
Concept explainers
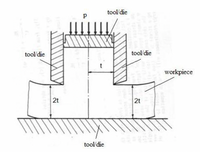
The figure below shows a symmetric plane-strain upsetting process. The process may also be thought of as a form of side extrusion. Observations show that the deformation is confined to two shear planes, each one being analogous to that seen in plane-strain cutting. You may assume that there is no friction between the work material and the tool/die walls; the uniaxial yield strength of the material is σy and is independent of strain rate and temperature, and the material behaves as a rigid plastic solid.
a) Calculate the pressure (p) required for the upsetting process in terms of σy.
b) If friction existed at the die walls and the frictional work (energy) dissipation was 30% of the energy required for shape change alone (part (a) above), then what would be the pressure (p)?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- 1) Drawing: Consider a cylindrical rod fabricated from a linear strain hardening material with a constitutive relationship of o=2000 + 20000 € (where o is in psi). The rod is drawn into a wire. If the original diameter of the rod is 0.75 in, what is the minimum possible diameter that can be drawn in the first pass? Assume that redundant work is 20% of the ideal work and that the frictional work is 15% of the ideal work of deformation. What is the drawing force required to complete this operation?arrow_forwardMECHANIC ENGIIERING THAN YOU SO MUCHarrow_forwardA spool of copper wire has a starting diameter of 2.5 mm. It is drawn through a die with an opening that is 2.1 mm. The entrance angle of the die = 18°. Coefficient of friction at the work die interface is 0.08. The pure copper has a strength coefficient = 300 MPa and a strain hardening coefficient = 0.50. The operation is performed at room temperature. Determine (a) area reduction, (b) draw stress, and (c) draw force required for the operation.arrow_forward
- A wire is drawn through a draw die with an entry angle = 15o. The starting diameter is 0.100 in. And the final diameter = 0.080 in. The coefficient of friction at the work-given interface = 0.07. The metal has a coefficient of resistance K = 30,000 psi and a strain hardening exponent of n = 0.20. Determine the stretching force and the stretching force in this operation.arrow_forwardShow that the true strain rate in extruding a round billet of radius r, as a function of distance x from the entry of a conical die can be given as: 2V,rtana where; V.: ram velocity = (ro-xtana)arrow_forwardA billet 100 mm long and 30 mm in diameter is to be extruded in a direct extrusion operation with extrusion ratio r, = 3.5. The extrudate has a round cross section. The die angle (half angle) = 60°. The work metal has a strength coefficient = 720 MPa, and strain hardening exponent = 0.17. Use the Johnson formula with a = 0.8 andb= 1.2 to estimate extrusion strain. Determine the following: 1. Diameter of the extrudate = mm 2. Butt volume = mm3 3. Actual extrudate length = mm 4. The pressure applied to perform the extrusion process = MPa 5. Ram force = N.arrow_forward
- A 200 mm wide and 42.0 mm thick plate made of low carbon steel is to be reduced in one pass in a rolling operation. As the thickness is reduced, the plate widens by 4%. The entrance speed of the plate is 15.0 m/min. The roll radius is 325 mm and the rotational speed is 49.0 rev/min. i. If the current horsepower of the available rolling machine is 950 HP, how much thickness could the machine reduce the plate thickness to? ii. If the required thickness needs to be 34.0mm, how could the original width of the plate be changed in order to use the same machine?arrow_forwardWhat is the linear variation in the shear strain?arrow_forwardThe quantity of work that can be done in the die may be used as a defining feature of forging processes. Please identify the following three broad classes that this sorting generates.arrow_forward
- Bar stock of initial diameter = 90 mm is drawn with a draft = 15 mm. The draw die has an entrance angle = 18°, and the coefficient of friction at the work‑die interface = 0.08. The metal behaves as a perfectly plastic material with yield stress = 105 MPa. Determine (a) area reduction, (b) draw stress, (c) draw force required for the operation, and (d) power to perform the operation if exit velocity = 1.0 m/minarrow_forwardA sheet 300mm wide 25mm thick with two drives, each with a radius of 250mmit is passed through a rolling stand with rollers. Work is thickness in one layer at 50 rpm roll speed 22reduced to mm. The work material has a yield curve determined by K = 275 MPa and n = 0.15.The friction coefficient between the rollers and the work is considered to be 0.12. Successful rolling of frictionDetermine if it is sufficient to allow its operation. If it is sufficient;a) Rolling force,b) Momentc) Calculate the power.arrow_forwardPlease answer all partsarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





