
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
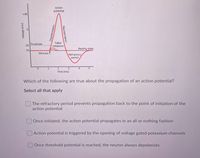
Transcribed Image Text:Action
potential
+40
Failed
-55 Threshold
initiations
Resting state
-70
Stimulus 1
Refractory
period
3.
Time (ms)
2
4.
Which of the following are true about the propagation of an action potential?
Select all that apply
The refractory period prevents propagation back to the point of initiation of the
action potential
Once initiated, the action potential propagates in an all or nothing fashion
Action potential is triggered by the opening of voltage gated potassium channels
Once threshold potential is reached, the neuron always depolarizes
Voltage (mV)
Depolarization
Repolarization
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Why does the action potential not go back to where it came from? (Multiple answers possibly) the absolute refractory period prevents this from happening Sodium voltage gated ions in the area where the action potential just came from are fully activated or inactivated Sodium voltage gated ions bind to the Na+ ions, preventing them from diffusing backwards Na+ only diffuses forward in the axon 2. When neurotransmitter binds to _______________ at the dendrites, it results in a _____________ potential Ligand gated ion channels | action Voltage gated ion channels | action Voltage gated ion channels | graded Ligand gated ion channels | gradedarrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forwardPhysiology questionarrow_forward
- What is the arrow identifying in the picture below? soma dendrite O action potential Oaxons axon hillock < Previous Marrow_forwardName and describe the roles of key molecules and membrane structures in maintaining axon membrane resting potential of-70 mV Name and describe the roles of key molecules and membrane structures in propagation of axon membrane action potentials during depolarization at +35 mV Explain why they myelin sheath of white matter neurons allows faster action potential transmission than that of neurons found in gray matter.arrow_forward1.25 p Question 22 Which statement below best describes why action potentials travel in only one direction? O The all-or-none principle explains this. O They have a refractory period. O The diameter of the axon explains this. O Only sodium- and potassium-gated channels are found on the axon. O They have myelinated axons. • Previous Next Not saved Submiarrow_forward
- threshold resting membrane potential decrease calcium channels increase action potentials The autonomic nervous system influences the heart rate. A sympathetic signal (norepinephrine) results in opening. This accelerates the process of reaching thereby resulting in a in time between successive action potentials. A parasympathetic signal (acetylcholine) results in the dropping to -70mV. This results in an in time for cells to reach threshold, thereby increasing the time between successivearrow_forwardAn action potential Membrane potential (mV) -40 40 -65 II -80 0 -Overshoot Rising Falling phase phase III Voltage threshold Resting potential Undershoot 1 2 3 4 Time (ms) In the figure above, which arrow best represents the point where the voltage-gated sodium channels are inactivated and locked? OI ○ III O IV ○ IIarrow_forwardneurotransmitters 1 In what way may drugs be used to affect neurotransmitters? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. A drug may prevent the binding of a neurotransmitterto a receptor. b, A drug may increase the amount of neurotransmitter released. A drug may prevent the release of aneurotransmitter, d. A drug may affect the degradation of a neurotransmitter Drugemay affect neurotranemitters usng al of the mechanismslsted. Unansweredarrow_forward
- 4,5,6 and 7 if possiblearrow_forwardDescribe the 6 step sequence of events that occurs at the NMJ in response to a nerve Action Potential.arrow_forward1. What is action potential? Please describe the ionic mechanisms of depolarization and repolarization phase of action potential in the squid giant axon. please write more and morearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education