
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
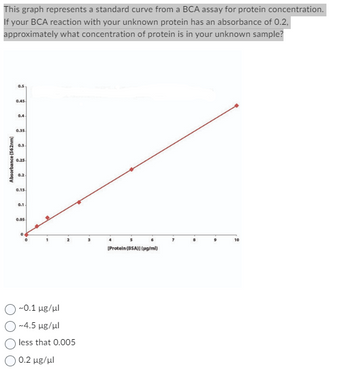
Transcribed Image Text:This graph represents a standard curve from a BCA assay for protein concentration.
If your BCA reaction with your unknown protein has an absorbance of 0.2,
approximately what concentration of protein is in your unknown sample?
Absorbance (562nm)
0.5
0.45
3
0.35
0.3.
0.25
0.15.
0.1-
0.05
~0.1 μg/ml
~4.5 μg/ul
less that 0.005
| 0.2 μg/μ.
[Protein (BSA)) (pg/ml)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Standard curve can be constructed by using the known concentrations of a sample and their corresponding absorbance values.
This standard curve can be used to determine the concentration of unknown sample by comparing its absorbance value with the known reference values .
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- G418 disulfate (FW 692.7) is an antibiotic used to select transfected mammalian cells in tissue culture. The standard working concentration for selection is 400 µg/mL of active ingredient in culture medium. The bottle states that it contains 71% active ingredient. You need to make a 100x stock in medium and adjust the pH before you apply it to cells. How much powder should be added to make 10 mL of stock solution? How much do you add to a 2 mL culture dish?arrow_forwardThis is a visible spectra between 390-590 nm obtained during the protein separation process of haemoglobin and cytochrome c using CM Sephadex chromatography. I'd like the results shown on the image interpreted. Look for characteristic peaks or patterns that correspond to the absorption properties of these proteins in the visible range.arrow_forwardYou are studying a protein-protein interaction in 2 proteins. You decide to test both these proteins in different buffers and see if the interaction is preserved. You run the assay in the following buffers, pH 7.4, pH 7.4 with BME, pH 4.5, pH 3.5, pH 11, pH 12.5. The SDS gels from the assays are attached. a. What type of protein-protein interaction do these results suggest? b. What amino acids are most likely involved in this interaction? (Guess based on assay)arrow_forward
- A gel filtration column with a fractionation range of 1.5-20 kDa is used to separate out the proteins shown below. If these proteins are collected into separate fractions in between the void volume and total volume, in which order will they elute? Indicate if any of the proteins are found in the void volume or total volume fractions. Protein Z - 3330Da Protein Y - 13kDa Protein X - 1.3kDa I. Total volume fraction II. Third protein fraction III. Second protein fraction IV. First protein fraction V. Void volume fractionarrow_forwardDoes this calculation look correct? My goal isto have a target mass of 10 µg of my protein with a total volume of 30 µl. Protein was measured and found to have a concentration of at 308.35 µg/ml Recall, mass = concentration * volume 10 µg = 308.35 µg/ml * V V = 0.01 mg/ 0.30835 mg/mL = 0.032430679 mL = 32.43067942 µL Note: cannot measure this amount; two dilutions required. Dilute by 1/40: measure 2.5 µl of protein at 0.30835 µg/µl and add it to 97.5 diluent to prepare a solution of protein at 7.71 mg/ml. This diluted sample will be used further. Mass = concentration * volume 10 µg = 7.71 mg/ml * V V = 0.01 mg/ 7.71 mg/ml = 1.3 µL Therefore, will measure 1.3 µl of protein at 7.71 mg/ml and add it to 28.7 µl of diluent.arrow_forwardYou are studying a protein-protein interaction in 2 proteins. You decide to test both these proteins in different buffers and see if the interaction is preserved. You run the assay in the following buffers, pH 7.4, pH 7.4 with BME, pH 4.5, pH 3.5, pH 11, pH 12.5. The SDS gels from the assays are attached. a. What type of protein-protein interaction do these results suggest? b. What amino acids are most likely involved in this interaction?arrow_forward
- A purified protein sample was used in a reaction, resulting in an activity of 696.7 nmol min-1. The reaction volume was 145.0 µL and the final volume before loading the plate was 1,050 µL. The total reaction time was 4.25 min. The amount of protein used in the reaction was 4.270 µg. Calculate the specific activity of the sample (in nmol min-1 µg-1).arrow_forwardPlease answer the question below and show all your work. You are given a pure protein sample to characterize and provided the following information: Its molar extinction coefficient, ε280, is 0.25 liters micromole^-1 cm^-1 Using a 0.5 cm pathlength cell, you measure the absorbance at 280 nm of a 20- fold dilution of your pure protein in solution (by this, we mean that 50 ul of the protein sample was diluted to a final volume of 1 ml) and find A280 = 0.40. What is the original concentration of the protein before dilution?arrow_forwardWhat is the chemistry behind of the effect of proteins when it is subjected to different temperatures done in three trials? see the data below to interpret Table 3.1 %Transmittance of Identical 10% albumin samples subjected to different temperatures done in three trials. Heating Tempt. (C) %Transmittance Trial 1 Trial 2 trial 3 Average Control (unheated) 62 62 62 62 55 60 59 58 59 60 2.5 4.5 4.5 11.5 65 1.52 1.6 1.52 1.55 70 1 1 1 1 Table 3.2 Absorbance of Identical 10% albumin solution subjected to different temperatures done in three trials. Heating Tempt. (C) Absorbance Readings (450nm) Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Average Control (unheated) 0.2076 0.2076 0.2076 0.2076 55 0.2218 0.2219 0.2366 0.2292 60 1.6021 1.3468 1.3468 0.9393 65 1.8182 1.7959 1.8182 1.897 70 2 2 2 2arrow_forward
- Make a table with a scale of absorbance and the concentration of protein in Chromatin sample from the following data for excel graph Absorbance=660nm following data are of tubes with concern A =0 B=0.036 C=0.011 D=0.001 E=0.027 F=0.020 G=0.032 H1=0.176 H2=0.183 I1=0.150 I2=0.171 also plot the graph??arrow_forwardYou perform a Bradford assay. You obtain the absorbance values listed below from the BSA samples; your protein sample yields an absorbance of 1.3; what is the protein concentration of your sample? How did you determine that? BSA (ug/ml) Absorbance @ 595 nm. 25 0.15 50 0.30 75 0.45 100 0.60 150 0.90 200 1.25arrow_forwardA sample mixture consists of three proteins with the following properties: Protein A MW (kDa) 200 Amino acid composition 40% nonpolar, 60% polar B 45 20% nonpolar, 80% polar C 98 85% nonpolar, 15% polar IpH 9 3 5 1. If the mixture is subjected to ammonium sulfate precipitation, which protein will precipitate out first? [Select] 2. If the mixture is subjected to isoelectric focusing, which protein will stop moving nearest to the positive electrode? [Select] 3. If the mixture is subjected to cation-exchange chromatography using a buffer at pH 7, which protein will bind to the resin? [Select] 4. If the mixture is subjected to SDS-PAGE, which protein will be at the bottommost portion of the gel? [Select] * Previous Nexarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON