
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
From this standard curve and chart below, does the separation of molecules in the mixture appear successful from the gel filtration? Is there a clearly
defined separation between molecules? Explain your conclusions.
Parameters required for calculation of coefficient (Kd) for unknown protein
|
|
Volume eluted (mL) |
Which variable does this volume represent in the equation for Kd? |
|
Fraction with maximal DNP-Aspartate detected |
36 |
Vt |
|
Fraction with maximal Protein detected |
24 |
Ve |
|
Fraction with maximal Blue dextran detected |
6 |
Vo |
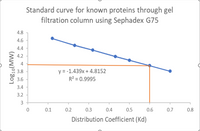
Transcribed Image Text:Standard curve for known proteins through gel
filtration column using Sephadex G75
4.8
4.6
4.4
4.2
4
y = -1.439x + 4.8152
R2 = 0.9995
3.8
3.6
3.4
3.2
3
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Distribution Coefficient (Kd)
Log10(MW)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Standard curves You are setting up a standard curve for lysozyme. You have a stock vial containing 2 mg/ml of lysozyme and you have 2 ml in the vial. You will want to have a minimum of 1 ml of each concentration for the spectrophotometer. How would you proceed? (Saline is added to make the various concentrations). Concentration Am't stock lysozyme or am't of a previous dilution (note which) Amount saline Total volume wanted 1.00 mg/ml 0.75 mg/ml 0.50 mg/ml 0.375 mg/mlarrow_forwardExplain how the Kirby-Bauer test works and what information it provides. Define minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Describe how the E-test works and what information it provides.arrow_forwardQ9) Given the following sample preparation 200 microliters of BSA (protein) at 240 micrograms/ mL 50 microliters H2O 1000 microliters of Lowry Reagent 100 microliters of Folin Reagent How would you prepare a blank tube? What is the purpose of the blank?arrow_forward
- A protein gives a single band on SDS gel electrophoresis, as shown in lanes 1 and 2 below. There is little, if any, effect from adding β-mercaptoethanol(BME) to the sample; if anything, the protein runs a little bit slower. When treated with the proteolytic enzyme thrombin and electrophoresis in the absence of BME, the protein migrates a bit more rapidly (lane 3). But if BME is present, two much more rapidly migrating bands are found (lane 4). Explain these results in terms of a model for the protein.arrow_forward8L.Part Iarrow_forwardThe Bradford reagent gives a linear response only from 0.1 mg/mL to 1.4 mg/mL of protein concentration. Would we be able to use an "absorbance vs. concentration" line graph for samples outside of the range indicated? Justify your response.arrow_forward
- Please answer the question below and show all your work. You are given a pure protein sample to characterize and provided the following information: Its molar extinction coefficient, ε280, is 0.25 liters micromole^-1 cm^-1 Using a 0.5 cm pathlength cell, you measure the absorbance at 280 nm of a 20- fold dilution of your pure protein in solution (by this, we mean that 50 ul of the protein sample was diluted to a final volume of 1 ml) and find A280 = 0.40. What is the original concentration of the protein before dilution?arrow_forwardCan we purify mCherry protein (His-tag attached) with immobilised metal ions affinity chromatography (Ni-IDA)? If so, how can we confirm whether the protein is purified and how to increase its purity?arrow_forwardFind a method that uses some form of HPLC for the analysis of proteins. What was the stationary phase used? How does this kind of stationary phase separate the proteins? What kind of mobile phase was used? Was the method isocratic or was a gradient used? How were the proteins detected?arrow_forward
- "If you count 70 colonies from a urine culture obtained using 0.001ml calibrated loop, how many colony forming units (CFU) will be reported?" 70 700 7000 70000 700000arrow_forwardWhich fractions measured from your gel filtration experiment had the most and least amount of protein detected? Which fraction likely contained the most myoglobin based off molecular weight and protein presence? Which fraction likely contained the most egg albumin based off molecular weight and protein presence? Which samples measured from your ion exchange experiment had the most protein detected? Calculate the approximate pI of your proteins using the ion exchange Table 2. Ion Exchange Samples Tested by Bradford Assay Concentration BSA (μg/mL) Concentration BSA (mg/mL) Volume of Sample added to Bradford Reagent (μL) Absorbance at 595 nm Standard 1 250 0.25 50 0.32 Standard 2 125 0.125 50 0.16 Standard 3 62.5 0.0625 50 0.08 Standard 4 31.25 0.03125 50 0.04 Standard 5 15.625 0.015625 50 0.02 Blank 0.00 0.00 0.00 Table 3. Gel Filtration Fractions Tested by Bradford Assay Fraction #:…arrow_forwardUse correct sig figs The concentration of a purified monoclonal antibody was measured using UV280 nm. The sample was diluted (200 μL of purified antibody in 800 μL buffer) prior to analysis using a spectrophotometer. Calculate the concentration of antibody in the purified fraction if the Abs=0.95 of the diluted antibody. The molar absorptivity is known to be 191,411.6 M-1cm-1 and the molecular weight is 150 kDa. The pathlength for the cuvette is 1 cm.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON