
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
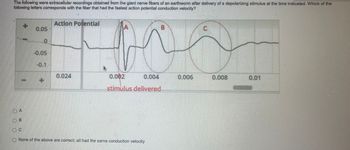
Transcribed Image Text:The following were extracellular recordings obtained from the giant nerve fibers of an earthworm after delivery of a depolarizing stimulus at the time indicated. Which of the
following letters corresponds with the fiber that had the fastest action potential conduction velocity?
I
OA
0.05
0
-0.05
-0.1.
+
Action Potential
0.024
B
W
0.002
0.004
stimulus delivered
A
OB
OC
None of the above are correct; all had the same conduction velocity
0.006
C
0.008
0.01
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Order the steps of the neuromuscular junction transmission using the following images. Then, usethe to describe what is happening in the step. Neuromuscular Junction Transmission - Contraction 1. Action potential travels from motor neuron cell body along the myelinated axon to neuromuscular junction. 2. Acetylcholine (ACh) is released from axon (neuron), crosses synapse (space between axon and sarcolemma).ACh binds to ACh receptors (channel) in sarcolemma. 3.ACh channels open. Ions (like sodium, Na+) flow into sarcolemma.Action potential spreads in sarcolemma and into transverse tubules. 4. Action potential causes the release of calcium (Ca2+) from sarcoplasmic reticulum into sarcoplasm 5.Ca2+ goes to the troponin, which moves the tropomyosin away from actin 6. Myosin head breaks down ATP, causing the sliding filament mechanism to shorten sarcomereMuscle contractsarrow_forwardShown attached are the recordings from one cell in the Swimmy CPG circuit. The first recording is under controlconditions, when the fish is swimming normally. The second recording is of the same neuron when every othercell in the CPG is hyperpolarized and not firing. The large black bars have been placed at the first spike in thecontrol condition. Which of the following can you conclude about this cell from the data shown below? Make sure to choose the most complete answer. a. This cell is tonically active.b. This cell is an endogenous burster cellc. This cell is an endogenous burster cell that is normally acted on by at least one inhibitory synapse.arrow_forwardThe plasma membrane of the giant squid axon becomes depolarized in response to action potential. true falsearrow_forward
- A Na+ 10 msec B 40mV Ca²+ C Na+ Ca²+ Each graph represents the depolarization activity during an action potential in Xenopus spinal cells at different stages of development. Referring to each electrical reading (A, B, and C), place the graphs in order of developmental stage, from earliest to latest. What are the major changes in action potential activity that occurs with development?arrow_forwardConduction velocity refers to the [a] at which an action potential travels along a neuron's axon. In invertebrates, conduction velocity can only be increased by [b]. However in vertebrates (exclusively), such as humans, conduction velocity can also be increased by [c]. This enables vertebrates to conserve [d] while still increasing conduction velocity. [a] [b] [c] [d] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ]arrow_forwardPlace the following events in chronological order from 1-8: Nat enters the cell, and depolarization occurs to approximately +30 mV. The voltage across the cell membrane is -70 mV, the resting membrane potential. Upon reaching the peak of the action potential, the VG Nat channels are inactivated by the closing of their inactivation gate and the activation gate of each VG K channel opens. VG K channels close by the closing of their activation gate, and the resting membrane potential is gradually restored. An excitatory post-synaptic potential depolarizes the membrane to threshold and the activation gate of VG Nat channels open. Upon returning to the resting membrane potential, VG Na channels are reset by opening of the inactivation gate and the closing of the activation gate. VG K+ channels are slow to close, resulting in an excess of K* efflux and hyperpolarization. Depolarization occurs as K+ flows out of the cell.arrow_forward
- hen an action potential arrives at the nerve terminal of a neuromuscular junction, which of the following statements best describes the events that occur? Depolarisation of the nerve terminal causes the release of ACh which activates nicotinic receptors on the skeletal muscle membrane to cause Ca2+ entry and muscle contraction. Depolarisation of the nerve terminal opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, Ca2+ entry brings vesicles containing ACh to the membrane which form fusion pores causing the release of ACh which activates voltage-gated Na+ channels at the end-plate. Depolarisation of the nerve terminal opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, Ca2+ entry brings vesicles containing ACh to the membrane which form fusion pores causing the release of ACh which binds to muscarinic receptors at the end plate. Depolarisation of the nerve terminal opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, Ca2+ entry brings vesicles containing ACh to the membrane which form fusion pores…arrow_forwardThe membrane potential labeled (0) is due to which of the following (when compared to (3) potential. (A) voltage-gated Na+ channels (B) voltage-gated K+ channels (C) voltage-gated slow Ca++ channels (D) voltage-gated fast Ca++ channels (E) voltage-gated transient Ca++ channels (F) funny channelsarrow_forwardChoose the type of information that the soft organ smooth muscle first order neuron are sending to the central nervous system: 1, sterogotic information 2, stretch information 3, proprioceptive information 4, temperature information This is the second time in 10 min I asked this question, the fomer one been rejected due to incompleted. But this is the whole inforamtion I had copied from my home work, no letter missed.arrow_forward
- Can you modify this experiment so that the mass lifted by the muscle contraction continues to increase for every trial? If yes, explain how it should be modified. If no, explain why.arrow_forwardBelow is a figure from a 2015 paper that characterizes the effect of venom from the spider Selenocosmia hainana on voltage-gated sodium channels. According to the I-V curve (current-voltage curve) in Figure panel B, what is the effect of the venom on voltage-gated sodium channels? Current is on the y-axis and voltage is on the x-axis during an action potential. The figure legend denotes the concentration of the venom being applied. A C rHNTX-IV (10 μM) -rHNTX-IV (100 nM) Control Control 5 nA 10 ms r 5 nA 10 ms rHNTX- IV (10 μM) B D -80 -80 -60 -60 A -40 -40 V (mv) -20 V(mv) -20 be TOLF 2-6 I (NA) -8 ON -12 10 -12 -14 -8 -10 (NA) Control 100 nM — 10 μΜ 40 -Control -- 10 μM 40arrow_forward1. What is action potential? Please describe the ionic mechanisms of depolarization and repolarization phase of action potential in the squid giant axon. please write more and morearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,
Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc., Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780135168059
Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, Jon
Publisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,

Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative Approach
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780078024283
Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa Bidle
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780321927040
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON