
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:=
=
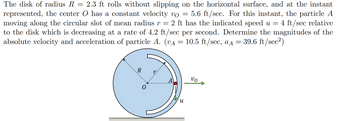
The disk of radius R 2.3 ft rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface, and at the instant
represented, the center O has a constant velocity vo 5.6 ft/sec. For this instant, the particle A
moving along the circular slot of mean radius r = 2 ft has the indicated speed u = 4 ft/sec relative
to the disk which is decreasing at a rate of 4.2 ft/sec per second. Determine the magnitudes of the
absolute velocity and acceleration of particle A. (v₁ = 10.5 ft/sec, aд = 39.6 ft/sec²)
R r
и
νο
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The disk rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface, and at the instant represented, the center O has the velocity vo = 3.6 m/s and acceleration ao = 4.9 m/s² with directions shown in the figure. For this instant, the particle A has the indicated speed u = 1.9 m/s and time rate of change of speed u = 7.1 m/s², both relative to the disk with directions shown in the figure. Determine the absolute velocity VA and acceleration aд of particle A. VA = VO Answers: aд = do ( ů -4.34 ( 1.40 0.47 m 0.64 m i + 0.00 i + i -1.15 j) m/s j) m/s²arrow_forwardThe small ball is moving along the radial slot of the rotating disk. At the instant shown, the disk has an angular velocity w = 4.1 rad/s which is decreasing at 1.7 rad/s per second, x = 230 mm, x = = 0.32 m/s, and ï = -0.2 m/s². Calculate the magnitudes of the absolute velocity and acceleration of the ball for this instant. (v₁ = 1.0 m/s, a₁ = 4.64 m/s²) = ω x 0 Aarrow_forwardThe disk rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface, and at the instant represented, the center O has the velocity vo = 2.0 m/s and acceleration ao = 5.9 m/s? with directions shown in the figure. For this instant, the particle A has the indicated speed u = 2.1 m/s and time rate of change of speed u = 5.5 m/s?, both relative to the disk with directions shown in the figure. Determine the absolute velocity Va and acceleration aa of particle A. u 0.49 m ao 0.63 m Answers: VA = (i i+ i j) m/s i+ j) m/s2 iarrow_forward
- The boom OAB pivots about point O, while section AB simultaneously extends from within section OA. Determine the velocity and acceleration of the center B of the pulley for the following conditions: 0 = 30°, 0 = 7 deg/sec, 0 = 8 deg/sec², 1 = 7 ft, 1 = 2.2 ft/sec, Ï = -2.3 ft/sec². The quantities and I are the first and second time derivatives, respectively, of the length / of section AB. Express your answers as vectors in the e, and en directions. 0 Answers: VB = ав = (i 26' 8 A O er + er + B eo) ft/sec eo) ft/sec²arrow_forward3.0 m/s relative to the bar as shown. The distances are L = 2.97 m and d 0.82 m The small collar A is sliding on the bent bar with speed Simultaneously, the bar is rotating with angular velocity w 1.34 rad/s about the fixed pivot B. Take the x-y axes to be fixed to the bar and determine the Coriolis acceleration acor of the slider for the instant represented. Interpret your result. BC Answer: acor =( | i ii j) m/s2arrow_forwardRotation of bar OA is controlled by the lead screw which imparts a horizontal velocity v = 31 mm/s to collar C and causes pin P to travel along with the smooth slot. The velocity of collar C is decreasing at a rate of 5 mm/s2 at the instant in question. Determine the values of r¨ and θ¨, where r = OP, if h = 245 mm and x = 185 mm.arrow_forward
- 4. As shown in the image below, the bucket of the backhoe traces the path of the cardioid r = C · (1 – cos 0) ft, where constant C= 28. At this instant angle 0 - = 121°, and the boom is rotating with an angular velocity of 0 = 2.3 rad/s and an angular acceleration of 0 = 0.19 rad/s?. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the bucket in rad/s². Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point. Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 58.7 ft/s^2. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardA uniform plate has a weight of 50 lb. Link AB is subjected to a couple moment of M = 10 lb # ft and has a clockwise angular velocity of 2 rad>s at the instant u = 30°. Determine the force developed in link CD and the tangential component of the acceleration of the plate’s mass center at this instant. Neglect the mass of links AB and CD. PLEASE EXPLAIN THE N-T COORDINATE SYSTEM (HOW DO YOU KNOW WHICH WAY IS THE N-DIRECTION AND T-DIRECTION)arrow_forward
- The hollow tube is pivoted about a horizontal axis through point O and is made to rotate in the vertical plane with a constant counterclockwise angular velocity =3 rad/s. If a 0.1kg particle is sliding in the tube toward O with a velocity of 1.2 m/s relative to the tube when the position= 30° is passed, calculate the magnitude N of normal force exerted by the wall of the tube on the particle at this instant.arrow_forwardThe body is formed of slender rod and rotates about a fixed axis through point O. At time t = 0, the body is in the orientation 0 = 0 and has an angular velocity wo = 0.3 rad/s and a constant angular acceleration a = 0.8 rad/s². Determine the vectors of velocity and acceleration of point A at t = 1 s. Use d = 2r = 0.8 m. (√₁ = 0.106î + 1.240ŷ m/s, da -1.289 + 1.019ĵ m/s²) ω, α y = d x Aarrow_forwardт A cylinder moves outward along the spinning platform with a speed of r = (5 · t) where t is in rad seconds. The platform rotates at a constant angular velocity of 0 = (3) Assume the cylinder starts from rest at the center. Using cylindrical coordinates, a. Determine the cylinders's radial and transverse components of velocity at t = 5 s, vr and ve. b. Determine the cylinders's radial and transverse components of acceleration at t = 5 s, ar and ae. c. Determine the cylinder's magnitude of the velocity at t = 5 s, v d. Determine the cylinder's magnitude of the acceleration at t = 5 s, aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY