
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
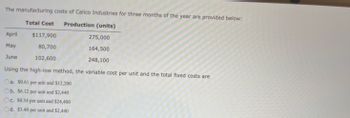
Transcribed Image Text:The manufacturing costs of Calico Industries for three months of the year are provided below:
Total Cost Production (units)
$117,900
80,700
102,600
April
May
June
275,000
164,500
248,100
Using the high-low method, the variable cost per unit and the total fixed costs are
Oa. $0.61 per unit and $12,200
b. $6.12 per unit and $2,440
c. $0.34 per unit and $24,400
Od. $3.40 per unit and $2,440
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The manufacturing costs of Kellam Industries for the first three months of the year follow: Total Costs Units Produced January $318,060 2,015 units February 357,640 3,850 March 494,760 5,115 Using the high-low method, determine (a) the variable cost per unit and (b) the total fixed cost. a. Variable cost per unit $fill in the blank 1 b. Total fixed cost $fill in the blank 2arrow_forwardPlease do not give image formatarrow_forwardPo.8.arrow_forward
- Lindquist Company has the following information for February: Line Item Description Amount Sales $370,000 Variable cost of goods sold 173,900 Fixed manufacturing costs 55,500 Variable selling and administrative expenses 40,700 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 22,200 Determine the following for Lindquist Company for the month of February: Line Item Description Amount a. Manufacturing margin $fill in the blank 1 b. Contribution margin $fill in the blank 2 c. Operating income $fill in the blank 3arrow_forwardSalem Company has the following costs information for June where production volume is 2,000 units: 7. The variable cost and fixed cost per unit respectively are: A) $8.75 and $1.50. B) $8.75 and $0.25. C) $4.25 and $3.00. D) $8.50 and $12.00. B) fixed cost per unit. C) total variable cost. D) total cost per unit. A) 1,000 B) 1,800 Direct materials Direct labor 8. If production changes to 2.200 units, which cost will remain the same? A) variable cost per unit. C) 3,200 D) 2,600 Straight-line depreciation Rent expenses other fixed costs 9.The production budget shows expected unit sales of 16,000. Beginning finished goods units are 1,800. Required production units are 16,800. What are the desired ending finished goods units? A) B) D) 10. The production budget shows expected unit sales are 50,000. The required production units are 52,000. What are the beginning and desired ending finished goods units, respectively? Ending Units 2,000 5,000 $8,500 $9,000 5800 Beginning Units 5,000 3.000…arrow_forwardJason Inc. provides the following manufacturing costs for the first four months of the year. Manufacturing Costs for the First Four Months Months Production in Units Total Costs January 2,500 $33,750 February 1,800 $29,900 March 3,000 $36,500 April 2,600 $34,300 Using the high-low method, determine the total fixed costs. (Round intermediate calculations to two decimal places, and the final calculation to the nearest dollar.) Group of answer choices $15,500 $20,000 $30,300 $16,500arrow_forward
- Marley Company has the following information for March: Sales $912,000 Variable cost of goods sold 474,000 Fixed manufacturing costs 82,000 Variable selling and administrative expenses 238,100 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 54,700 Determine the following for Marley Company for the month of March: a. Manufacturing margin $fill in the blank 1 b. Contribution margin $fill in the blank 2 c. Operating income $fill in the blank 3arrow_forwardNorwood Company has the following information for July: Sales $440,000 Variable cost of goods sold 198,000 Fixed manufacturing costs 70,400 Variable selling and administrative expenses 44,000 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 26,400 Determine the following for Norwood Company for the month of July: a. Manufacturing margin $fill in the blank 1 b. Contribution margin $fill in the blank 2 c. Operating income $fill in the blank 3arrow_forwardMarley Company has the following information for March: Sales $912,000 Variable cost of goods sold 474,000 Fixed manufacturing costs 82,000 Variable selling and administrative expenses 238,100 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 54,700 Determine (A) the manufacturing margin, (B) the contribution margin, and (C) income from operations for Marley Company for the month of Marcharrow_forward
- need answer of this Question Please Provide itarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardThe table below shows monthly data collected on production costs and on the number of units produced over a twelve month period. Month Total Production Costs Level of Activity (Units Produced) July $ 230,000 3,500 August 250,000 3,750 September 260,000 3,800 October 220,000 3,400 November 340,000 5,800 December 330,000 5,500 January 200,000 2,900 February 210,000 3,300 March 240,000 3,600 April 380,000 5,900 May 350,000 5,600 June 290,000 5,000 Required: Determine the variable cost per unit and the fixed cost using the high-low method. What is the equation of the total mixed cost function? Prepare the scatter diagram, clearly showing any outliers Using the line of best-fit, determine the company’s fixed cost per month and the variable cost per unit. (Use 0 & 5,000 units. In view of the department’s cost behaviour pattern, which of the two methods appear more appropriate?…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education