force**:
- A pink arrow labeled \( \mathbf{F} \) is shown pointing up the ramp. This illustrates the force that needs to be applied to keep the block stationary.
5. **Coordinate Indicators**:
- There are right-angle indicators and \( \theta \) angle indication for clarity on angles and force directions.
This setup requires the applied force \( \mathbf{F} \) to counteract the gravitational component along the incline and the tension from the rope to maintain equilibrium and keep the block stationary on the frictionless ramp.
#### Analysis:
To solve for the required force \( \mathbf{F} \), you would likely perform a force analysis along the inclined plane and perpendicular to it, considering the gravitational force components, the tension in the rope, and the applied force.
This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the statics involved in an inclined plane scenario, which is essential in fields such as physics, engineering, and mechanics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- what's the correct answer? A ray passing through the center of a thin lens surrounded by air on both sidesa) is bent downwardb) is bent upwardc) does not change directiond) becomes parallel to the optical axise) becomes perpendicular to the optical axisarrow_forwardA lens has a focal length of 5 cm. The object is 25 cm away from the center of the lens. Calculate the position of the image, in meters.arrow_forwardThe second image shows how I'm working it out. Can you explain to me what I'm doing wrong?arrow_forward
- A single concave spherical mirror produces an image which is?arrow_forwardHello. I cannot see the solution. There is an issue with the image here and i cannot see what is says past the first few words.arrow_forwardOn this question for v, it asked if it is a real or virtual image? How do i prove that?arrow_forward
- An image is formed using a convex lens, the image being 15 cm past the lens. A second lers is placed 25 cm past the first lens and another image is formed, this time 10 cm past the second lens. Which of the following statements is true? The last image is inverted with regard to the original object, The last image must be larger than the object. The first image is virtual. None of the above statements is true.arrow_forwardwhat's the correct answer: A virtual image is an image thata) is not sharpb) is stored in a computerc) can be seen only by looking through an optical systemd) can be seen by placing a screen in the image planee) is displayed on a computer monitorarrow_forwardA coin that is tossed straight up into the air. After it is released, it moves upward, reaches its highest point and falls back down again. Use one of the following choices (A through G) to indicate the acceleration of the coin during each of the stages of the coin's motion described below. Take up to be the positive direction. Answer choice J if you think that none is correct. A. The acceleration is in the negative direction and constant. B. The acceleration is in the negative direction and increasing. C. The acceleration is in the negative direction and decreasing. D. The acceleration is zero. E. The acceleration is in the positive direction and constant. F. The acceleration is in the positive direction and increasing. G. The acceleration is in the positive direction and decreasing. The coin is moving downward. A OF ΟΕ Barrow_forward
- If you look into the bowl of a metal spoon, you see yourself up- side down. Flip the spoon so you're looking at the back side, and now you're right-side up. Explain.arrow_forwardWhy are mirror images flipped horizontally but not vertically?arrow_forwardWalking along the edge of a pool, you see a quarter resting on the bottom of the pool. The light reflecting off the quarter enters your eyes at a 37o angle below the horizontal. Is the quarter closer or farther away from you than it appears?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON