
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
This type of experiment, where members of an outbred populations are introduced to an inbred population as mating partners, is sometimes called a “genetic rescue”. How might measuring the average heterozygosity at a number of loci in the Swedish snake population allow you to test whether the introduced snakes had actually bred successfully with the inbred Swedish snakes?
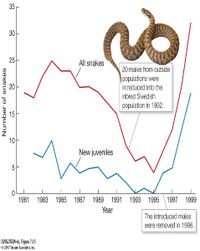
Transcribed Image Text:35
30
25
All snakes
20 males from outside
oopulations were
introduced into the
inbred Swedish
population in 1992.
15
10
New juveniles
5
1981 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999
Year
The introduced males
were removed in 1996.
EVOLUTION de, Figure 7.15
O2017 Sinauer kiwociates, Inc.
20
LO
Number of snakes
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a dense forest, a population of squirrels has been observed for their fur color. The fur color is determined by a single gene with two alleles: B (black) and b (brown). In a sample of 100 squirrels, you observed 30 black (BB), 50 black-brown (Bb), and 20 brown (bb) individuals. Determine if this population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and show your work.arrow_forwardYou are studying a population of snapdragon plants on Membata Island. In snapdragons, the dominant allele CR encodes red flowers and the recessive allele CW encodes white flowers. Plants with a heterozygous CRCW genotype have pink flowers. You have counted 10,000 snapdragon plants on Membata Island. You have recorded that 9025 plants have red flowers, 950 plants have pink flowers, and 25 plants have white flowers. If this population is at a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what are the values of p and q in this population? Show your calculations.arrow_forwardA particular deer population has 50 M individuals, 30 MN individuals, and 70 N individuals. What are the allele frequencies?arrow_forward
- A hypothetical species of plant has flowers whose color is controlled by a single gene with two alleles, blue (B) and yellow (Y), where blue is dominant and yellow is recessive. A population of 2430 of these plants includes 190 plants with yellow flowers.Assuming that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what is the frequency of the yellow allele?arrow_forwardIn a population of frogs in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, a single gene controls the skin lor. Green is dominant to brown. You sample the frog's gene pool, and find that the frequency of the daminant green allele is 0.678. What is the froquency of the recessive allele? What is the frequency of homozygous dominant frogs? What is the frequency of heterozygous frogs? What is the frequency of homozygous recessive frogs?arrow_forwardIn an imaginary three-toed sloth population at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, where T = three toes and t = four toes, the frequency of the recessive allele is 0.14. What percentage of the population has three toes? Assume complete dominance.arrow_forward
- Assume you are studying a population of fire toads and want to predict what happens after a selection event. There is a freeze event. Before the freeze event you measured body size and found the average body size was 50 grams. After the freeze event you measured the surviving toads and their average body size was 70 grams. Based on your previous studies you know that the narrow-sense heritability is 0.5 What is the response to selection in this population? a. 5 grams b. 10 grams c. 20 grams d. None of the abovearrow_forwardIf the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what is the expected (projected) frequency of heterozygous cats in the next generation? Question 4 options: 0.68 0.89 0.435 0.84arrow_forwardFor goldfish, solid orange coloring is dominant while orange with black spots is recessive. A total of 2500 goldfish were stocked in an outdoor pond, 2275 solid orange and 225 orange with black spots. Since the fish came from a protected, indoor, stable environment, you may assume the stocked population was in equilibrium. What are the and genotype frequencies in the original stocked population?arrow_forward
- Researchers studied the blood types of indigenous populations in the Andes. They used a two-allele typing system (M and N alleles). In one population the genotypic frequencies were: f (MM) = 0.70, f (MN) = 0.20, f (NN) = 0.10. What are the frequencies of M and N alleles for this population? Answer choices f(M) = 0.80 and f(N) = 0.20 f(M) = 0.70 and f(N) = 0.30 f(M) = 0.49 and f(N) = 0.01 f(M) = 0.90 and f(N) = 0.10 f(M) = 0.50 and f(N) = 0.50arrow_forwardWhat is the chi-square value of the pumpkin population? round up and use four decimal points After doing some crosses and genotyping some individuals, you determined that the number of individuals homozygous dominant for the largest pumpkin allele is 98, 80 are heterozygous for medium size, and 20 are homozygous recessive for small size.arrow_forwardIn carnations, the red pigment (RR) is incompletely dominant to white (rr). The heterozygote (Rr) is pink. In a randomly mating field of carnations, 42 plants were red, 178 plants were pink, and 180 plants were white (total =400). What is the best estimate of the allele ferequency, for the red allele in this population?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education